Siege is another command-line open source tool to test load and performance. Siege is an HTTP/FTP load tester and benchmarking utility. It is designed for developers and administrators to measure the performance of their applications under load. It can send a configurable number of simultaneous requests to a server and those requests that place the server under a siege.
Its installation is simple and easy. For Linux and Mac OS X, first download Siege by issuing the following command in the terminal:
wget http://download.joedog.org/siege/siege-3.1.4.tar.gz
It will download the Siege TAR compressed file. Now, uncompress it by issuing the following command:
tar –xvf siege-3.1.4.tar.gz
Now, all the files will be in the siege-3.1.4 folder. Build and install it by issuing the following commands one by one in the terminal:
cd siege-3.1.4 ./configure make make install
Now, Siege is installed. To confirm this, issue the following command to check the Siege version:
siege –V
If it displays the version with some other information, then Siege is installed successfully.
Now, let's have a load test. A basic load test can be executed by running the following command:
siege some_url_or_ip
Siege will then start the test. We have to enter the application URL or server IP that we want to load test. To stop the test, press Ctrl + C, and we will have an output similar to the following:
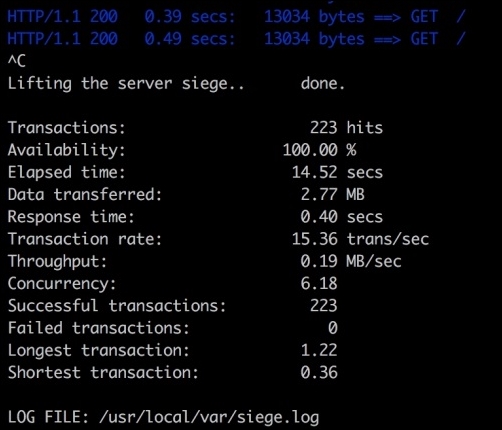
In the preceding screenshot we can see Transactions, Response time, and Transaction rate along with Longest transaction and Shortest transaction.
By default, Siege creates 15 concurrent users. This can be changed by using the –c option, which is done by making the following alteration in the command:
siege url_or_ip –c 100
However, Siege has a limitation for the concurrent users, which may be different for each OS. This can be set in the Siege configuration file. To find out the config file location and concurrent user limit, issue the following command in terminal:
siege -C
A list of the configuration options will be displayed. Also the resource file or config file location will be displayed. Open that file and find the config concurrent and set its value to an appropriate required value.
Another important feature of Siege is that a file that has all the URLs that need to be tested can be used. The file should have a single URL in each line. The –f flag is used with Siege as follows:
siege -f /path/to/url/file.txt –c 120
Siege will load the file and start load testing each URL.
Another interesting feature of Siege is the internet mode, which can be entered using the –i flag in the following command:
siege –if path_to_urls_file –c 120
In the internet mode, each URL is hit randomly and mimics a real-life situation, in which it can't be predicted which URL will be hit.
Note
Siege has lots of useful flags and features. A detailed list can be found in the official documentation at https://www.joedog.org/siege-manual/.
