PHP DebugBar is another awesome tool that displays a nice and full information bar at the bottom of the page. It can display custom messages added for the purposes of debugging and full request information including $_COOKIE, $_SERVER, $_POST, and $_GET arrays along with the data if any of them have. Besides that, PHP DebugBar displays details about exceptions if there are any, database queries executed, and their details. Also it displays the memory taken by the script and the time the page is loaded in.
According to the PHP Debug website, DebugBar integrates easily in any application project and displays debugging and profiling data from any part of the application.
Its installation is easy. You can either download the complete source code, place it somewhere in your application, and set up the autoloader to load all the classes, or use composer to install it. We will use composer as it is the easy and clean way to install it.
Note
Composer is a nice tool for PHP to manage the dependencies of a project. It is written in PHP and is freely available from https://getcomposer.org/. We assume that composer is installed on your machine.
In your project's composer.json file, place the following code in the required section:
"maximebf/debugbar" : ">=1.10.0"
Save the file and then issue the following command:
composer update
The Composer will start updating the dependencies and install composer. Also, it will generate the autoloader file and/or the other dependencies required for DebugBar.
After it is installed, the project tree for the DebugBar can be as follows:
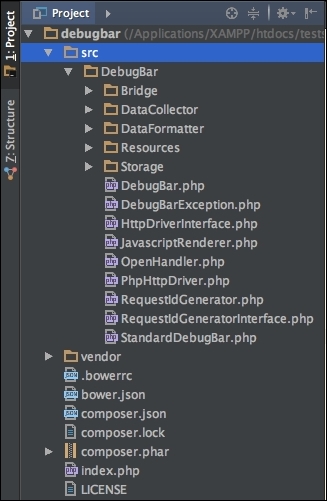
The directories' structure may be a little bit different, but normally, it will be as we previously noted. The src directory has the complete source code for DebugBar. The vendor directory has some third-party modules or PHP tools that may or may not be required. Also, note that the vendor folder has the autoloader to autoload all the classes.
Let's check our installation now to see whether it is working or not. Create a new file in your project root and name it index.php. After this, place the following code in it:
<?php
require "vendor/autoloader.php";
use Debugbar\StandardDebugBar;
$debugger = new StandardDebugBar();
$debugbarRenderer = $debugbar->getJavascriptRenderer();
//Add some messages
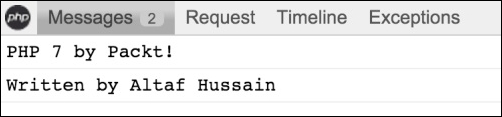
$debugbar['messages']->addMessage('PHP 7 by Packt');
$debugbar['messages']->addMessage('Written by Altaf Hussain');
?>
<html>
<head>
<?php echo $debugbarRenderer->renderHead(); ?>
</head>
<title>Welcome to Debug Bar</title>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Debug Bar</h1>
<!—- display debug bar here -->
<?php echo $debugbarRenderer->render(); ?>
</body>
</html>In the preceding code, we first included our autoloader, which is generated by composer for us to autoload all the classes. Then, we used the DebugBar\StandardDebugbar namespace. After this, we instantiated two objects: StandardDebugBar and getJavascriptRenderer. The StandardDebugBar object is an array of objects that has objects for different collectors, such as message collectors and others. The getJavascriptRenderer object is responsible for placing the required JavaScript and CSS code at the header and displaying the bar at the bottom of the page.
We used the $debugbar object to add messages to the message collector. Collectors are responsible for collecting data from different sources, such as databases, HTTP requests, messages, and others.
In the head section of the HTML code, we used the renderHead method of $debugbarRenderer to place the required JavaScript and CSS code. After this, just before the end of the <body> block, we used the render method of the same object to display the debug bar.
Now, load the application in the browser, and if you notice a bar at the bottom of the browser as in the following screenshot, then congrats! DebugBar is properly installed and is working fine.

On the right-hand side, we have the memory consumed by our application and the time it is loaded in.
If we click on the Messages tab, we will see the messages we added, as shown in the following screenshot:
DebugBar provides data collectors, which are used to collect data from different sources. These are called base collectors, and some of the data collectors are as follows:
- The message collector collects log messages, as shown in the preceding example
- The TimeData collector collects the total execution time as well as the execution time for a specific operation
- The exceptions collector displays all the exceptions that have occurred
- The PDO collector logs SQL queries
- The RequestData collector collects data of PHP global variables, such as
$_SERVER,$_POST,$_GET, and others - The config collector is used to display any key-value pairs of arrays
Also, there are some collectors that provide the ability to collect data from third-party frameworks such as Twig, Swift Mailer, Doctrine, and others. These collectors are called bridge collectors. PHP DebugBar can be easily integrated into famous PHP frameworks such as Laravel and Zend Framework 2 too.
Note
A complete discussion of PHP DebugBar is not possible in this book. Therefore, only a simple introduction is provided here. PHP DebugBar has a nice documentation that provides complete details with examples. The documentation can be found at http://phpdebugbar.com/docs/readme.html.
