In this section, we will review how XOR works and then give you an example, and then present you with two challenges.
So, here is one of the XOR programs we discussed before:
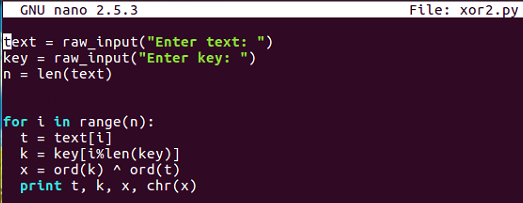
You input arbitrary texts and an arbitrary key, and then go through the bytes one by one, picking out one byte of text and one byte of key before combining them with XOR and printing out the results. So, if you put in HELLO and qrs, you'll get encrypted stuff, encrypted with XOR.
Here's an example:

It will scramble into EXAMPLE. So, this undoes encryption; remember that XOR undoes itself.
If you want to break into one of these, one simple procedure is just to try every key and print out the results for each one, and then read the key is readable.
So, we try all single-digit keys from 0 to 9.
The result is that you feed in the ciphertext, encrypt it with each of these, and when you hit the correct key value, it will turn into readable text.
Let's take a look at that:
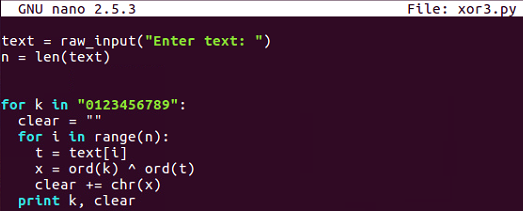
Here's the decryption routine, which simply inputs texts from the user and then tries every key in this string, 0 through 9. For each one of those it combines, think the XORed text into a variable named clear, so it can print one line for each key and then the clear result. So, if we run that one and put in my ciphertext, it gives us 10 lines.:
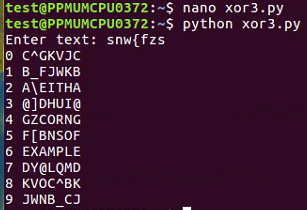
We just scanned through these lines and saw which one becomes readable, and you can see the correct key and the correct plaintext at 6. The first challenge is here:

This is similar to the one we saw earlier. The key is a single digit, and it will decrypt into something readable. Here's a longer example that is in a hexadecimal format:

The key is two digits of ASCII, so you'll have to try 100 choices to find a way to turn this into a readable string.
