Here's the HTML we're going to use in this example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Mastering RWD with HTML5 & CSS3</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/site-styles.css">
<!--[if lt IE 9]>
<script src="//html5shiv.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/html5.js">
</script>
<![endif]-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>Basic Layout Using a Custom CSS Grid</h1>
<main class="container-12 clear" role="main">
<header class="grid-12" role="banner">Header (.grid-12)</header>
<nav class="grid-4" role="navigation">Nav (.grid-4)</nav>
<section class="grid-8">
<div class="row">
<div class="grid-6 black">.grid-6</div>
<div class="grid-6 black">.grid-6</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="grid-4 black">.grid-4</div>
<div class="grid-4 black">.grid-4</div>
<div class="grid-4 black">.grid-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="grid-3 black">.grid-3</div>
<div class="grid-3 black">.grid-3</div>
<div class="grid-3 black">.grid-3</div>
<div class="grid-3 black">.grid-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="grid-2 black">.grid-2</div>
<div class="grid-7 black">.grid-7</div>
<div class="grid-3 black">.grid-3</div>
</div>
<p>Content (.grid-8)</p>
</section>
<footer class="grid-12" role="contentinfo">Footer (.grid-12)</footer>
</main>
</body>Notice that there are several nested containers inside their own row (black background). The idea here is to highlight the nested content sections that add up to 12 columns.
Nesting columns are a major advantage of any grid system. In this book, we are harnessing this power so we don't limit the design in any way.
On small screens (320px wide), this is what the container looks like:
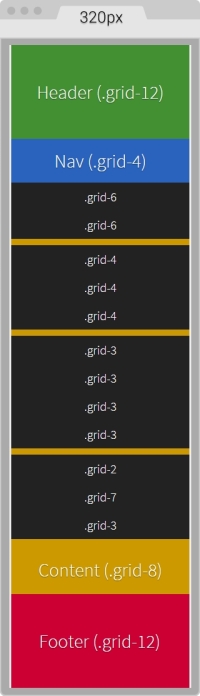
On large screens starting at 40em (640px) wide, this is what the layout looks like:
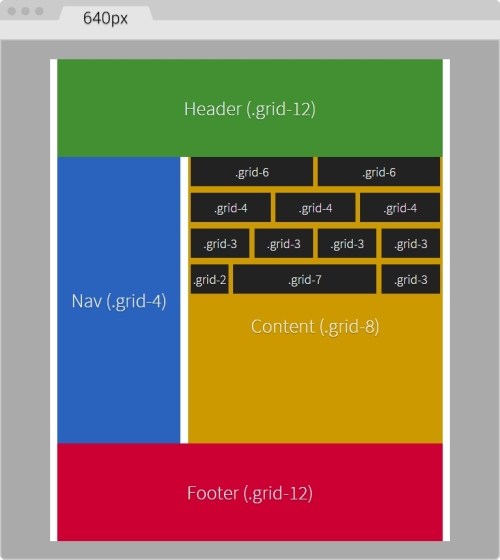
You can see the demo I created on CodePen at http://codepen.io/ricardozea/pen/d6ab6e0293be9b6bac2e16ad37942ed5.
