There is always a need to monitor the performance of database servers. For this purpose, there are many tools available that make it easy to monitor MySQL servers and performance. Most of them are open source and free, and some provide a GUI. The command-line tools are more powerful and the best to use, though it takes a little time to understand and get used to them. We will discuss a few here.
This is the most famous, web-based, open source, and free tool available to manage MySQL databases. Despite managing a MySQL server, it also provides some good tools to monitor a MySQL server. If we log in to phpMyAdmin and then click on the Status tab at the top, we will see the following screen:
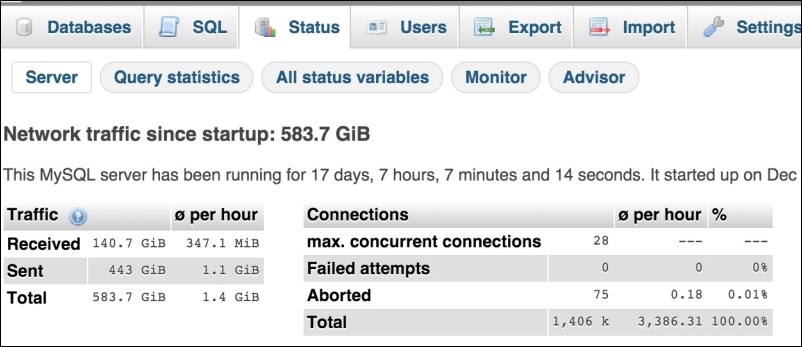
The Server tab shows us basic data about the MySQL server, such as when it started, how much traffic is handled from the last start, information about connections, and so on.
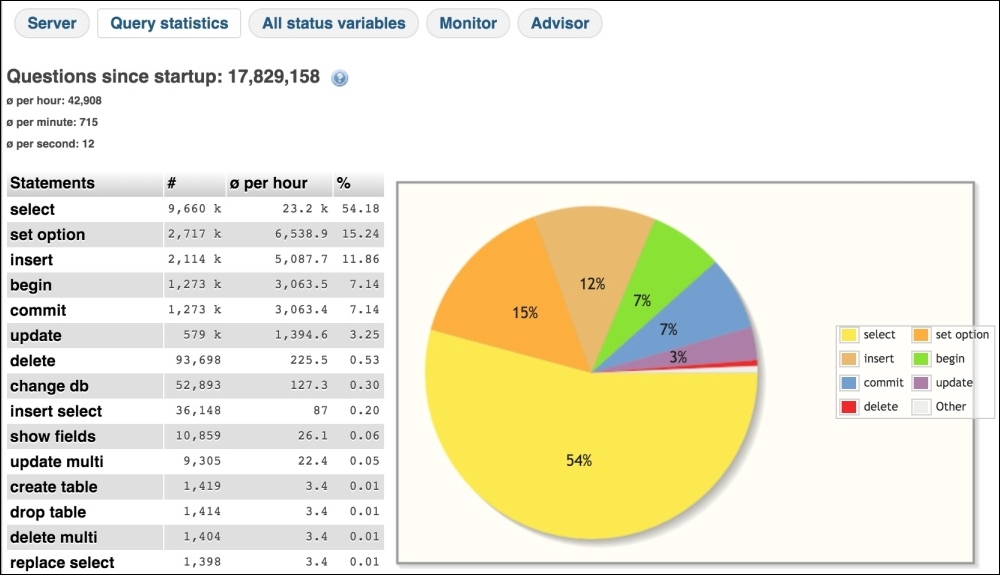
The next is Query Statistics. This section provides full stats about all of the queries executed. It also provides a pie chart, which visualizes the percentage of each query type, as shown in the following screenshot.
If we carefully look at the chart, we can see that we have 54% of the SELECT queries running. If we use some kind of cache, such as Memcached or Redis, these SELECT queries should not be this high. So, this graph and statistics information provides us with a mean to analyze our cache systems.
