End devices have a Desktop tab, which provides a lot of utilities for testing and debugging the network. We will learn about each utility in this section.
The following utilities are available for PCs, laptops, PDAs, and tablet PCs.
We have already used the IP Configuration utility in Chapter 1, Getting Started with Packet Tracer, when we created a simple topology. This option is used to choose between a dynamic and static IP address. Entering a static IP address fills the Subnet Mask field; according to the class of the IP address, this field can also be edited if required. If DHCP is configured on Server-PT, choosing DHCP here obtains an IP address dynamically. Starting with Packet Tracer Version 6, this utility also has a section for configuring IPv6 addresses.
A modem dialer, this utility can be used if the PC-HOST-NM-1AM module is plugged in. This utility is available only on PC-PT and Laptop-PT devices as other end devices do not have the NM-1AM module. A cloud-PT device with phone numbers is required to be connected to this PC on one end and a router on the other end with a modem interface. A username/password combination is also required in the router; after this is done, entering them in this utility creates a connection.
We used this utility in Chapter 2, Network Devices, for accessing the CLI through the console port. In most cases, the settings in this utility can be left to their defaults; but if you change the baud rate of the network device, it has to be changed here so that they match. This module is not available on the Server-PT device as it doesn't have an RS-232 interface.
This utility simulates the command line offered in Windows Operating Systems. Only a limited set of commands are available but they are enough to test the network. The following are the commands available:
? arp delete dir ftp help ipconfig ipv6config netstat nslookup ping snmpget snmpgetbulk snmpset ssh telnet tracert
Each command's supported parameters can be found by entering a command without any options as shown in the following screenshot:
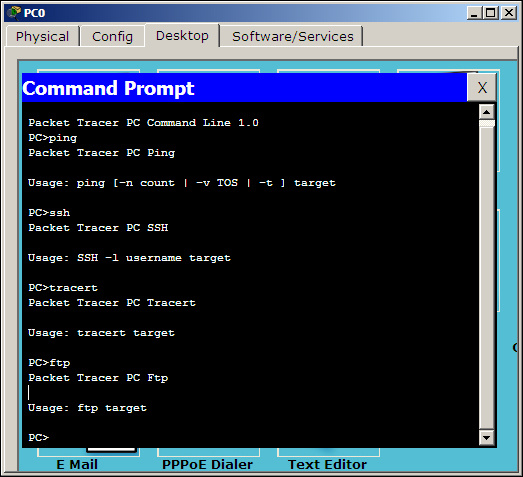
Displaying arguments for each command
Web Browser is a utility with minimal options, which can be used if you have a Server-PT device configured with HTTP. This can also be used if there is a Linksys-WRT300N device to access its web interface. This utility has only back, forward, go, and stop buttons and does not store any cache or history.
This utility is designed for the Linksys-WMP300N module. It displays signal strength information and also has options for choosing a wireless network and modifying profiles to connect to wireless routers that are not broadcasting their SSID. These settings can also be saved, imported, or exported. Wireless networking will be explained in detail in Chapter 9, Setting Up a Wireless Network. This utility is available only on PC-PT and Laptop-PT devices, as other end devices do not have the Linksys module.
The VPN utility is used to create a VPN connection for secure communication. A router has to be configured as a VPN server for this to work. A sample topology is available at Cisco Packet Tracer 6.0.1\saves\PC\VPN\Vpn_Easy.pkt.
This utility is similar in functionality to the Add Simple PDU and Add Complex PDU tools in the common tools bar. It is used to create customized packets and send them at periodic intervals. This is immensely useful for simulating a real environment.
The MIB (Management Information Base) Browser utility sends out SNMP requests. This allows you to retrieve router and switch data or make changes to the devices. A get request is sent to fetch a value, whereas a set request is sent to modify a value. A router has to be configured with an RO (Read Only) community string and RW (Read Write) community string. This utility is not available on the Server-PT device. A sample topology is available at Cisco Packet Tracer 6.0.1\saves\PC\MIB_Browser\SNMP_Router.pkt.
Cisco IP Communicator is a Cisco software that can be used to turn a computer into an IP phone. This utility is available in Packet Tracer to make and answer calls using a PC or laptop. Clicking on it opens a phone GUI that can be used to dial numbers; the default TFTP server can also be changed by navigating to the Preferences… option, as shown in the next screenshot. This utility is not available on the Server-PT device.
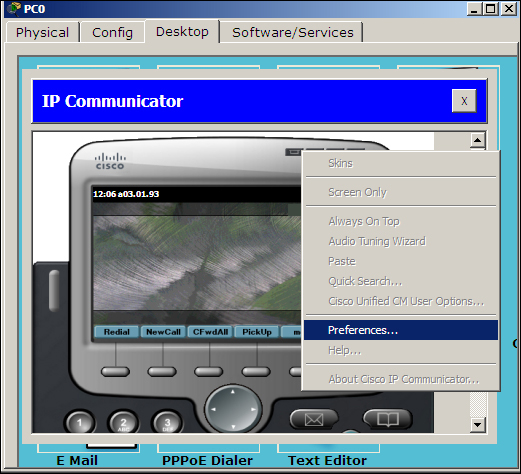
Cisco IP Communicator on the PC
This is an e-mail client utility that can be used to send and receive e-mails. The first time it is opened, it has to be configured with the Incoming mail server (POP3), Outgoing mail server (SMTP), and credentials. A Server-PT device has to exist in the topology with its EMAIL section configured. This utility is not available on the Server-PT device. A sample topology is available at Cisco Packet Tracer 6.0.1\saves\Server\Mail\mail_2Server_2PC.pkt.
This utility is required to establish a connection using a DSL-Modem-PT device. On one end, the modem device connects this PC over Ethernet and on the other end, it has a cloud connected by a phone wire. A router has to be configured as a PPPoE server with a username and password. A sample topology is available at Cisco Packet Tracer 6.0.1\saves\Router\PPPOE\client.server.modem.pppoe.pkt.
