To perform CRUD operations in DynamoDB, select DynamoDB from the database services in the AWS Account Service section, as shown in the following screenshot:
Once you select DynamoDB from the section, it will redirect you to the DynamoDB console, where it will show an option for creating the table:
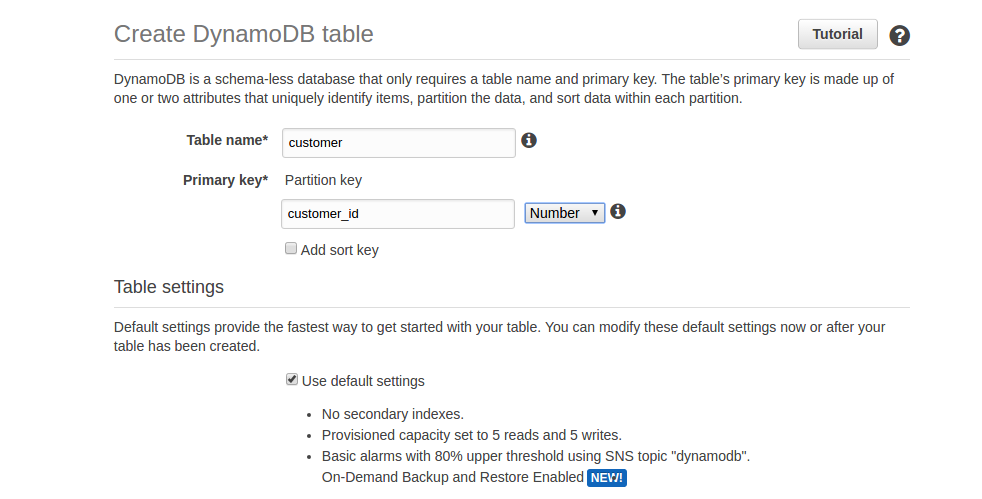
To create a table, click on the Create table button. This will take you to the Create table screen. During the creation of the table, you have to provide the primary key, along with the table name.
Here, we are creating a table called customer, and each customer is identified by customer_id:
Once the table is created, it is listed in the console, and other operations that can be performed on the table, such as delete table, insert item, and so on, are also shown:
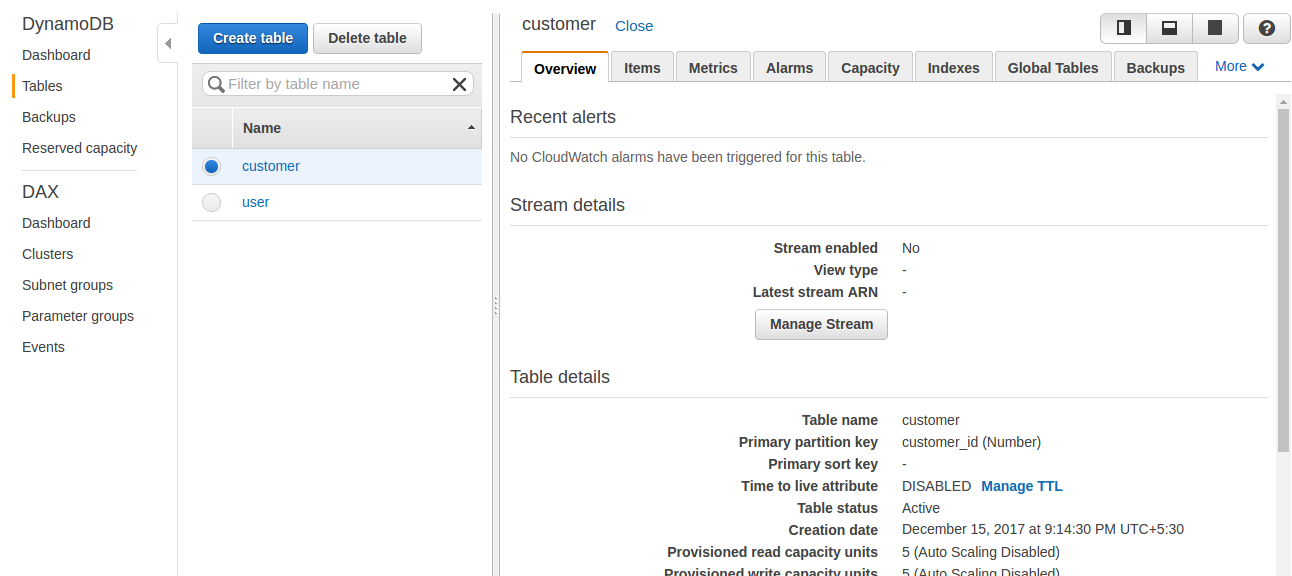
Here, we can select the table from the list of created tables and click on the Delete table button to delete the table.