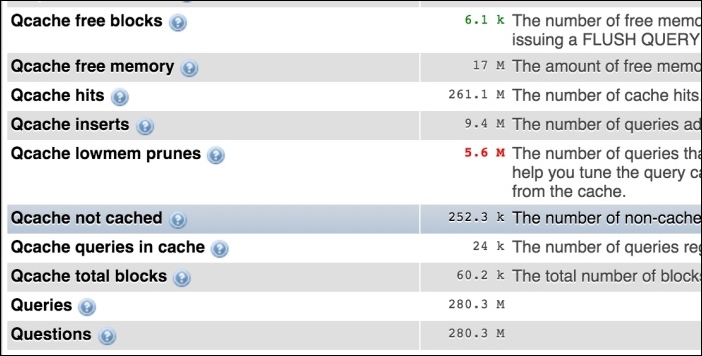
The next option is All Status Variables, which lists all of the MySQL variables and their current values. In this list, one can easily find out how MySQL is configured. In the following screenshot, our query cache variables and their values are shown:
The next option that phpMyAdmin provides is Monitor. This is a very powerful tool that displays the server resources and their usages in real time in a graphical way.
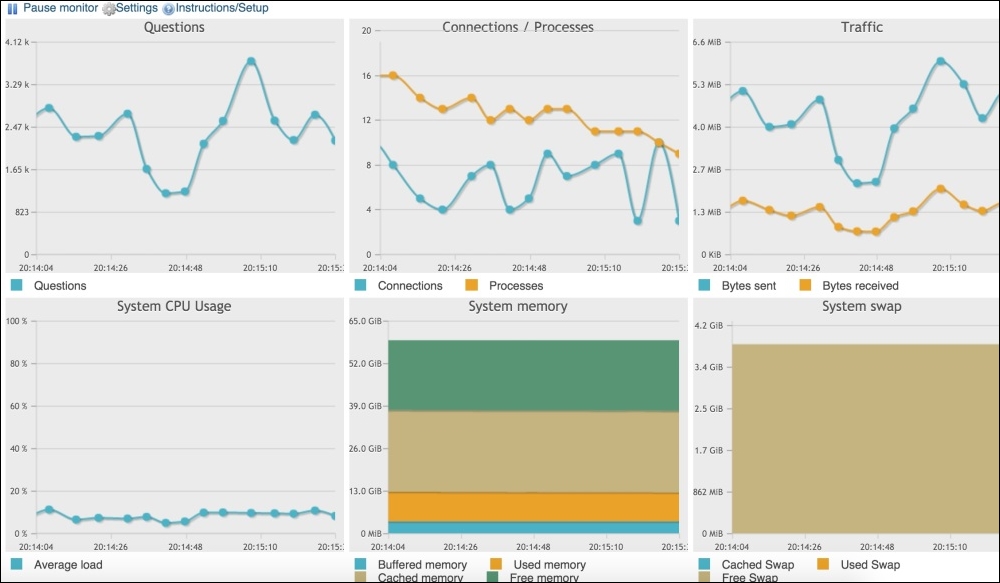
As shown in the preceding screenshot, we can see Questions, Connections/Processes, System CPU Usage, Traffic, System Memory, and System swap in a nice graphical interface.
The last important section is Advisor. This gives us advice regarding the settings for performance. It gives you as many details as possible so that the MySQL server can be tuned for performance. A small section from the advisor section is shown in the following screenshot:
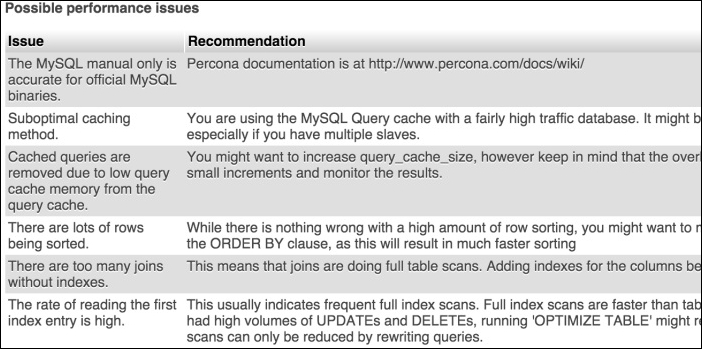
If all these advices are applied, some performance can be gained.
