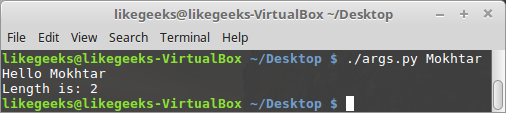
As previously mentioned, the script name is the first argument at index 0 of the array. So, if we try to count the arguments, then the count should always be at the very least 1. In other words, if we have not supplied arguments, the argument count will be 1. To count the items in an array, we can use the len() function.
If we edit the script to include a new line we will see this work, as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
print("Hello " + sys.argv[1])
print( "length is: " + str(len(sys.argv)) )
Executing the code as we have earlier, we can see that we have supplied two arguments—the script name and then the string Mokhtar:
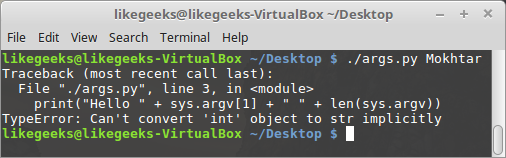
If we try and have a single print statement to print the output and the number of arguments, then it will produce an error because we can't concatenate integers with strings. The length value is an integer and this cannot be mixed with strings without conversion. That's why we used the str function to convert the integer to a string. The following code will fail:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
print("Hello " + sys.argv[1] + " " + len(sys.argv))
If we try to run the script and omit to supply an argument, then there will be a null value in the array when we reference index 1. This will give an error, as shown in the following screenshot:

We of course need to handle this to prevent the error; enter the concept of significant whitespace.
