In the previous section, the CUT was independent with no dependency, hence the way it tested the code was straightforward. However, let's discuss how we can unit test the CUT that has dependencies. For this, refer to the following image:
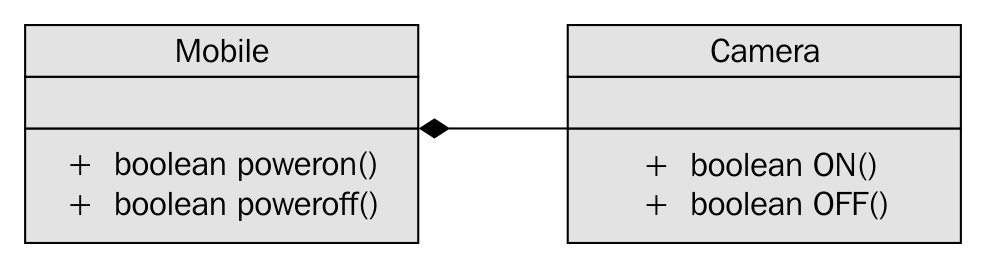
In Figure 7.42, it is apparent that Mobile has a dependency on Camera and the association between Mobile and Camera is composition. Let's see how the Camera.h header file is implemented in a legacy application:
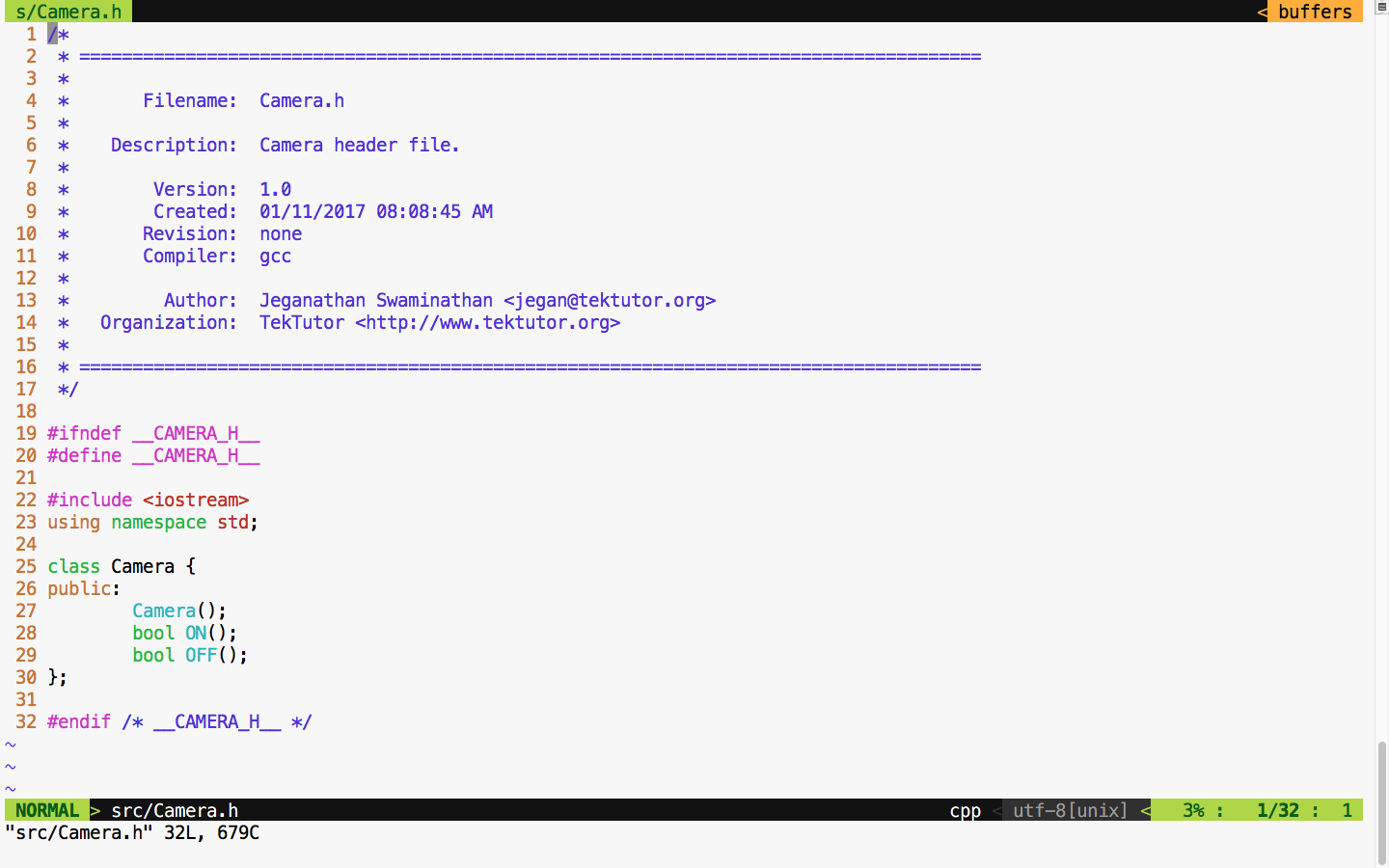
For demonstration purposes, let's take this simple Camera class that has ON() and OFF() functionalities. Let's assume that the ON/OFF functionality will interact with the camera hardware internally. Check out the Camera.cpp source file in Figure 7.44:
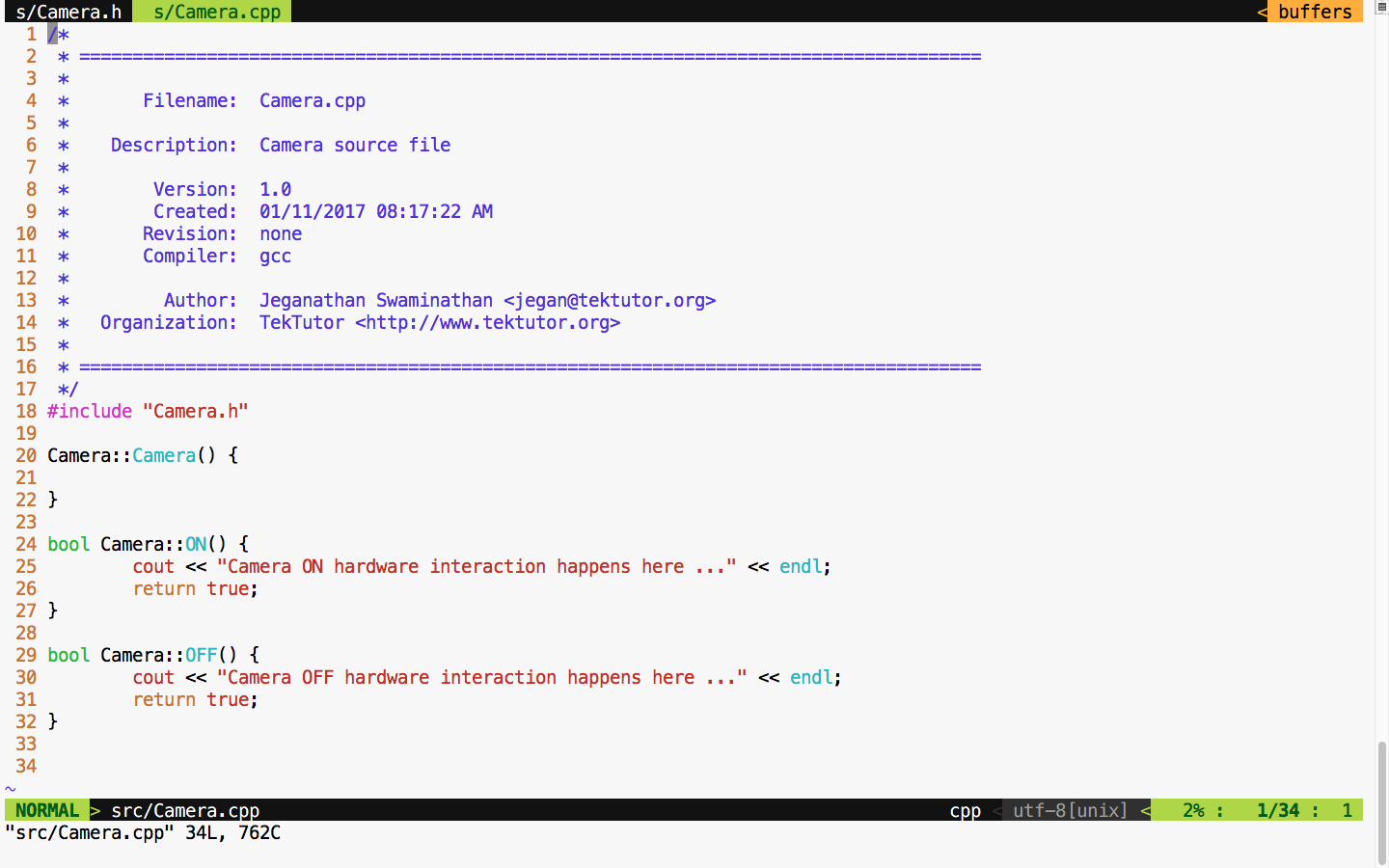
For debugging purposes, I have added some print statements that will come in handy when we test the powerOn() and powerOff() functionalities of mobile. Now let's check the Mobile class header file in Figure 7.45:
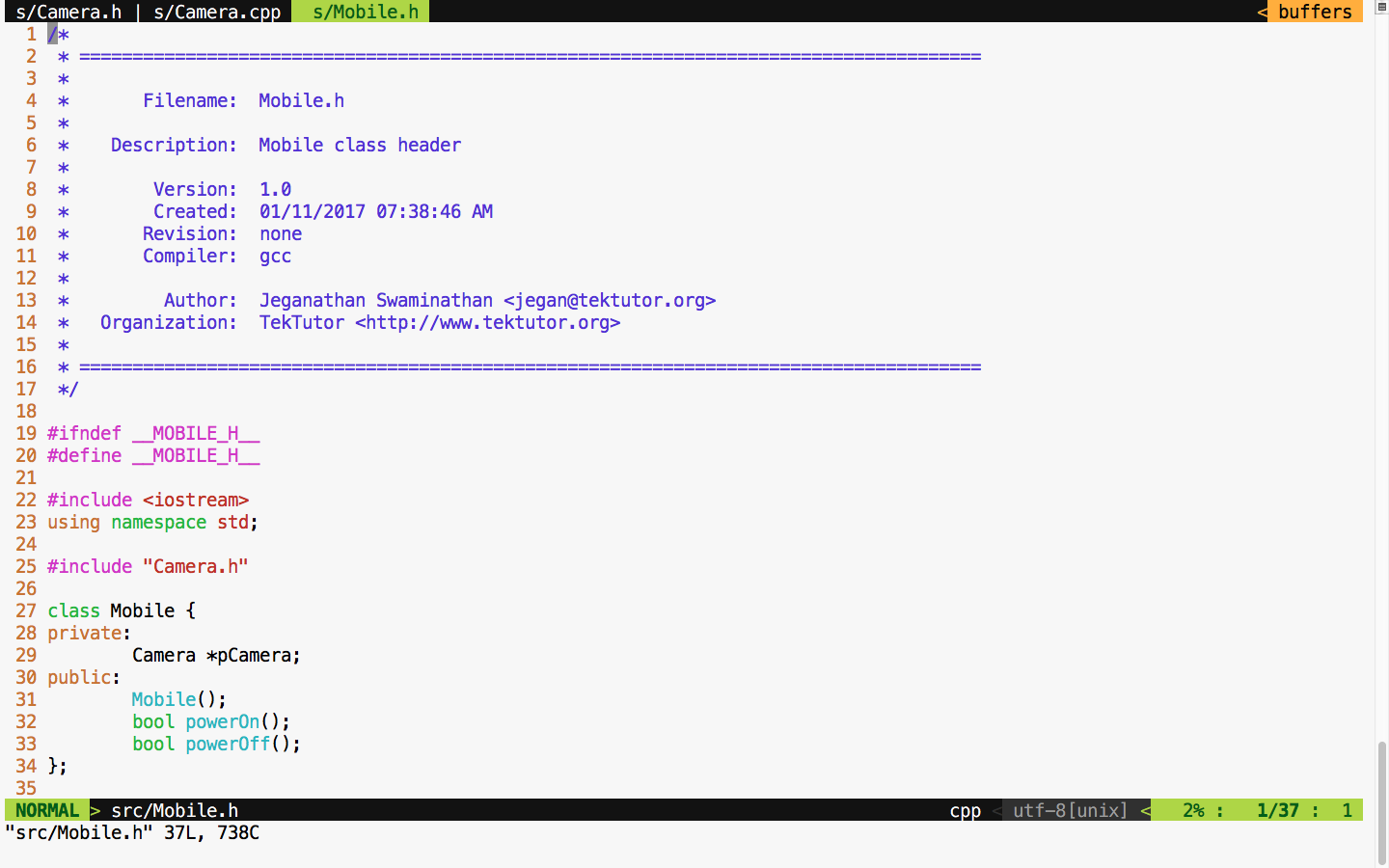
We move on to the mobile implementation, as illustrated in Figure 7.46:
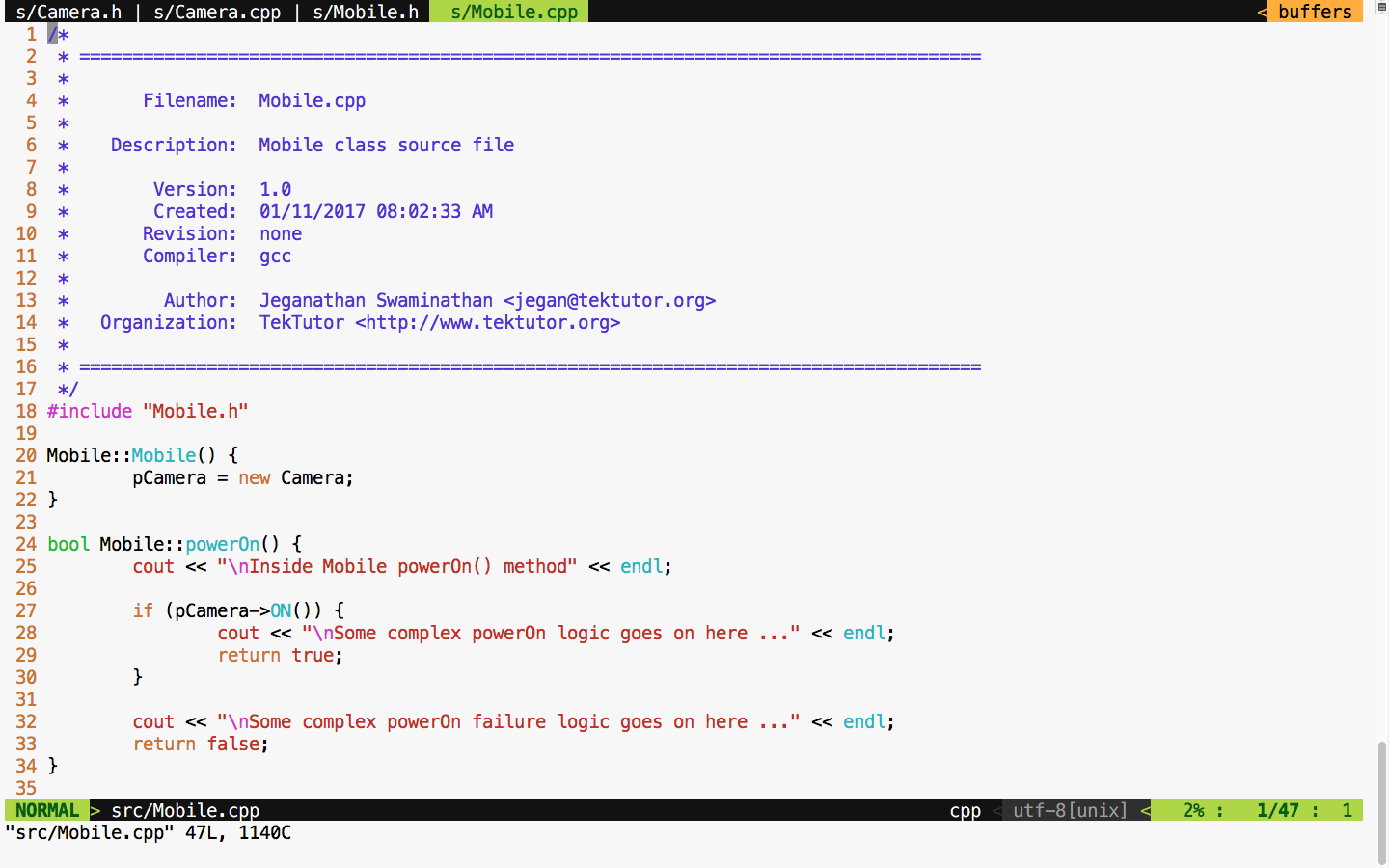
From the Mobile constructor implementation, it is evident that mobile has a camera or to be precise composition relationship. In other words, the Mobile class is the one that constructs the Camera object, as shown in Figure 7.46, line 21, in the constructor. Let's try to see the complexity involved in testing the powerOn() functionality of Mobile; the dependency has a composition relationship with the CUT of Mobile.
Let's write the powerOn() test case assuming camera On has succeeded, as follows:
TEST ( MobileTest, testPowerOnWhenCameraONSucceeds ) {
Mobile mobile;
ASSERT_TRUE ( mobile.powerOn() );
}
Now let's try to run the Mobile test case and check the test outcome, as illustrated in Figure 7.47:
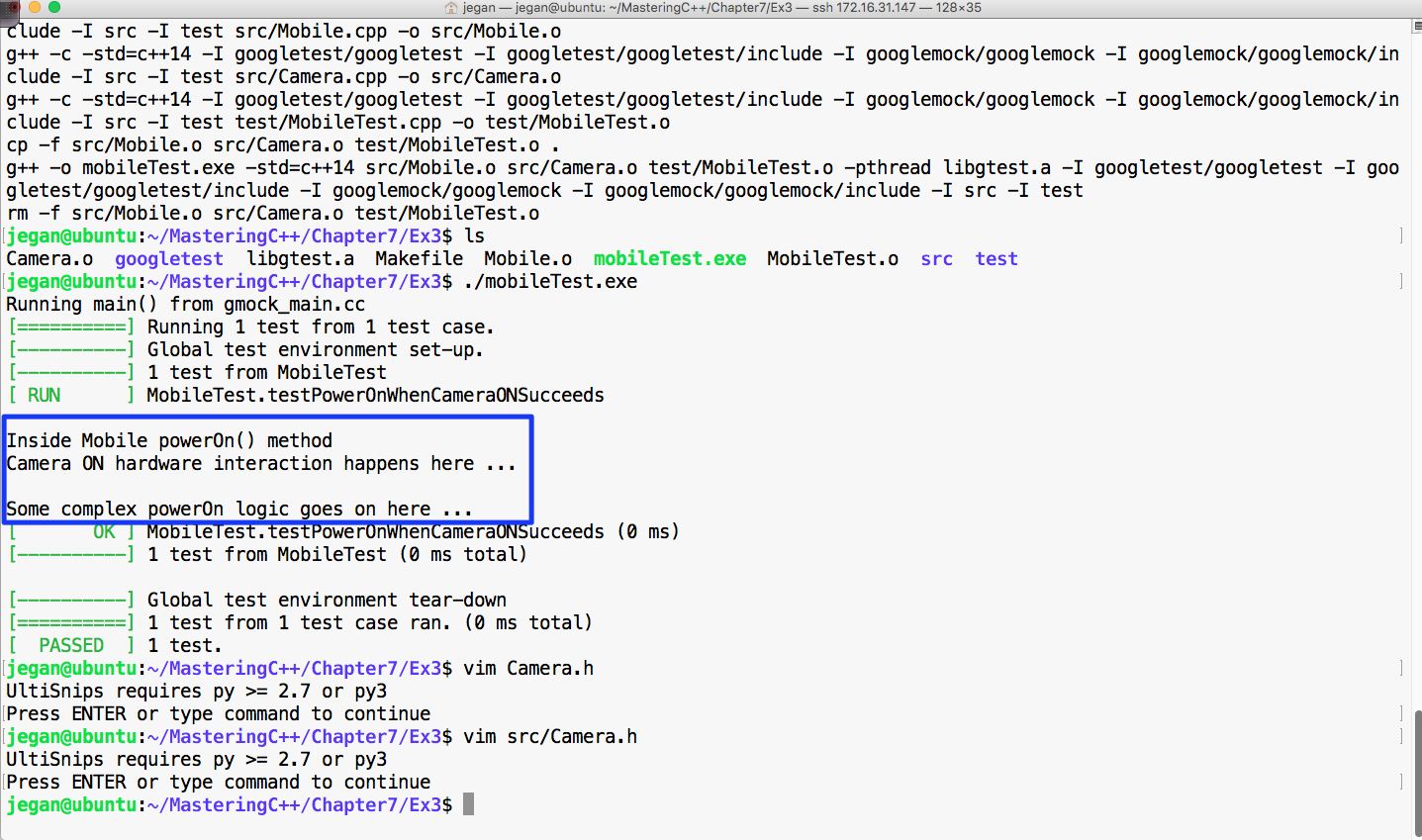
From Figure 7.47, we can understand that the powerOn() test case of Mobile has passed. However, we also understand that the real ON() method of the Camera class also got invoked. This, in turn, will interact with the camera hardware. At the end of the day, it is not a unit test as the test outcome isn't completely dependent on the CUT. If the test case had failed, we wouldn't have been able to pinpoint whether the failure was due to the code in the powerOn() logic of mobile or the code in the ON() logic of camera, which would have defeated the purpose of our test case. An ideal unit test should isolate the CUT from its dependencies using dependency injection and test the code. This approach will help us identify the behavior of the CUT in normal or abnormal scenarios. Ideally, when a unit test case fails, we should be able to guess the root cause of the failure without debugging the code; this is only possible when we manage to isolate the dependencies of our CUT.
The key benefit of this approach is that the CUT can be tested even before the dependency is implemented, which helps test 60~70 percent of the code without the dependencies. This naturally reduces the time to market the software product.
This is where the Google mock or gmock comes in handy. Let's check how we can refactor our code to enable dependency injection. Though it sounds very complex, the effort required to refactor code isn't that complex. In reality, the effort required to refactor your production code could be more complex, but it is worth the effort. Let's take a look at the refactored Mobile class shown in Figure 7.48:
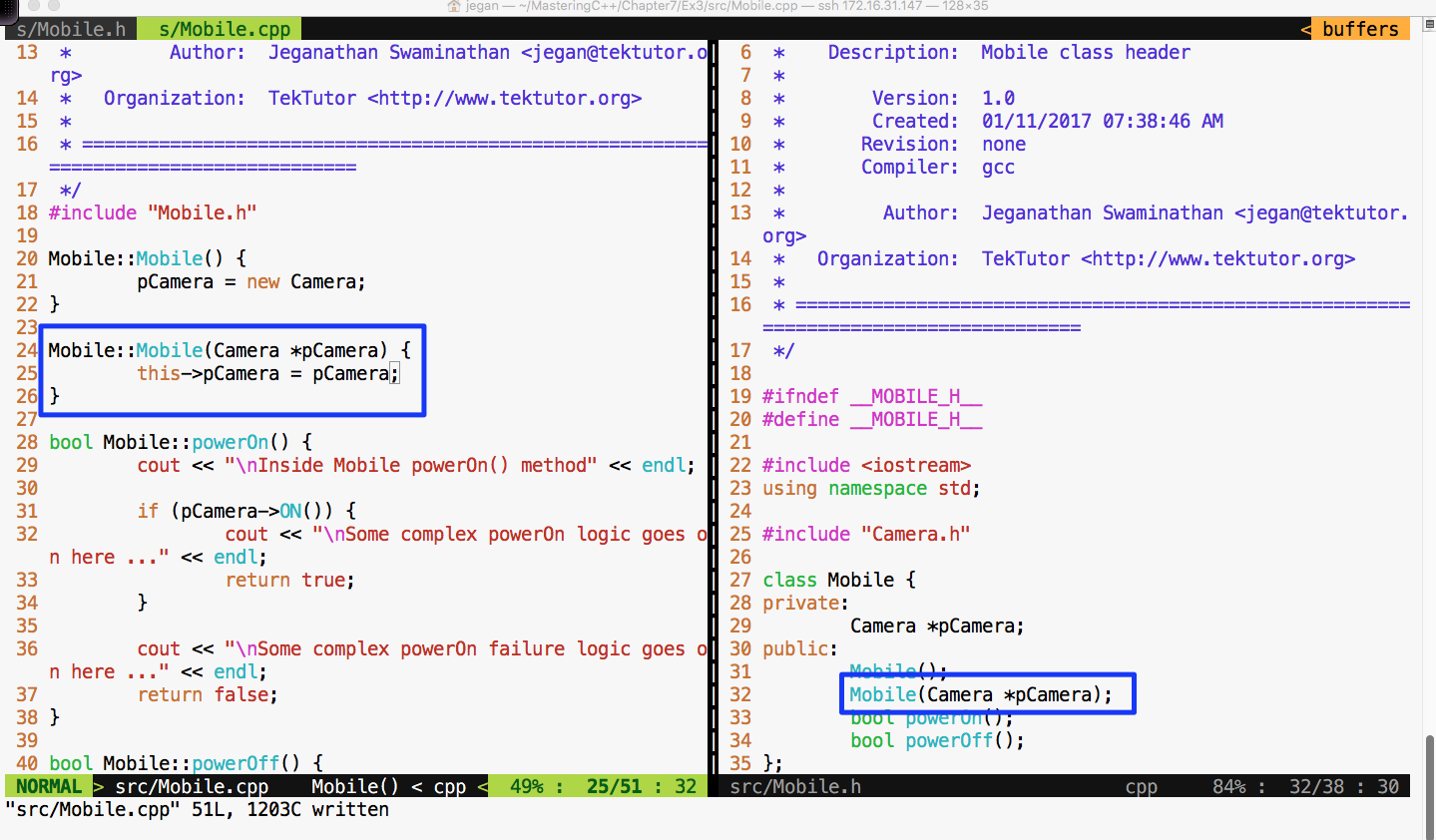
In the Mobile class, I have added an overloaded constructor that takes camera as an argument. This technique is called constructor dependency injection. Let's see how this simple yet powerful technique could help us isolate the camera dependency while testing the powerOn() functionality of Mobile.
Also, we must refactor the Camera.h header file and declare the ON() and OFF() methods as virtual in order for the gmock framework to help us stub these methods, as shown in Figure 7.49:
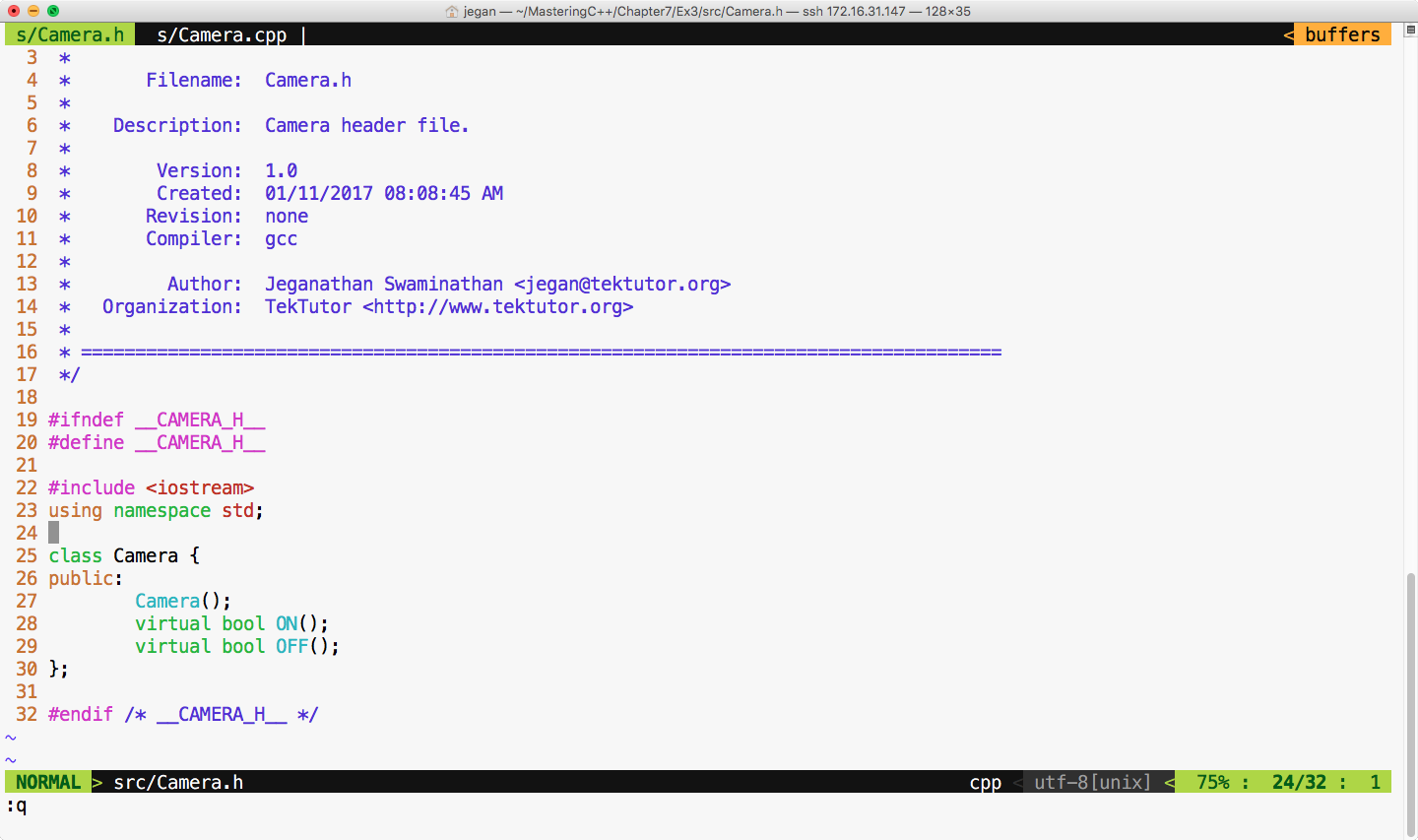
Now let's refactor our test case as shown in Figure 7.50:
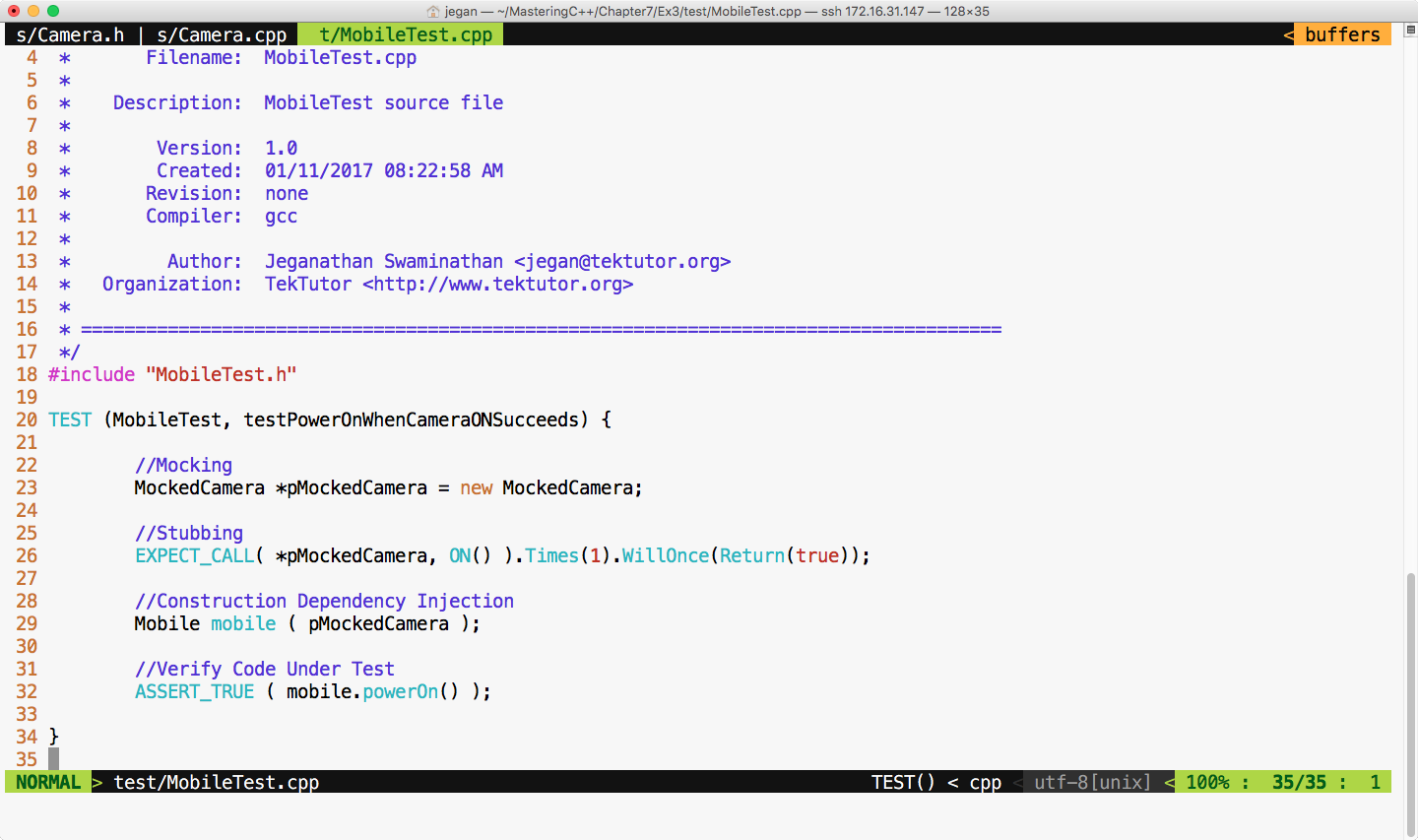
We are all set to build and execute the test cases. The test outcome is expected as shown in Figure 7.51:
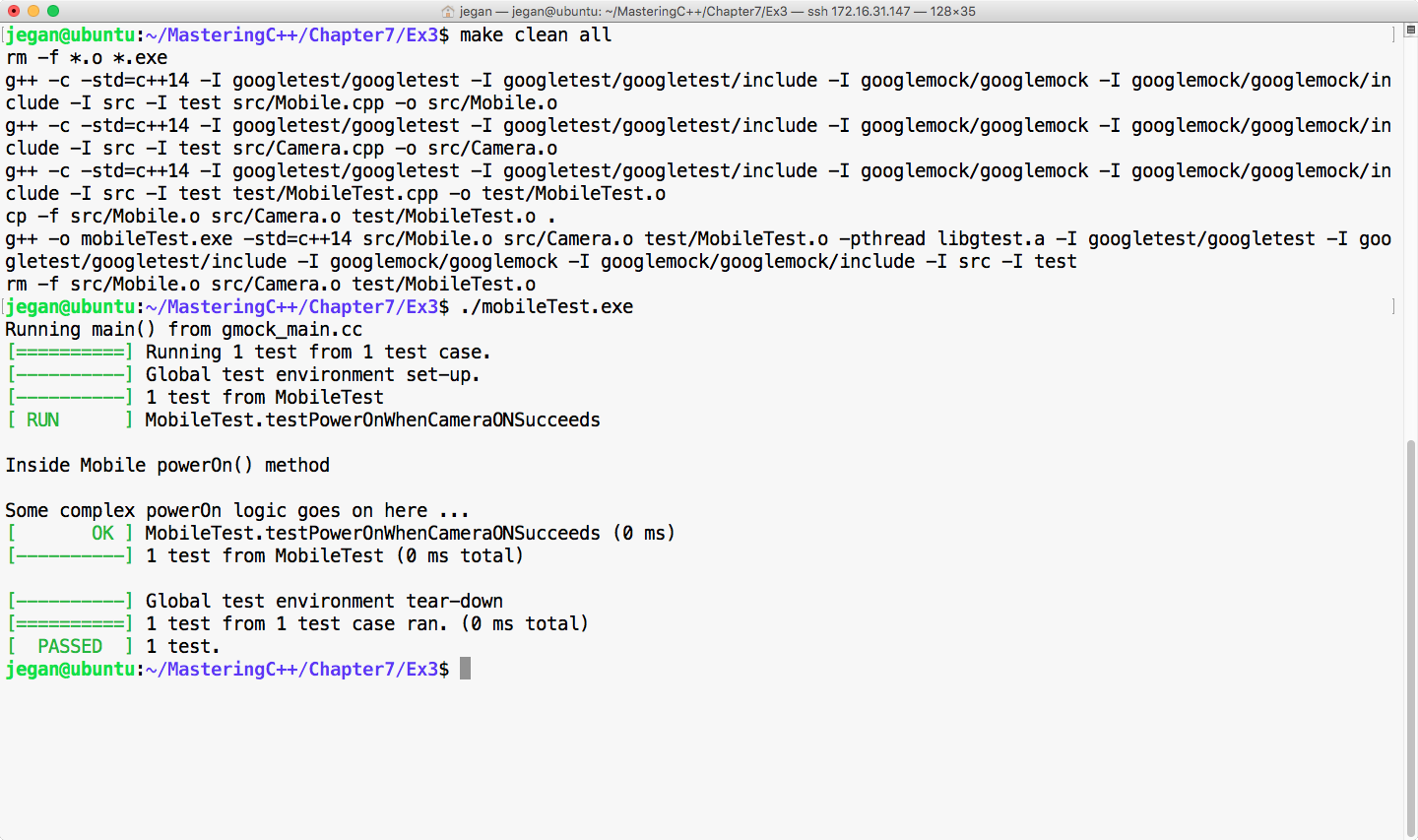
Cool! Not only has our test case passed, but we have also isolated our CUT from its camera dependency, which is evident as we don't see the print statements from the ON() method of camera. The bottom line is you have now learned how to unit test code by isolating its dependencies.
Happy TDD!
