In our first example, we'll split a polygon (county boundary) using a line (river). We will use an ST_Split function for that.
This function accepts two arguments: a geometry to be split, which can be of the (Multi)Polygon or (Multi)LineString type, and a blade, which can be a LineString for polygons and LineStrings or a Point for lines:.
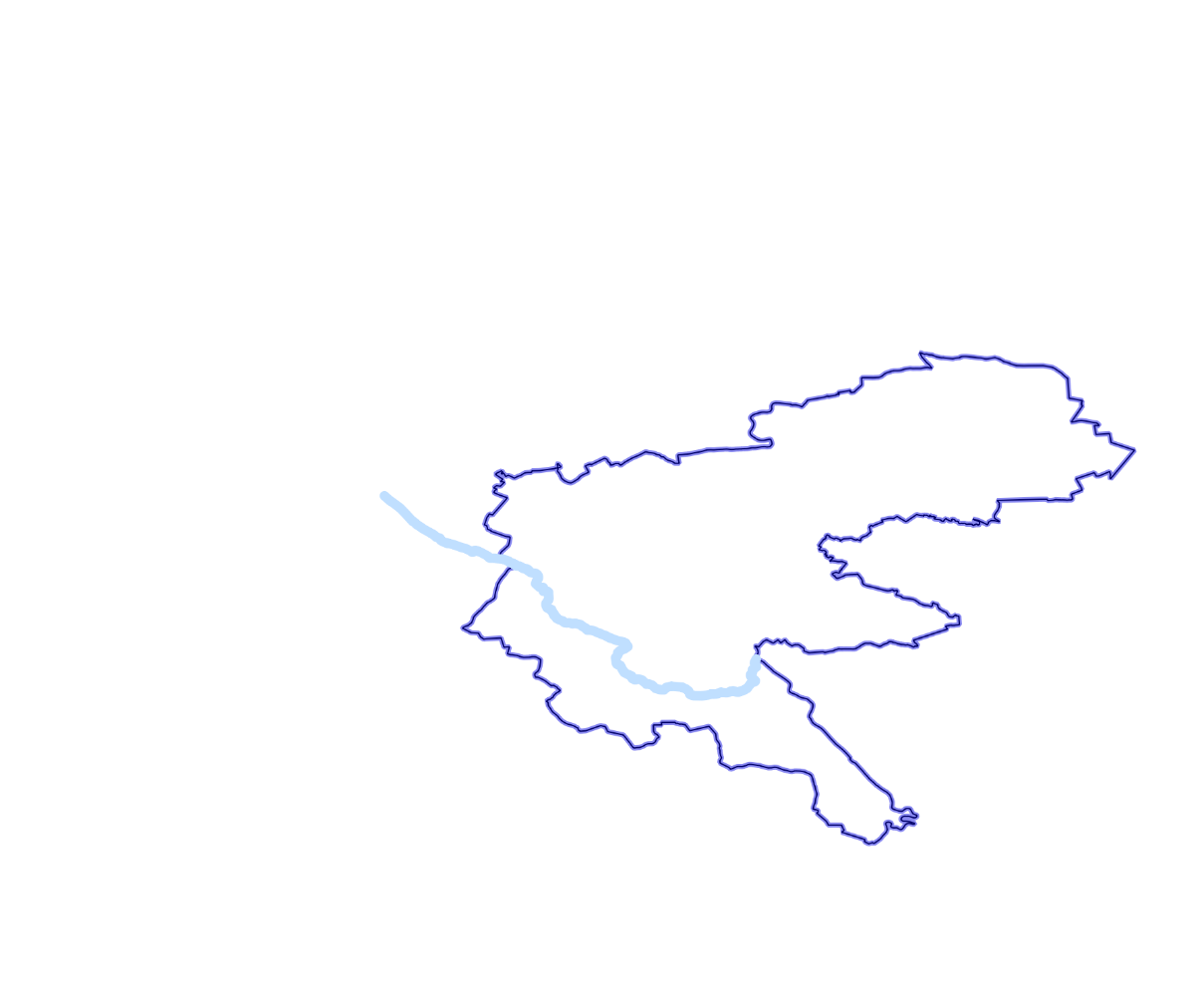
A polygon about to be split with a LineString used as a blade
SELECT ST_Split(
(SELECT wkb_geometry FROM multipolygons WHERE osm_id = '2417246'),
(SELECT wkb_geometry FROM lines WHERE osm_id = '224461074'))
This yields a GeometryCollection, which isn't supported in most GIS software, including QGIS. To extract individual parts after splitting, and to visualize the result in QGIS, we'll need to use the ST_Dump function:.
SELECT (ST_Dump(ST_Split(
(SELECT wkb_geometry FROM multipolygons WHERE osm_id = '2417246'),
(SELECT wkb_geometry FROM lines WHERE osm_id = '224461074')))).geom
This converts a GeometryCollection into a set of rows, each with a polygon geometry, which can be visualized by any PostGIS-supporting software without any problems.
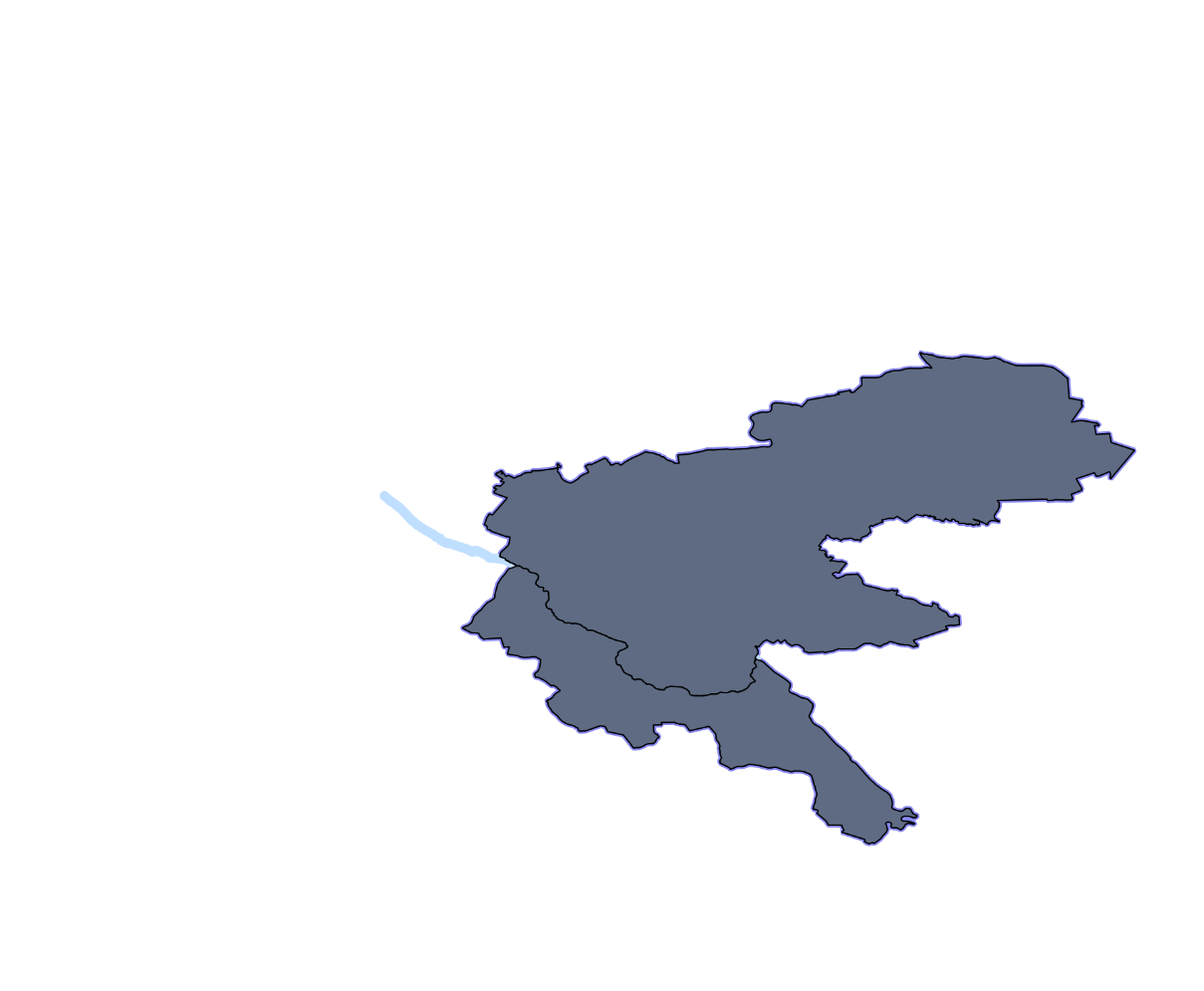
Two polygons after executing an ST_Split function