If you want to list events on the table, you can click the Manage Stream button. The records are inserted if insert, update, and delete operations are performed on the table.
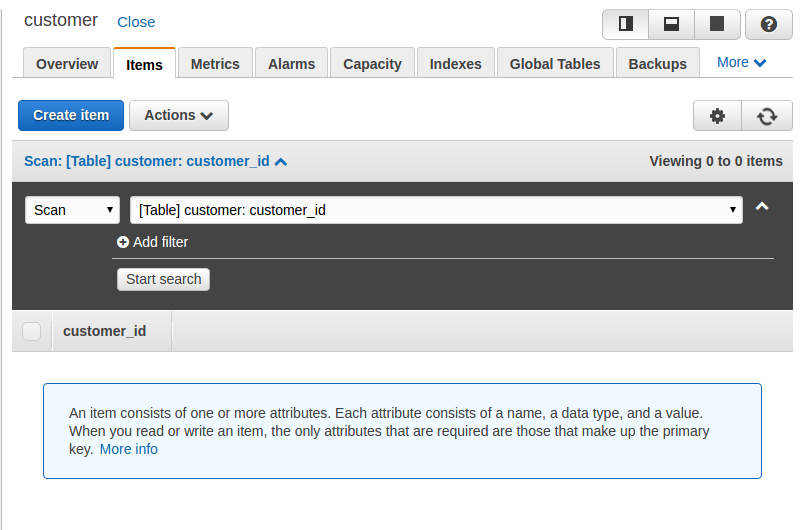
If we click on the Items tab on the left side of the pan console, it will list all the items that exist in that table using the scan operation, as shown in the following screenshot:
We can insert an item in the table using the Create item option and provide an item value, as shown in the following screenshot:
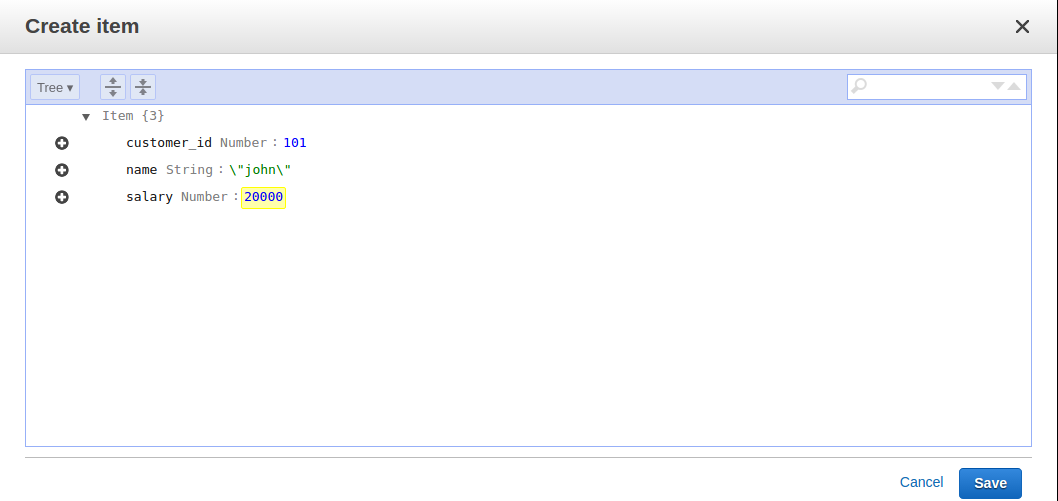
