In the real world, each wireless device has a range upto which it can provide wireless connectivity. Packet Tracer simulates this range with the use of physical workspaces. We can see what happens when a laptop with a wireless interface is moved out of wireless range. For this exercise, we'll use the following topology:
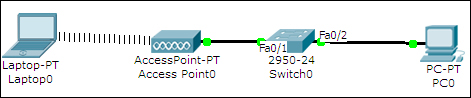
This topology has a wireless access point (Access Point0) connected to a switch (Switch0), which is connected to a PC (PC0). We also have a laptop with a wireless interface.
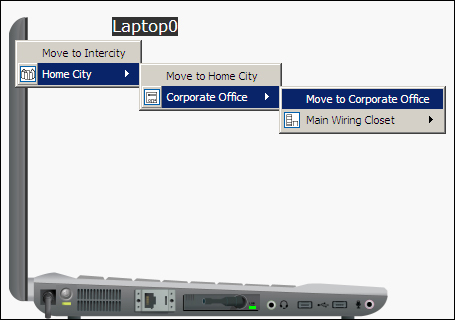
Configure IP addresses on both the PC and laptop; we'll use IP addresses 10.0.0.1 and 10.0.0.2 respectively. Now ping these devices from one another to test connectivity. Moving to the physical workspace, navigate to Home City | Corporate Office. You'll find a round mesh that represents the range of the wireless access point. We are now going to move the laptop to the new office building, out of the wiring closet, and place it in the corporate office, as shown in the following screenshot:
Going back to the corporate office, move the laptop out of this wireless range and test the connectivity by pinging the PC. We will find that this fails because the laptop is out of range, as shown in the following screenshot:
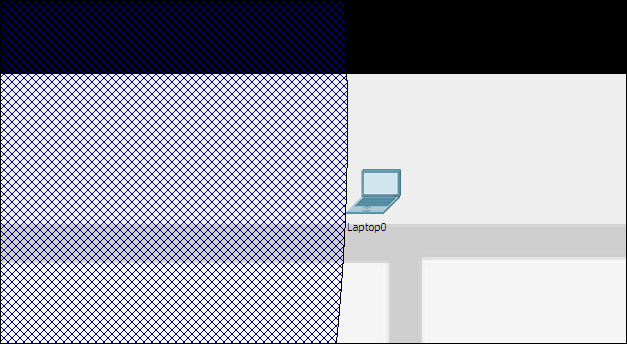
Thus, we've demonstrated the range of wireless devices using the physical workspace.
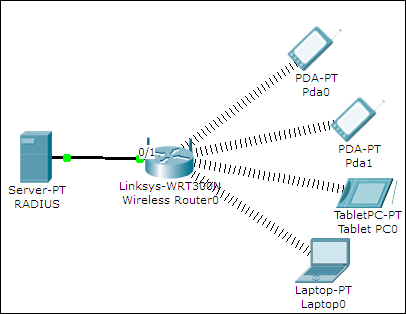
So far, we have configured wireless networks without additional features such as encryption or DHCP. In this section, we'll use the Linksys devices available in Packet Tracer and create a topology with all these features.
We will also add a server (RADIUS) to this topology and enable RADIUS authentication. WPA2-PSK enterprise will be the mode of authentication we will choose in the Linksys router (Wireless Router0). After building this topology, switch the default module of the laptop (Laptop0) with a Linksys-WMP300N module. Open the Linksys router, go to the GUI tab, navigate to the Wireless tab, and change the SSID field. We'll be using Linksys for this demo, as shown in the following figure:
Open the server, navigate to the Config tab, select AAA, and configure RADIUS authentication with four user credentials. Configuration will be as follows.
Network configuration will be as follows:
|
ClientName |
ClientIP |
ServerType |
Key |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Radius |
|
User setup will be as follows:
|
UserName |
Password |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure a static IP for the server as 192.168.0.50. Next, under the GUI tab of the Linksys router, navigate to Wireless | Wireless security and enter the following settings:
|
Security Mode |
WPA2 Enterprise |
|---|---|
|
Encryption |
AES |
|
RADIUS Server |
|
|
RADIUS Port |
1645 |
|
Shared Secret |
|
Move on to the wireless end devices, go to the Config tab, select Wireless, and enter the following settings:
- SSID:
Linksys - Authentication: WPA2
- User ID:
john - Password:
secr3t
Make sure you use a different pair of credentials for each wireless end device. Once this is configured, the end device will get an IP address and you'll see the wireless link indicating a connection.
Now, we'll configure the laptop that has the Linksys module. Go to the Desktop tab, open the PC Wireless utility, choose the Profiles tab, and click on New. Enter any name here, you'll see a list with the SSID name shown, click on Advanced Setup and a wizard will guide you through the process.
Use the simple PDU tool to test the connectivity. If you use the simulation mode before a wireless connection is established between two devices, you will see the RADIUS packet being sent to the server by the router.