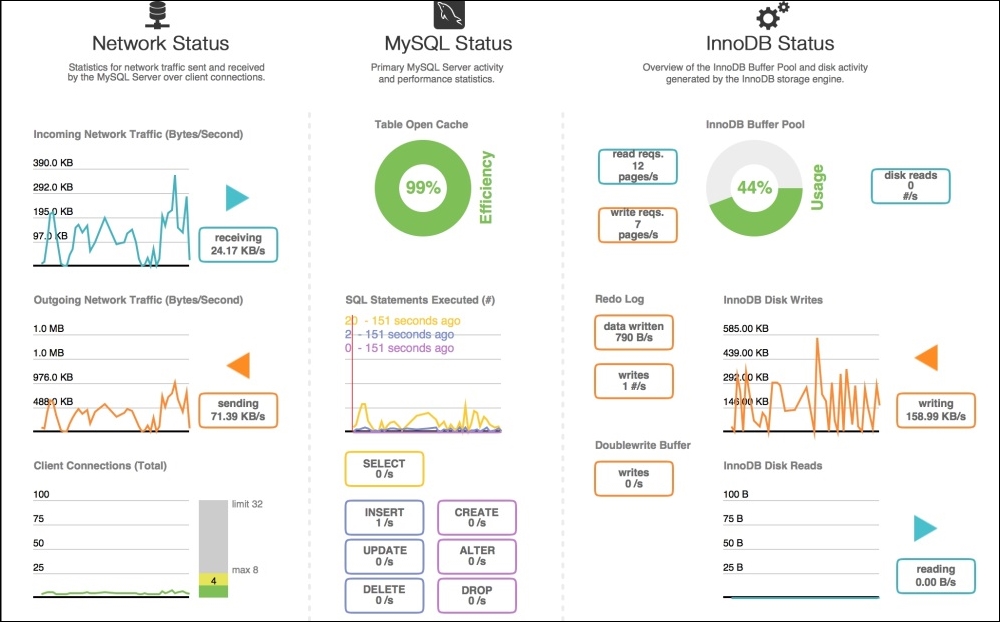
This is a desktop application from MySQL and is fully equipped with tools to manage and monitor the MySQL server. It provides us with a dashboard for performance in which all the data related to the server can be seen in a beautiful and graphical way, as shown in the screenshot that follows:
All the tools mentioned before are good and provide some visual information about our database server. However, they are not good enough to show us some more useful information or provide more features that can make our lives easy. For this purpose, another command-line toolkit is available, which is called Percona Toolkit.
Percona Toolkit is a set of more than 30 command-line tools, which includes those used to do an analysis of slow queries, archive, optimize indices and many more.
Note
Percona Toolkit is free and open source and is available under GPL. Most of its tools run on Linux/Unix-based systems, but some can run on Windows too. An installation guide can be found at https://www.percona.com/doc/percona-toolkit/2.2/installation.html. A complete set of tools can be found at https://www.percona.com/doc/percona-toolkit/2.2/index.html.
Now, let's discuss a few tools in the subsections to follow.
This tool analyzes queries from slow, general, and binary log files. It generates a sophisticated report about the queries. Let's run this tool for slow queries using the following command:
Pt-query-digest /var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
After entering the preceding command in the terminal, we will see a long report. Here, we will discuss a short part of the report, as shown in the following screenshot:
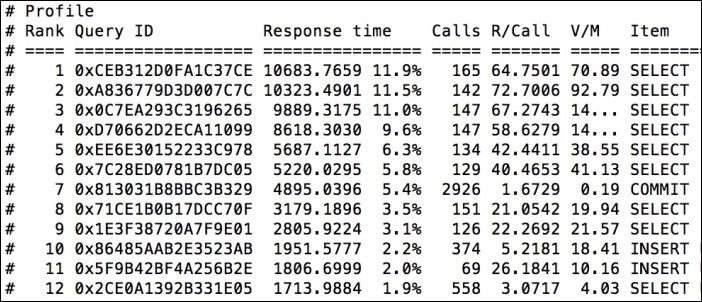
In the preceding screenshot, slow queries are listed with the slowest at the top. The first query, which is a SELECT query, takes the most time, which is about 12% of the total time. The second query, which is also a SELECT query, takes 11.5% of the total time. From this report, we can see which queries are slow so that we can optimize them for the best performance.
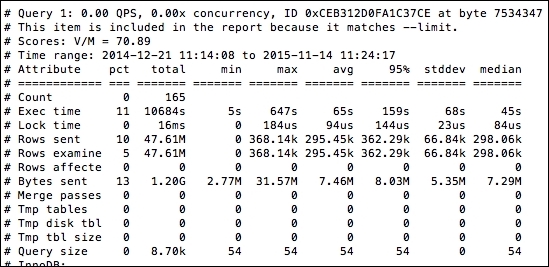
Also, pt-query-digest displays information for each query, as shown in the following screenshot. In the screenshot, data about the first query is mentioned, including the total timing; percentage (pct) of time; min, max, and average time; bytes sent; and some other parameters:
This tool finds duplicate indices and duplicate foreign keys either in a set of specified tables or in a complete database. Let's execute this tool again in a large database using the following command in the terminal:
Pt-duplicate-key-checker –user packt –password dbPassword –database packt_pub
When executed, the following output is printed:
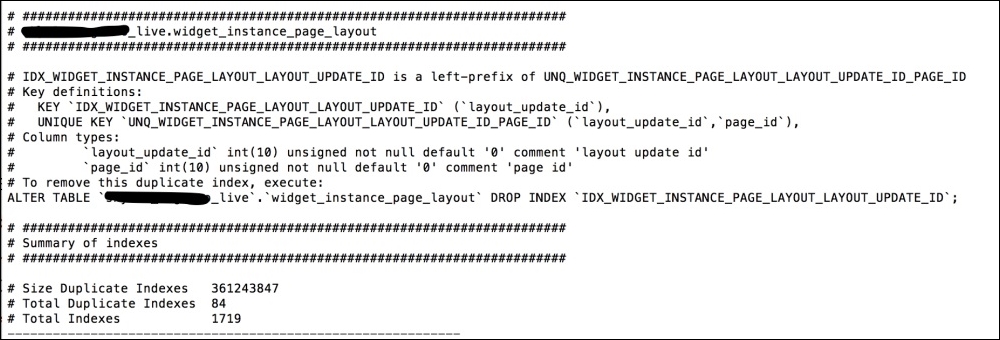
At the end of the report, a summary of the indices is displayed, which is self-explanatory. Also, this tool prints out an ALTER query for each duplicate index that can be executed as a MySQL query to fix the index, as follows:
Pt-variable-advisor
This tool displays MySQL config information and advice for each query. This is a good tool that can help us set up MySQL configurations properly. We can execute this tool by running the following command:
Pt-variable-advisor –user packt –password DbPassword localhost
After execution, the following output will be displayed:
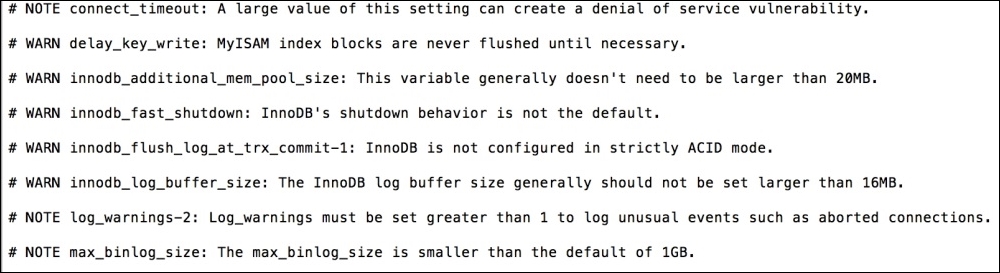
There are many other tools provided by Percona Toolkit that are out of the scope of this book. However, the documentation at https://www.percona.com/doc/percona-toolkit/2.2/index.html is very helpful and easy to understand. It provides complete details for each tool, including its description and risks, how to execute it, and other options if there are any. This documentation is worth reading if you wish to understand any tool in Percona Toolkit.