Click on Save to create an item:
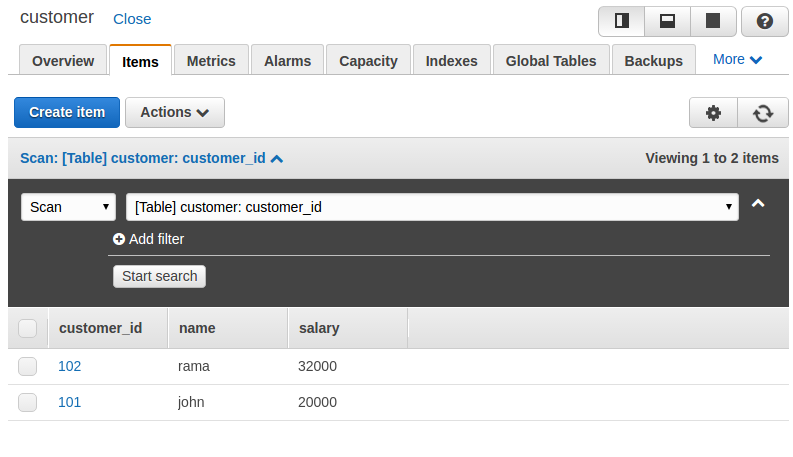
Now we have two items inserted in our table, the first with customer_id 101 and the second with customer_id 102. We can have different attributes for items. As a new customer has been added, we are going to insert a mobile number for him, as shown in the following screenshot:
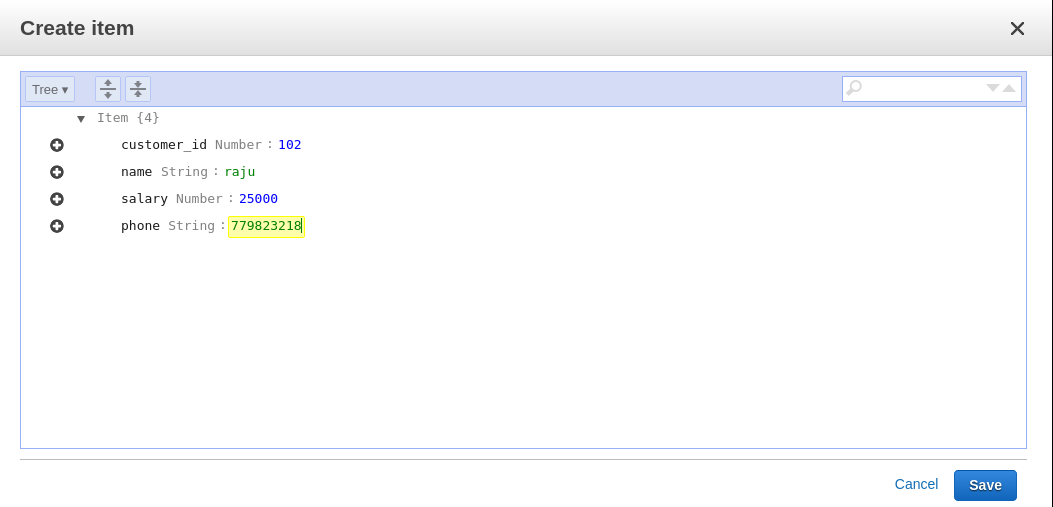
If we list the items now, we can see that the items can vary in the number of attributes for different items:
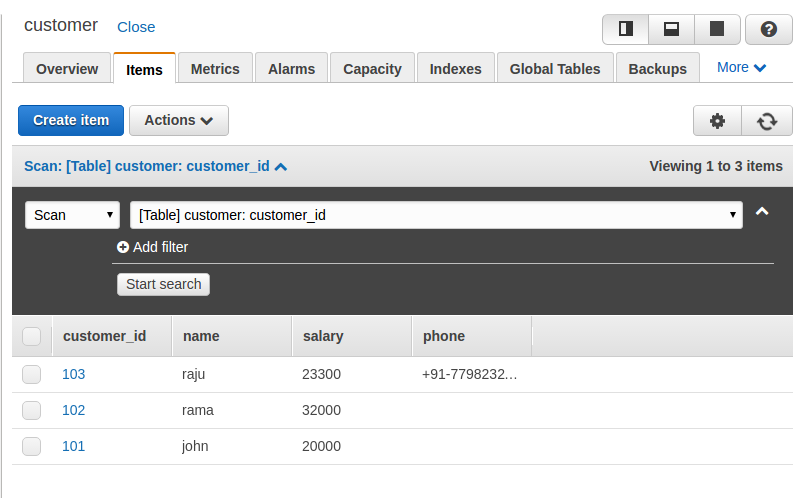
You can delete the item by selecting the Delete option from the drop-down list, as shown in the following screenshot:
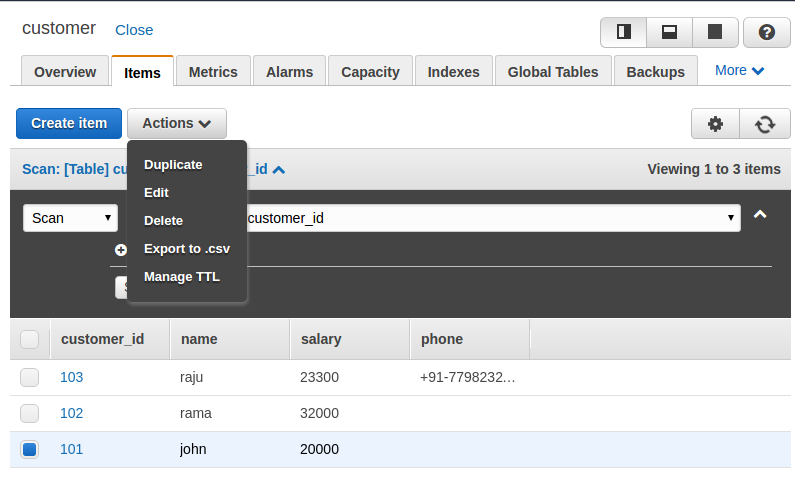
To update the items, we have to choose the Edit option from the drop-down list shown in the previous screenshot, which opens a popup to edit the information, as shown in the following screenshot:
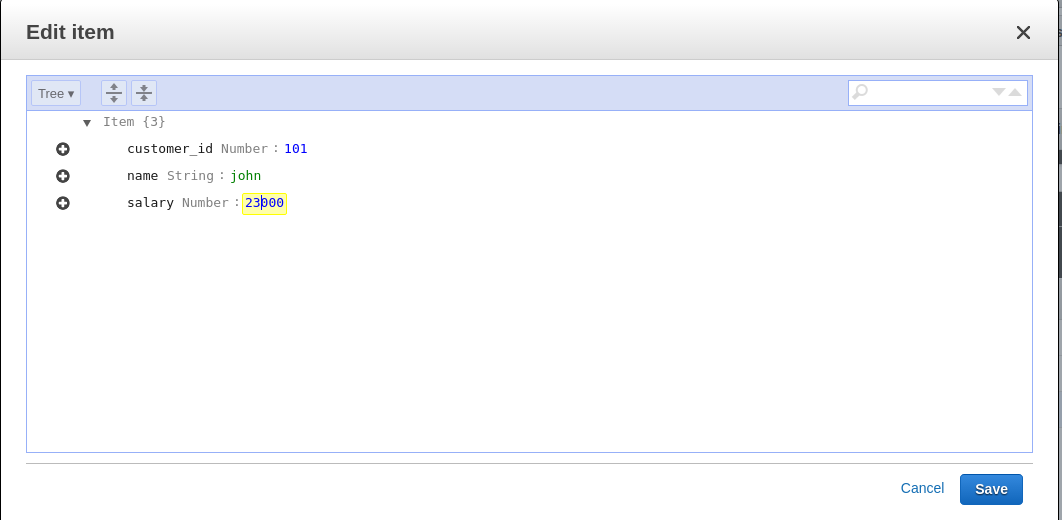
Here, we can update the information and click Save to save it. We can see the updated information in the console by listing all the items. Here we can see that John's salary is updated to 23,000 from 20,000.
We can also perform CRUD operations using local installation. Here, we need to use request and API calls to perform the operation. Open the shell and start working with CRUD operations:
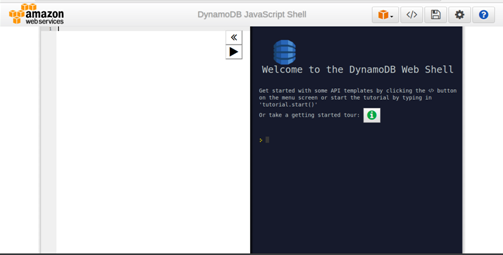
The local shell also provides the template of the request. If you click the Template option, you can see the various sample requests:
Let us start by checking the list of all the tables that exist in the database. This request requires you to specify the limit of entries it should return at a time:
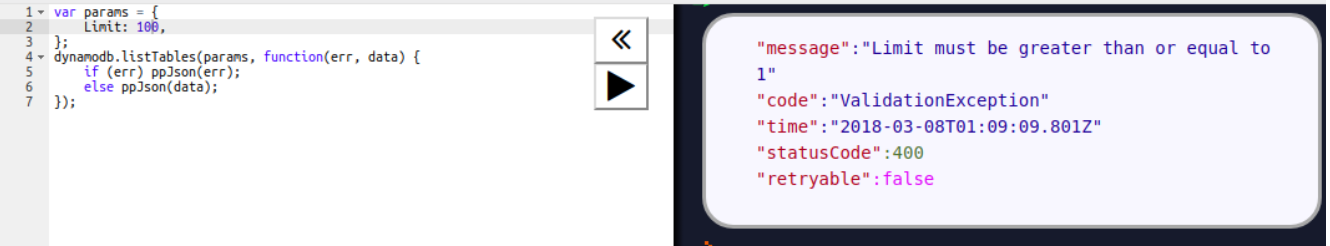
We have to write our request in the left-hand side panel and the result will be displayed in the right-hand side panel. Here we can see the tables that are listed with TableNames.
Let us create the table Person. To create the table, we have to provide the primary key attribute. In this example, we are defining PersonID as a primary key; the other schemas will vary:
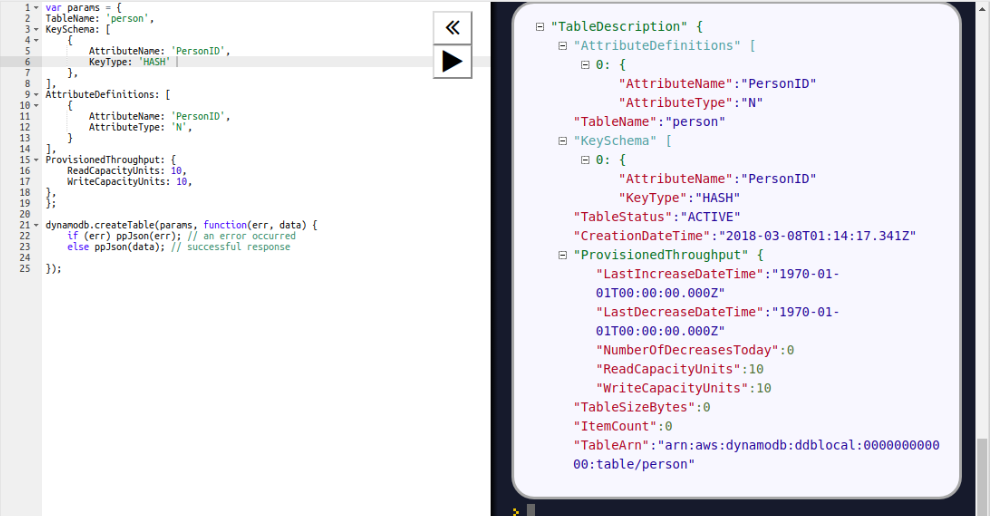
Here, we need to provision throughput when we create the table.
Now we will add an item to the Person table, using the PutItem API call. For the PutItem request, we have to provide the table name and the item to be inserted. We are inserting an item with PersonID 101, as shown in the following screenshot:
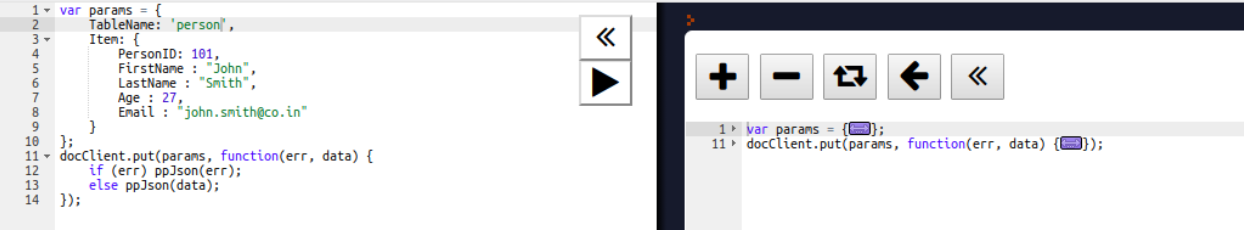
To retrieve an item from the table, we have to use a GetItem call, which needs the table name and the primary key attribute value to retrieve the item:
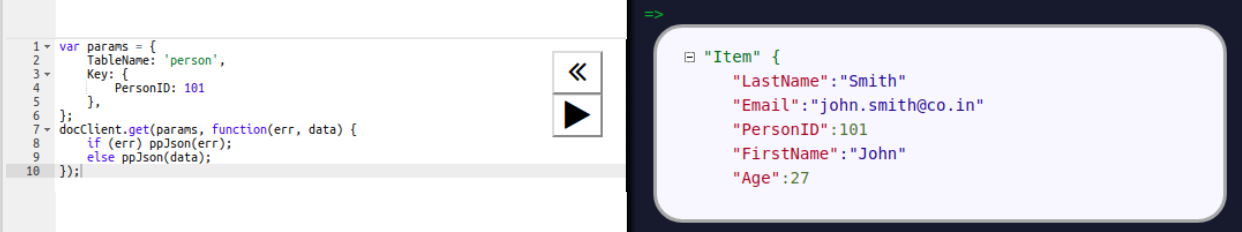
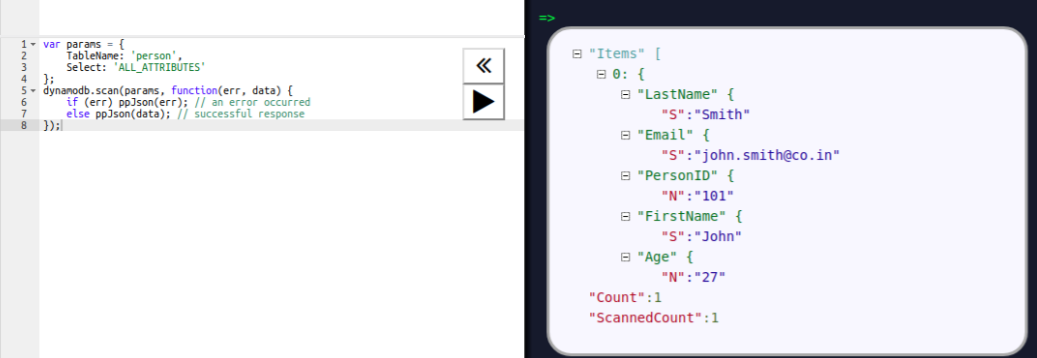
Here, the item with PersonID 101 is retrieved. To retrieve all the items, we can use the scan operation, as shown in the following screenshot:
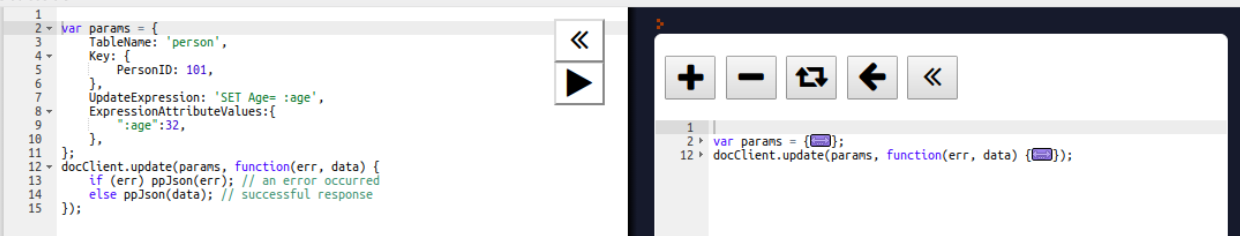
Now we will update the age of the person to 32. To update the item's attribute value, we are using the UpdateItem API. Here, we have to pass the primary key attribute to search the item in the table and pass the UpdateExression parameter to set the attribute value:
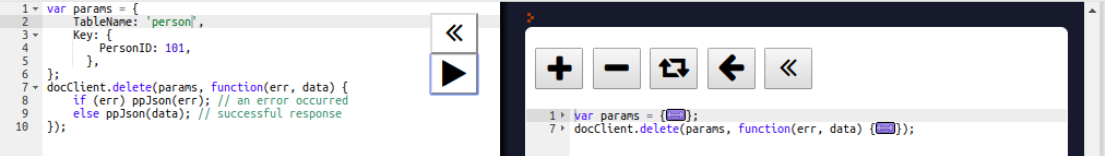
For deletion, we have to use the DeleteItem call. We have to provide the primary key value of the item to be deleted. We are deleting a person with PersonID 101 in the following operation: