Table attributes are the various properties of a table. This section discusses the settings for some of them.
The first attribute we can change is called Storage Engine.
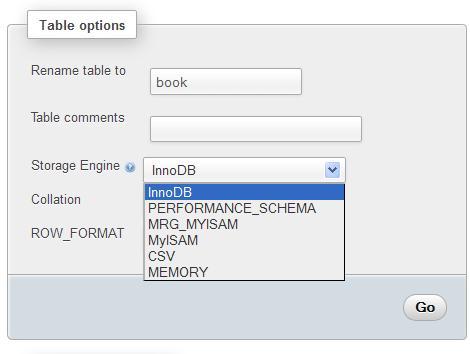
This controls the whole behavior of the table—its location (on disk or in memory), the index structure, and whether it supports transactions and foreign keys. The drop-down list varies depending on the storage engines supported by our MySQL server.
Table comments option allows us to enter comments for the table.
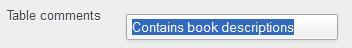
These comments will be shown at appropriate places, for example, in the navigation panel, next to the table name in the Table view, and in the export file. The following screenshot shows what the navigation panel looks like when the $cfg['ShowTooltip'] parameter is set to its default value of TRUE:
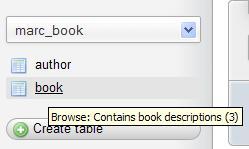
The default value (FALSE) of $cfg['ShowTooltipAliasDB'] and $cfg['ShowTooltipAliasTB'] produces the behavior we saw earlier—the true database and table names are displayed in the navigation panel and in the Database view for the Structure page. Comments appear as a tooltip (when the cursor is hovered over a database or table name). If one of these parameters is set to TRUE, the behavior is reversed—showing the comment by default and the true name as a tooltip. This is convenient when the real table names are not meaningful.
There is another possibility for $cfg['ShowTooltipAliasTB']— the 'nested' value. Here is what happens if we use this feature:
- The true table name is displayed in the navigation panel
- The table comment (for example,
project__)is interpreted as the project name and is displayed as it is (refer to the Nested display of tables within a database section in Chapter 3)
When we browse a table, or execute a statement such as SELECT * from book without specifying a sort order, MySQL uses the order in which the rows are physically stored. This table order can be changed with the Alter table order by dialog. We can choose any column and the table will be reordered once on this column. We choose author_id in the example, and after we click on Go, the table gets sorted on this column.
Reordering is convenient if we know that we will be retrieving rows in this order most of the time. Moreover, if we use an ORDER BY clause later on, and the table is already physically sorted on this column, we might get better performance.
This default ordering will last as long as there are no changes in the table (no insertions, deletions, or updates). This is why phpMyAdmin shows the (singly) warning.
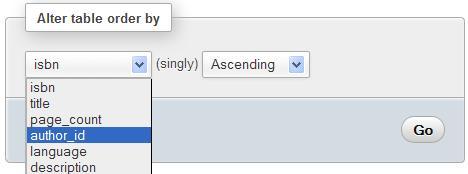
After the sort has been done on author_id, books for author 1 will be displayed first, followed by the books for author 2, and so on (we are talking about a default browsing of the table without explicit sorting). We can also specify the sort order as Ascending or Descending.
If we insert another row, describing a new book from author 1, and then click on Browse, the book will not be displayed along with the other books for this author because the sort was done before the insertion.
Character-based columns have a collation attribute that describes which character set is used to interpret the contents, and rules for sorting. The name column currently has a latin1_swedish_ci collation, as can be seen via the Structure page. On the Operations page, if we change the collation for table author from latin1_swedish_ci to, say, utf8_general_ci, this generates the following statement:
ALTER TABLE `author` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci
Therefore, we only changed the default collation for future columns that will be added to this table; no collation was changed for existing columns.
Other attributes that influence the table's behavior may be specified using the Table options dialog:
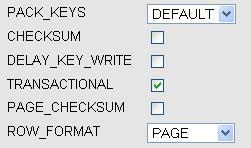
The options are:
- PACK_KEYS: Setting this attribute results in a smaller index. This can be read faster but takes more time to update. Available for the
MyISAMstorage engine. - CHECKSUM: This makes MySQL compute a checksum for each row. This results in slower updates, but finding of corrupted tables becomes easier. Available for
MyISAMonly. - DELAY_KEY_WRITE: This instructs MySQL not to write the index updates immediately, but to queue them for writing later. This improves performance but there is a negative trade-off—the index might need to be rebuilt in case of a server failure (refer to http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.1/en/miscellaneous-optimization-tips.html). Available for
MyISAMonly. - TRANSACTIONAL, PAGE_CHECKSUM: Applies to the
Ariastorage engine, previously known asMaria. The TRANSACTIONAL option marks this table as being transactional; however, the exact meaning of this option varies as future versions of this storage engine will gain more transactional features. PAGE_CHECKSUM computes a checksum on all index pages. Currently documented at http://kb.askmonty.org/en/aria-storage-engine. - ROW_FORMAT: To the storage engines that support this feature
(MyISAM, InnoDB, PBXT, andAria), a choice of row format is presented. The default value being the current state of this table's row format. - AUTO_INCREMENT: This changes the auto-increment value. It is shown only if the table's primary key has the auto-increment attribute.
