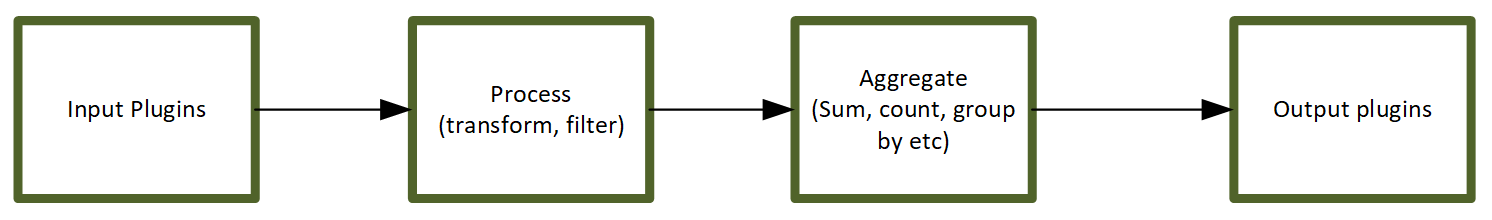
Telegraf gets input from input plugins, and then processes data via filter and transformation. After the process step is complete, it will start the aggregation step and run the aggregation functions to get results, and finally use the output plugin to write data into InfluxDB:
Consider the upcoming example. Let's use Telegraf to collect a matrix from a UNIX system CPU, memory, and swap usage and load it onto InfluxDB. Here are the detailed steps:
- Create a new database in InfluxDB:
create database telegraf
- Install Telegraf:
$ wget http://get.InfluxDB.org/telegraf/telegraf_0.10.2-1_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i telegraf_0.10.2-1_amd64.deb
- Generate telegraf.conf using the sample-config option. Define the input filter for cpu, mem, and swap. Define the output filter as InfluxDB:
$ telegraf -sample-config -input-filter cpu:mem:swap -output-filter InfluxDB > telegraf.conf
Quick review generates the configuration file (telegraf.conf). It contains the related input and output configuration:
[[inputs.cpu]], [[inputs.mem]],[[inputs.swap]] and output configuration: [[outputs.InfluxDB]].
- Run Telegraf with the generated configuration file:
$ telegraf -config telegraf.conf
- Check the data in InfluxDB to verify that the data is loaded:
> use telegraf;
Using database telegraf
> show measurements;
name: measurements
name
----
cpu
mem
net
swap
> select cpu, host, usage_softirq, usage_steal, usage_system, usage_user from cpu limit 3;
name: cpu
time cpu host usage_softirq usage_steal usage_system usage_user
---- --- ---- ------------- ----------- ------------ ----------
2017-12-03T00:08:00Z cpu-total bwu-pc 0 0 0.20046775810221984 3.1406615436011274
2017-12-03T00:08:00Z cpu2 bwu-pc 0 0 0 3.3066132264534605
2017-12-03T00:08:00Z cpu1 bwu-pc 0 0 0.20060180541627498 3.2096288866598295
Now, Telegraf is integrated with InfluxDB.
