To Drupal, a role has the same meaning as it does outside of Drupal: the functional aspect of the user, sometimes considered a persona. It's worth mentioning that Drupal does blur the line a bit between a role and a user type, because it comes with three roles predefined, and they are the user types mentioned earlier. While administrator makes sense as a role, authenticated and anonymous are not really roles, but appear there to simplify things, for administrators, at least.
So, let's take a look at the default user roles inside of Drupal before we move on to discussing why you would want additional ones. If you are using the menus, click People in the Admin menu (admin/people), and then click the tab labeled Roles, as in the following:
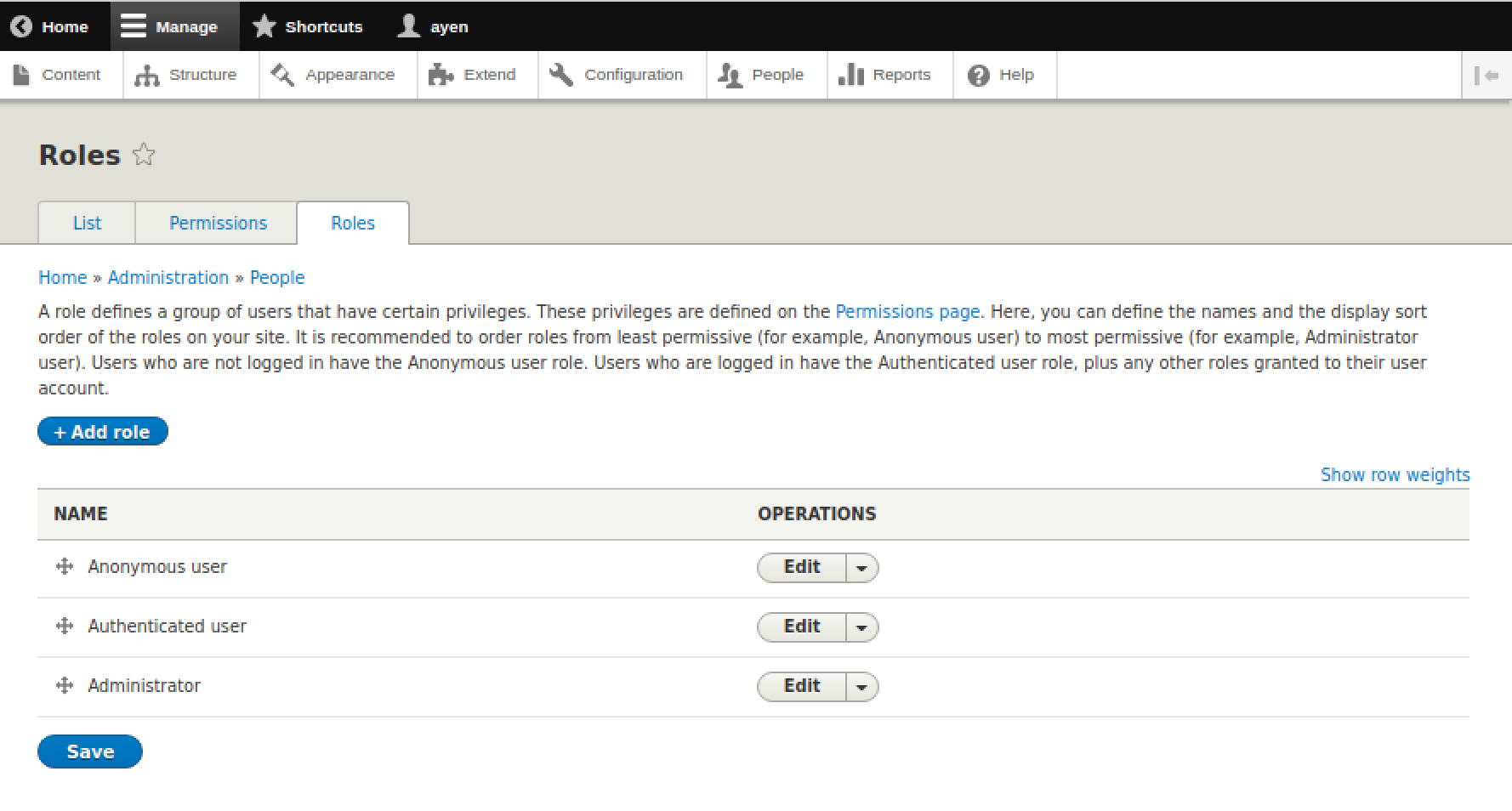
The preceding screenshot shows the roles that are predefined in Drupal. I disagree with the given description of a role, because it is unclear. The order of operation in Drupal is that privileges are assigned to roles, and roles are assigned to users. We'll discuss that more when we add a user and when we assign some permissions, later in this chapter.
For now, let's focus on the default Drupal roles themselves. As I mentioned earlier, anonymous and authenticated are actually more user types than roles, but in Drupal they are referred to as roles. When would these three roles, alone, be sufficient? One example would be a site where all users with logins can create content, and all users that have no login can only view that content. If those are the limits to your organizational and site complexity, you can jump ahead to the section on User Creation if you'd like.
Let us consider. The anonymous role stands on its own. Why? Because it is defined as a user with no account or login, which is to say, a user that is not identified. We would not assign the role of Anonymous to a user account, because if there is an account, the user of it is no longer anonymous. There would be no sense in creating different roles for anonymous users, because there would be no user accounts to assign those roles. So, that leaves us with the other two roles, and we can use those to derive examples.
On our site, we will have four types of non-administrative authenticated users. The first will be authenticated users in general. That is, users with this role will be able to login, and in addition to being able to see the Article and Page site content that Anonymous and all users can see, they will be able to see content of the Appointment type we defined, as well.
This could be our use of the Authenticated role, since all users logging in will have those capabilities at a minimum, but we won't use that role for it. Why? Because we have to account for the possibility that later there might be the need to have some users who can log in but cannot access appointment data. In general, I prefer to leave the predefined roles unchanged for that reason...use them as a model instead, or as is. So, we will call the new role Client.
There will be three additional roles for authenticated users on our site: Client, who is able to view appointments; Consultant, who is able to create and edit appointments; and Editor, who is able to create and edit content other than appointments. The complete list of our user roles and their use are given in this table:
|
Role |
Use |
|---|---|
| Anonymous |
Unknown users. Able to read Article and Page content. |
| Authenticated |
Users with accounts. Able to comment on Article content. |
| Client |
Authenticated + able to view Appointment content |
| Consultant |
Authenticated + able to perform Appointment CRUD* |
| Editor |
Authenticated + able to perform Article and Page CRUD* |
| Administrator |
Authenticated + able to access Drupal admin functions and manage user accounts |
Follow these steps to add the Client role:
- Click the +Add role button, which leads to the page admin/people/roles/add
- Enter the role name, Client
- Click Save
Notice that the role list now includes Client. Follow the steps above for the Consultant and Editor roles as well. The role list should now appear as shown in the following screenshot:
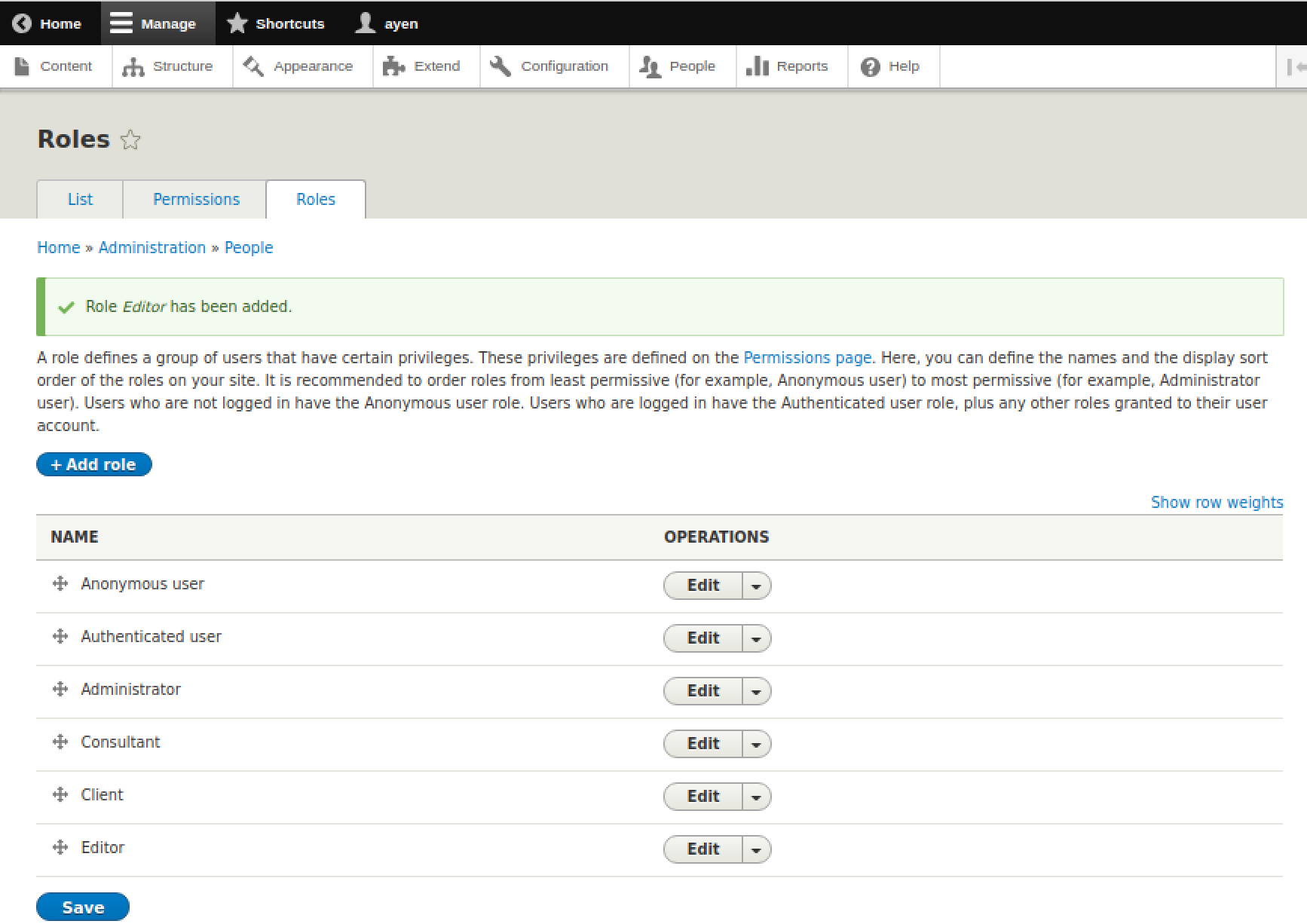
All roles are now available for use. However, their capabilities have not yet been defined. Since we've covered all that we need to regarding the creation of roles, let's move on to the topic of permissions.
