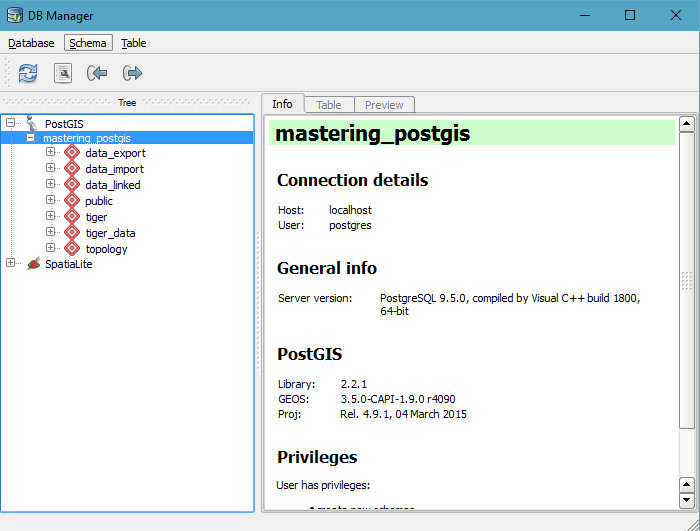
In order to connect to PostGIS from QGIS, go to Database\DB Manager and pick DB Manager. DB Manager is a very powerful tool that lets one not only simply connect and read data from a database, but also manage the database objects, such as tables, their columns, constraints, and indexes. In this scenario, we will not go into the details of how to manage a database using QGIS DB Manger, but instead we will focus on the task and simply use it to get to the data we want exported.
First, let's make sure we can connect to our database. When you expand the database node, you will see the schemas present in the database:
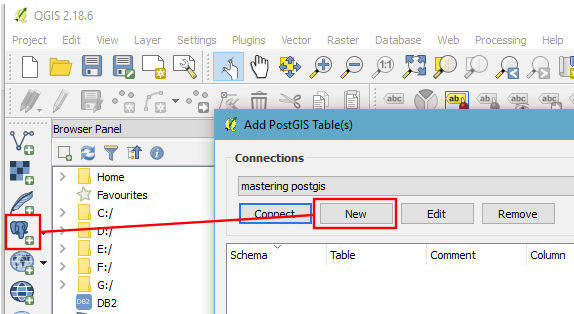
If you happen to not have any connections available, you may add one by using the Add PostGIS Table(s) tool, as shown in the following screenshot:
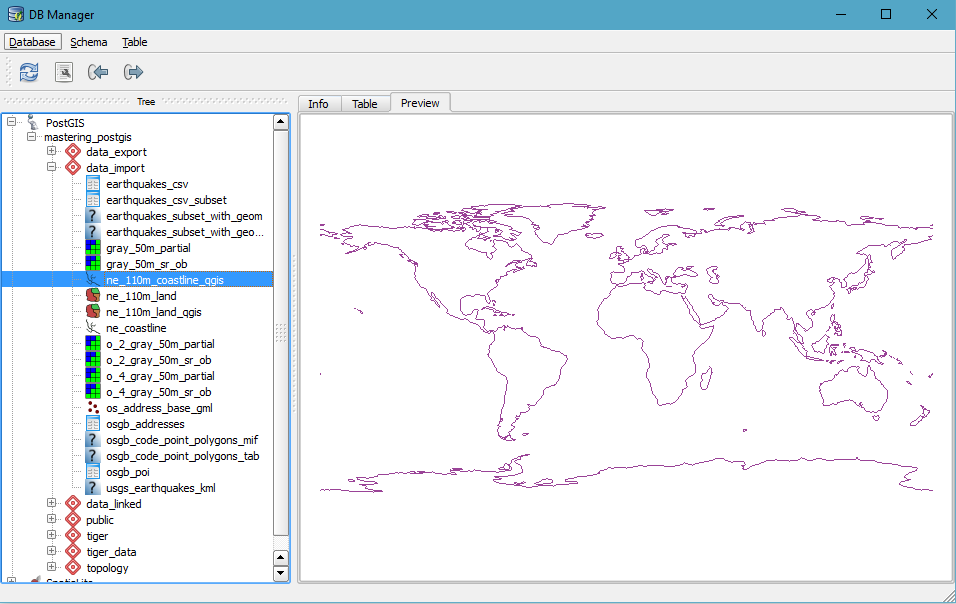
The nice thing about DB Manager is that it allows you to preview the data not only in a tabular form, but also in its spatial representation:
You have two options now:
- You can use the export button in the DB Manager's toolbar (the one with the arrow pointing right or to the top in the newer QGIS versions) and it will let you output the vector to SHP. At the time of writing (QGIS Las Palmas, 2.18.x), trying to export a PgRaster table to a file results in an error. I guess it will be fixed at some point.
- You can right-click a layer you are interested in and choose the Add to canvas option. This will bring the linked database data into QGIS's workspace.
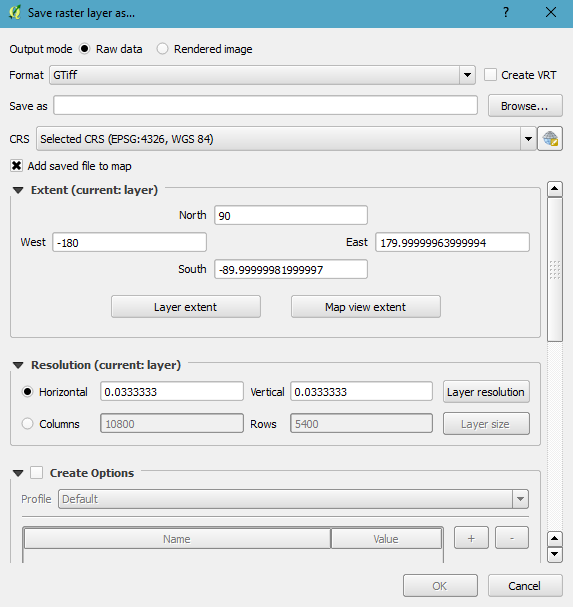
Once the data is in QGIS, our export options are much, much broader. We can export to any vector format supported by QGIS to write output. In order to export vector data from QGIS, simply right-click the layer to display its context menu and choose the Save as option, and you will be presented with the vector data export dialog. As you see, you now have more to choose from:
The very same approach can be applied to PgRaster tables. Simply bring the table to the QGIS workspace by right-clicking the table in the manager and choosing Add to canvas. Once in QGIS, our export options are way more flexible: