Trade exchanges allow users to trade assets of value. However, most of these exchanges are centralized. Centralized exchanges hold assets of their users. If a user wants to start trading with their 1,000 XRP, they need to send this money to Ripple address of the centralized exchange to start trading. The problem with being centralized is that exchanges are highly vulnerable. In the past decade, a lot of centralized exchanges were hacked and assets worth billions of dollars were stolen.
The following is a list of past attacks and the assets stolen:
| Exchange Name | Date | Asset Stolen |
| MtGox | March 2014 | 850,000 BTC |
| Cryptsy | July 2014 | 300,00 LTC & 13,000 BTC |
| Mintpal | December 2014 | 3,894 BTC |
| Bitstamp | January 2015 | 19,000 BTC |
| Bter | February 2015 | 7,000 BTC |
| Bitfinex | August 2016 | 120,00 BTC |
| Nicehash | December 2017 | 4000 BTC |
| Coincheck | January 2018 | 523,000,000 NEM |
| Bitgrail | February 2018 | 17,000,000 NANO |
| CoinSecure | April 2018 | 483 BTC |
An alternative to centralized exchanges is decentralized exchanges. Decentralized exchanges enable the exchange of value without holding the user's assets. You don't have to transfer your asset to a third party for you to start trading. Here, transactions happen directly between users and no middleman is involved. Hence, decentralized exchange improves security and drastically reduces cost at the same time.
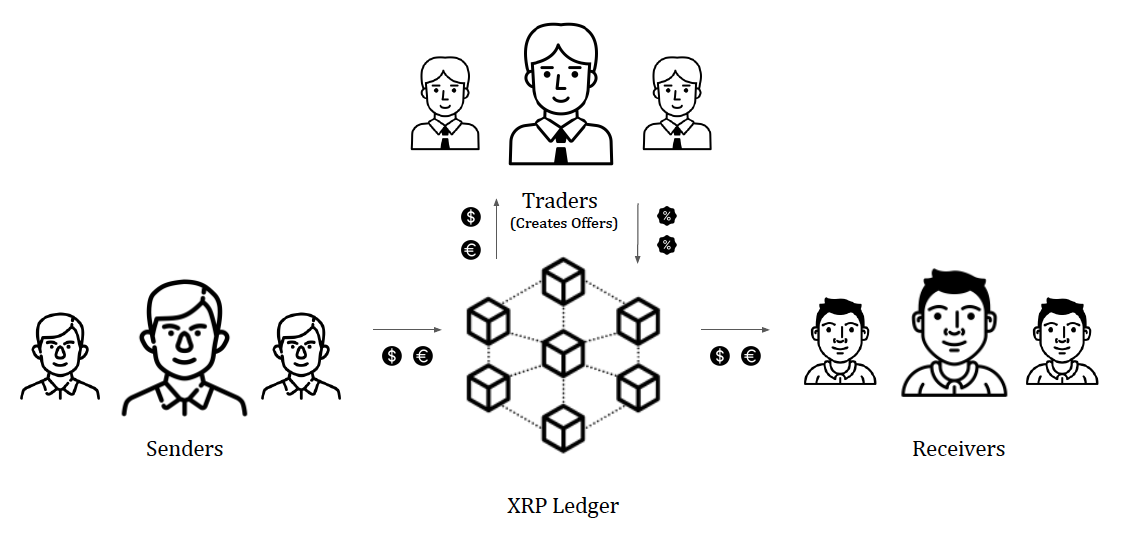
Ripple contains a functional decentralized exchange that allows users to trade issued currencies for XRP or each other. Traders who wish to buy or sell currencies can create offers on Ripple. These offers are utilized for cross-currency payments, where the sender's money is bought by the trader through their offer; later the trader's money is sent to the receiver and the currency exchange is completed. Ripple has the feature of AutoBridging to reduce exchange cost. If the direct exchange from INR to USD is costly, then Ripple automatically exchanges INR to XRP and XRP to USD to reduce exchange costs.
The following demonstrates the functionality of a decentralized exchange inside Ripple: