InfluxDB uses particular terms to describe the various components of time-series data, and the techniques used to categorize this data to make InfluxDB unique.
InfluxDB organizes data by database, time series, and point of events. The database is quite similar to other traditional databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL. It is an organized collection of time-series data and retention policies. The point of events are similar to SQL rows.
The following table is a simple example of a table called tickers in a SQL database with the unindexed columns (close, high, low, open, and volume) and the indexed columns (ticker, company, and time):
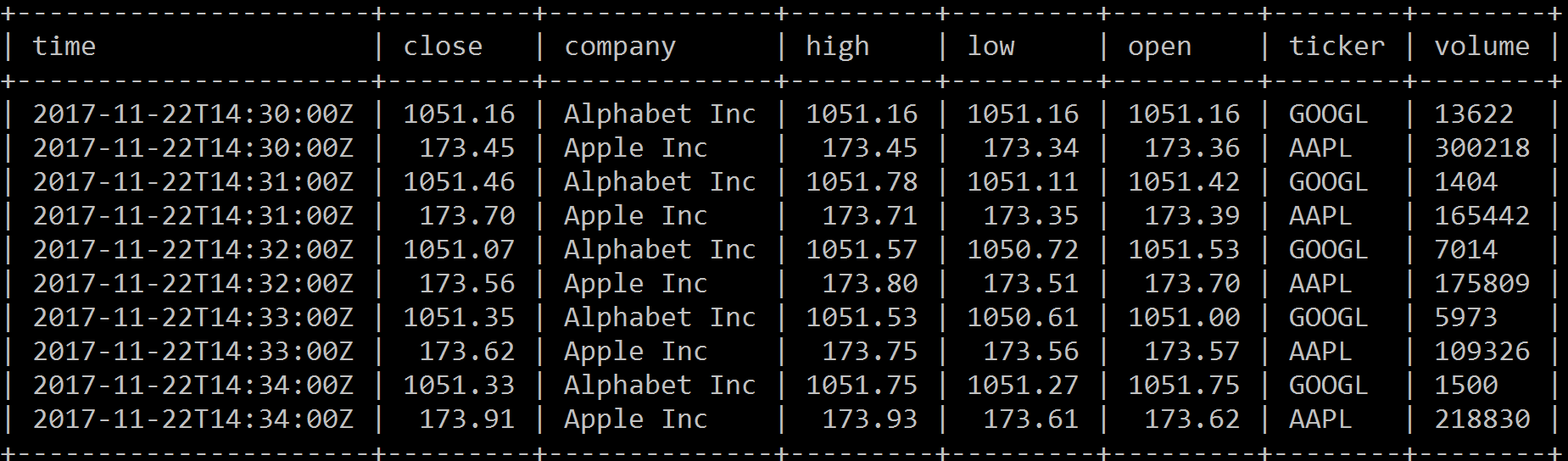
The same data is shown in InfluxDB as follows:
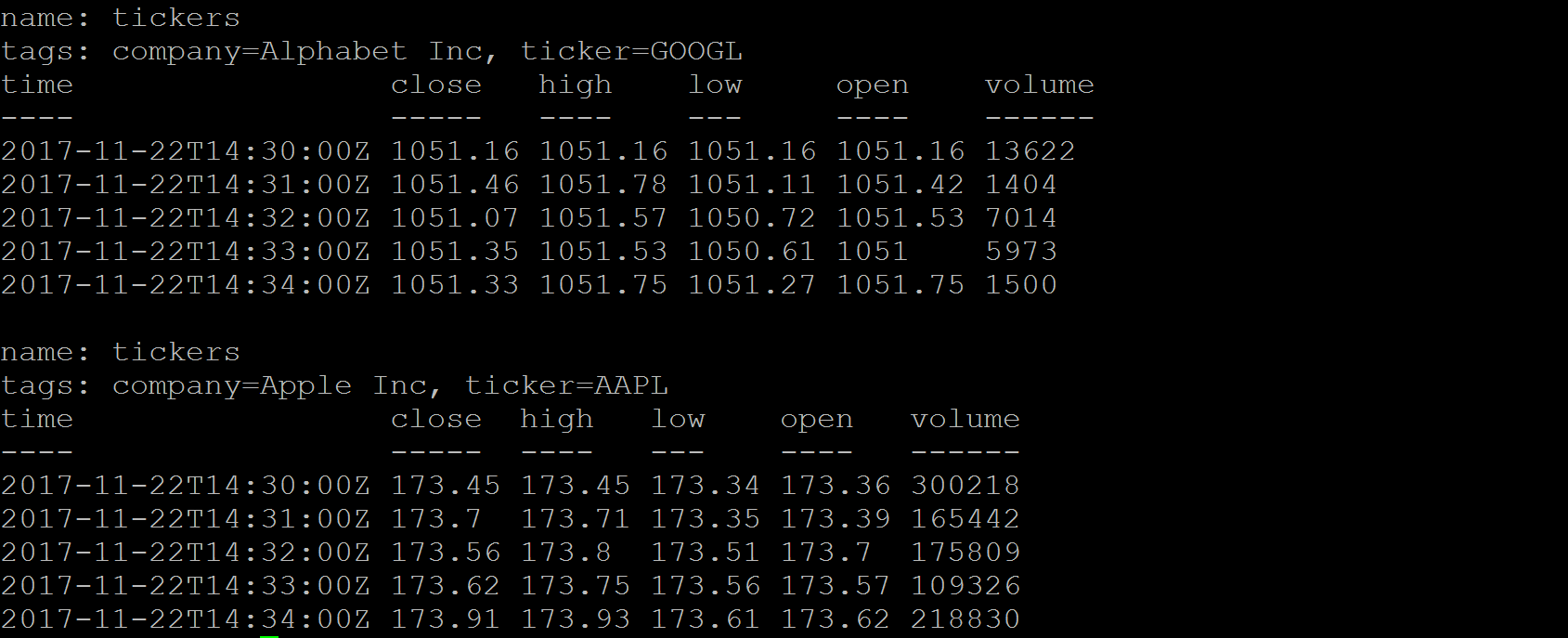
By comparing the preceding examples, we can see that InfluxDB terms are similar to SQL:
- An InfluxDB database is similar to an SQL database
- An InfluxDB measurement (tickers) is similar to an SQL database table (tickers)
- InfluxDB tags (ticker) are similar to SQL table indexed columns (ticker)
- InfluxDB fields (close, high, and low) are similar to an SQL table with unindexed columns (close, high, and low)
The following is the list of important terms used in InfluxDB:
- Measurement: This is similar to an SQL database table. The measurement contains the timestamps, fields, and tags; it is a string. The measurement can have many retention policies.
- Field set: This is a collection of field keys and field values on a point.
- Field key: This is a key part for the field set key-value pair. The key is a string type and stores the metadata.
- Field value: This is similar to an SQL table's unindexed columns; it stores your data. It is the value part in a field set key-value pair.
- Tags: This is similar to indexed columns in an SQL database. Tag keys and tag values are of the type string and record metadata. It is optional.
- Continuous query: Continuous queries in InfluxDB are similar to SQL database's stored procedures.
- Line protocol: This is the text-based format for writing points to InfluxDB.
- Point: This is similar to an SQL database with a single row of record. It consists of a single collection of fields in a series. Each point is uniquely identified by its series and the given timestamp. For example:

- Retention Policy (RP): This describes the duration of data points that are kept in InfluxDB and how many data copies are stored in the cluster. It can have shard duration (for example, 7d). Each RP is unique in the database. The default RP is autogen. For example:
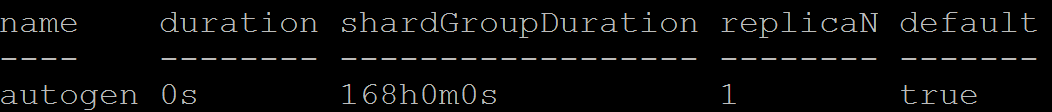
- Series: This is the collection of data in InfluxDB data structure that share a RP, measurement, and tag set.
- Timestamps: This is the date and time associated with a point. The time in InfluxDB is UTC. The time is stored in the RFC 3339 UTC format, for example, 2017-11-22T14:30:00Z.
- Time Structured Merge (TSM) tree : This is a data storage engine for InfluxDB.
- Write Ahead Log (WAL): This is the temporary cache for recently written points, it allows for efficient batching of the writes into the TSM.
Here is quick overview of some comparison:
|
InfluxDB |
SQL Database |
|
Database |
Database |
|
Measurement |
Table |
|
Points |
Rows |
|
Tags |
Indexed columns |
|
Fields |
Unindexed columns |
|
Continuous queries |
Stored procedures |
