Let's work on the smoothScrollTo function. This is the function that detects the scrolling motion to make sure it is smooth. The smoothScrollTo function is used to move the scroll to the bottom of the page when the page loads. You could use this function in other scenarios to click a button where its click event uses the function to go to a specific section. In our case, we only want to go straight to the bottom. Let's take a look at the function.
Inside its braces, create a callback function. The first line should list the variables time, start, and factor, left undefined. Next, create a return function, injecting the variables target and duration. Let's take a quick look at what we have so far:
window.smoothScrollTo = (function () {
var timer, start, factor;
return function (target, duration) {
};
}());Inside the return function, create new variables: offset for the window 's pageYOffset property and delta for the value of pageYOffset subtracted from the target variable. Next, set duration to be equal to duration || 1000, start equal to the now() method of Date, and factor equal to 0. Here's the code:
var offset = window.pageYOffset, delta = target - window.pageYOffset; // Y-offset difference duration = duration || 1000; // default 1 sec animation start = Date.now(); // get start time factor = 0;
Next, add a logical test that clears an interval on the timer if the timer value is not false:
if( timer ) {
clearInterval(timer); // stop any running animations
}Now, we will create a new function called step to animate the scrolling. Inside it, first create a new variable called y, then define factor as the value of start subtracted from the Date's now() method, and divide the result by duration. Next, if factor is equal or less than 1, use the clearInterval method on timer to stop the animation, and on the next line, inside the if condition, set factor to equal 1.
After the if conditional statement, set y equal to the result of factor multiplied by the sum of delta and offset. Finally, in this function, call the scrollBy method of the window object with the values 0 and y - window.pageYOffset. Check out this code example:
function step() {
var y;
factor = (Date.now() - start) / duration; // get interpolation factor
if( factor >= 1 ) {
clearInterval(timer); // stop animation
factor = 1; // clip to max 1.0
}
y = factor * delta + offset;
window.scrollBy(0, y - window.pageYOffset);
}After this function, set timer equal to the setInterval method with its variables set to step and 10. Then, return timer and close the function:
*** //previous parts of the function timer = setInterval(step,10); return timer; } }());
Now, if you reload your browser, you will see some stuff finally happening. But there are a couple of things to see happening here. The first is the obvious big blue blob that does nothing. We will get to that soon.
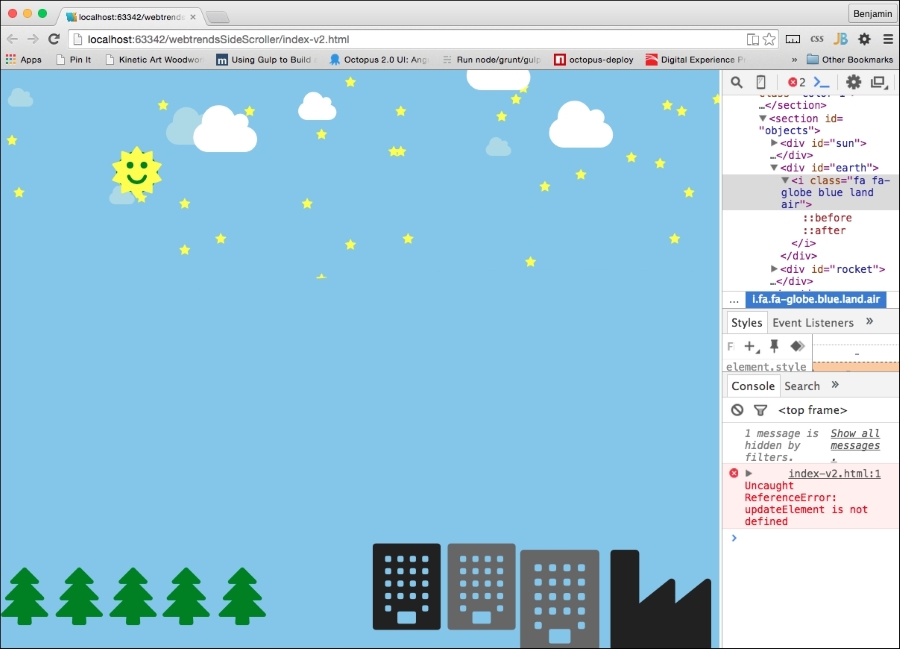
The other problem is in the developer console. We see that there is an error. The browser is complaining about our function call to updateElement, which we have not defined yet. If we take a test-driven development approach, this is a failure that will lead us to success. We need to fix this error. Look at this screenshot: