PHP 7 allows you to specify a data type for the return value of a function. Unlike scalar type hinting, however, you don't need to add any special declarations.
- This example shows you how to assign a data type to a function return value. To assign a return data type, first define the function as you would normally. After the closing parenthesis, add a space, followed by the data type and a colon:
function returnsString(DateTime $date, $format) : string { return $date->format($format); } - Anything returned by the function, regardless of its data type inside the function, will be converted to the declared data type as a return value. Notice, in this example, the values of
$a,$b, and$care added together to produce a single sum, which is returned. Normally you would expect the return value to be a numeric data type. In this case, however, the return data type is declared asstring, which overrides PHP's type-juggling process:function convertsToString($a, $b, $c) : string return $a + $b + $c; } - You can also assign classes as a return data type. In this example, we assign a return type of
DateTime, part of the PHPDateTimeextension:function makesDateTime($year, $month, $day) : DateTime { $date = new DateTime(); $date->setDate($year, $month, $day); return $date; }Note
The
makesDateTime()function would be a potential candidate for scalar type hinting. If$year,$month, or$dayare not integers, aWarningis generated whensetDate()is called. If you use scalar type hinting, and the wrong data types are passed, aTypeErroris thrown. Although it really doesn't matter whether a warning is generated or aTypeErroris thrown, at least theTypeErrorwill cause the errant developer who is misusing your code to sit up and take notice! - If a function has a return data type, and you return the wrong data type in your function code, a
TypeErrorwill be thrown at runtime. This function assigns a return type ofDateTime, but returns a string instead. ATypeErrorwill be thrown, but not until runtime, when the PHP engine detects the discrepancy:function wrongDateTime($year, $month, $day) : DateTime { return date($year . '-' . $month . '-' . $day); }
First, place the functions mentioned previously into a library file called chap_03_developing_functions_return_types_library.php. This file needs to be included in the chap_03_developing_functions_return_types.php script that calls these functions:
include (__DIR__ . '/chap_03_developing_functions_return_types_library.php');
Now you can call returnsString(), supplying a DateTime instance and a format string:
$date = new DateTime(); $format = 'l, d M Y'; $now = returnsString($date, $format); echo $now . PHP_EOL; var_dump($now);
As expected, the output is a string:
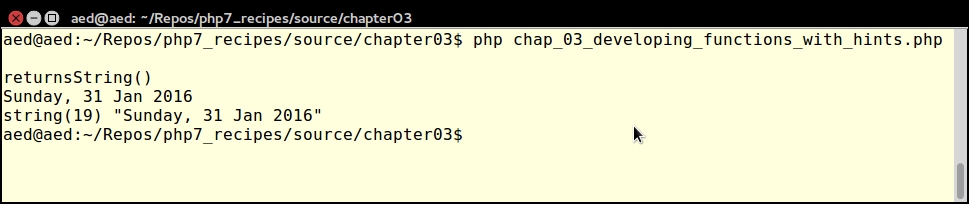
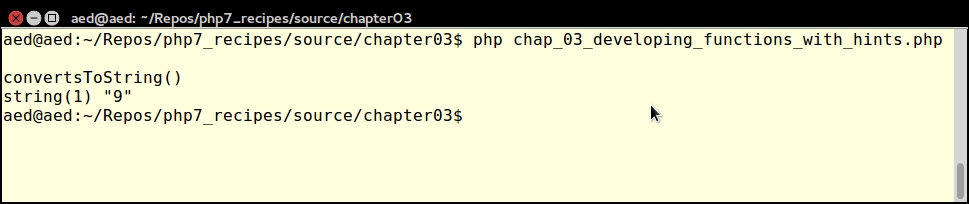
Now you can call convertsToString() and supply three integers as arguments. Notice that the return type is string:
echo "\nconvertsToString()\n"; var_dump(convertsToString(2, 3, 4));
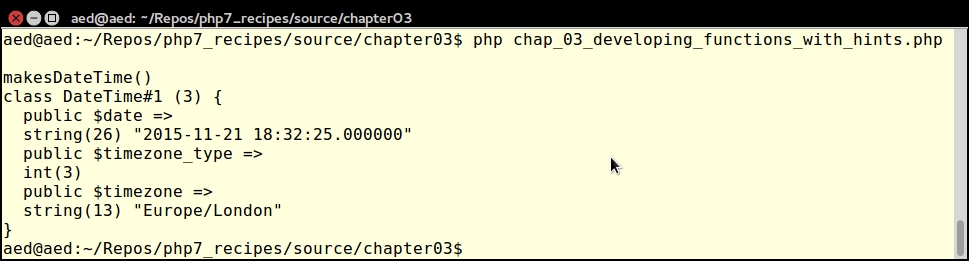
To demonstrate that, you can assign a class as a return value, call makesDateTime() with three integer parameters:
echo "\nmakesDateTime()\n"; $d = makesDateTime(2015, 11, 21); var_dump($d);
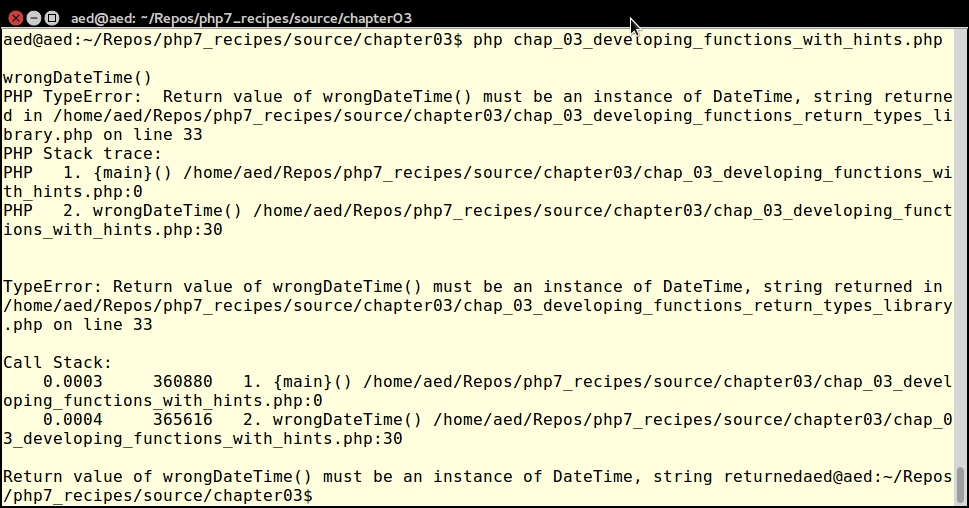
Finally, call wrongDateTime() with three integer parameters:
try {
$e = wrongDateTime(2015, 11, 21);
var_dump($e);
} catch (TypeError $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}Notice that a TypeError is thrown at runtime:
PHP 7.1 adds a new return value type, void. This is used when you do not wish to return any value from the function. For more information, please refer to https://wiki.php.net/rfc/void_return_type.
