Now that you have understood the basics of creating scripts in Python, let's create a script that will actually be useful to you. In later chapters, you will need to know your local and public IP addresses for each interface, hostname, Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, and Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). The script that follows here demonstrates how to execute all of these. A few of the concepts here may still seem foreign, especially how IP and MAC addresses are extracted from interfaces. Do not worry about that; this is not the script you are going to write. You can use this script if you like, but it is here to show you that you can salvage components of scripts—even seemingly complex ones—to develop your own simple scripts.
Note
This script uses a technique to extract IP addresses for Linux/Unix systems by querying the details based on an interface that has been used in several Python modules and examples. The specific recipe for this technique can be found in many places, but the best documented reference to this technique can be found at http://code.activestate.com/recipes/439094-get-the-ip-address-associated-with-a-network-inter/.
Let's break down the script into its components. This script uses a few functions that make execution cleaner and repeatable. The first function is called get_ip. It takes an interface name and then tries to identify an IP address for that interface:
def get_ip(inter): s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) ip_addr = socket.inet_ntoa(fcntl.ioctl(s.fileno(), 0x8915, struct.pack('256s', inter[:15]))[20:24]) return ip_addr
The second function, called get_mac_address, identifies the MAC address of a specific interface:
def get_mac_address(inter): s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) info = fcntl.ioctl(s.fileno(), 0x8927, struct.pack('256s', inter[:15])) mac_address = ''.join(['%02x:' % ord(char) for char in info[18:24]])[:-1] return mac_address
As you can see, these functions rely on the low-level network interface language of the socket library. Your concentration should not be on understanding every detail about this function, but more on the flow of information, the types of variables being used, and how the libraries are integrated. The reason for this is that you are going to generate a script later that requires fewer components and replicates the activity of grabbing a public IP address later.
The third function gets the details of the host and returns them to the main part of the script. It determines whether the host is Windows or not so that the correct functions are called. The function accepts two lists, one for Ethernet interfaces and the wireless interfaces typical in Linux/Unix. These interfaces are processed through the previous functions called in this bigger function. This allows the decision-making to be handled by the get_localhost_details function, and then returns the values for the host that will be represented by the print statements at the end of the script:
def get_localhost_details(interfaces_eth, interfaces_wlan):
hostdata = "None"
hostname = "None"
windows_ip = "None"
eth_ip = "None"
wlan_ip = "None"
host_fqdn = "None"
eth_mac = "None"
wlan_mac = "None"
windows_mac = "None"
hostname = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
if hostname.startswith("127.") and os.name != "nt":
hostdata = socket.gethostbyaddr(socket.gethostname())
hostname = str(hostdata[1]).strip('[]')
host_fqdn = socket.getfqdn()
for interface in interfaces_eth:
try:
eth_ip = get_ip(interface)
if not "None" in eth_ip:
eth_mac = get_mac_address(interface)
break
except IOError:
pass
for interface in interfaces_wlan:
try:
wlan_ip = get_ip(interface)
if not "None" in wlan_ip:
wlan_mac = get_mac_address(interface)
break
except IOError:
pass
else:
windows_ip = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
windows_mac = hex(getnode()).lstrip('0x')
windows_mac = ':'.join(pos1+pos2 for pos1,pos2 in zip(windows_mac[::2],windows_mac[1::2]))
hostdata = socket.gethostbyaddr(socket.gethostname())
hostname = str(hostdata[1]).strip("[]\'")
host_fqdn = socket.getfqdn()
return hostdata, hostname, windows_ip, eth_ip, wlan_ip, host_fqdn, eth_mac, wlan_mac, windows_macThe final function in this script is called get_public_ip, which queries a known website for the IP address that is connected to it. This IP address is returned to the web page in a simple, raw format. There are a number of sites against which this can be done, but make sure you know the acceptable use and terms of service authorized. The function accepts one input, which is the website you are executing the query against:
def get_public_ip(request_target):
grabber = urllib2.build_opener()
grabber.addheaders = [('User-agent','Mozilla/5.0')]
try:
public_ip_address = grabber.open(target_url).read()
except urllib2.HTTPError, error:
print("There was an error trying to get your Public IP: %s") % (error)
except urllib2.URLError, error:
print("There was an error trying to get your Public IP: %s") % (error)
return public_ip_addressFor Windows systems, this script utilizes the simple socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname()) function request. This does work for Linux, but it relies on the /etc/hosts file to have the correct information for all interfaces. Much of this script can be replaced by the netifaces library, as pointed out by the previous reference. This would greatly simplify the script, and examples of its use will be shown in the following Chapter. The netifaces library is not installed by default, and so you will have to install it on every host on which you want to run this script. Since you typically do not want to make any impact on a host's integrity, this specific script is designed to avoid that conflict.
Tip
The final version of this script can be found at https://raw.githubusercontent.com/funkandwagnalls/pythonpentest/master/hostdetails.py.
The following screenshot shows the output of running this script. Components of this script will be used in later chapters, and they allow the automated development of exploit configurations and reconnaissance of networks.
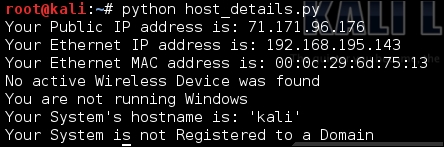
So your useful script is going take components of this script and only find the public IP address of the system you are on. I recommend that you try doing this prior to looking at the following code (which shows what the actual script looks like). If you want to skip this step, the solution can be seen here:
import urllib2
def get_public_ip(request_target):
grabber = urllib2.build_opener()
grabber.addheaders = [('User-agent','Mozilla/5.0')]
try:
public_ip_address = grabber.open(target_url).read()
except urllib2.HTTPError, error:
print("There was an error trying to get your Public IP: %s") % (error)
except urllib2.URLError, error:
print("There was an error trying to get your Public IP: %s") % (error)
return public_ip_address
public_ip = "None"
target_url = "http://ip.42.pl/raw"
public_ip = get_public_ip(target_url)
if not "None" in public_ip:
print("Your Public IP address is: %s") % (str(public_ip))
else:
print("Your Public IP address was not found")The output of your script should look similar to this:
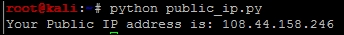
Tip
This script can be found at https://raw.githubusercontent.com/funkandwagnalls/pythonpentest/master/publicip.py.
