If you have Windows, you have to download and install Python.
Here are the steps which you need to follow:
- Download Python from https://www.python.org/downloads/
- Run it in a Command Prompt window
- Start interactive mode with Python
- Close with exit()
To create a script, you just use Notepad, enter the text, save the file with Ctrl + S, and then run it with python followed by the script name. Let's get started with the installation.
Open the Python page using link given previously and download Python. It offers you various versions of Python. In this book, we will use Python 2.7.12.
Sometimes, you can't install it right away because Windows marks it as untrusted:
- You have to unblock it in the properties first so that it will run, and run the installer
- If you go through the steps of the installer, you'll see an optional step named Add python.exe to path. You need to choose that selection
The purpose of that selection is to make it so Python can run from the command line in a Terminal window, which is called Command Prompt on Windows.
Now let's proceed with our installation:
- Open the Terminal and type the following command:
$ python
- When you run it, you can see that it works. So, now we will type a command:
print "HELLO"
Refer to the following screenshot:
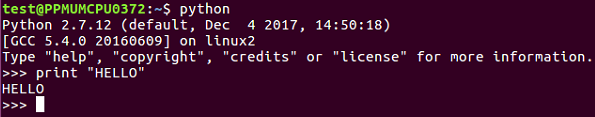
- We can exit using the exit() command as shown earlier.
- Now, if we want to make a script, we type the following command:
notepad hello.py
- This opens up Notepad:
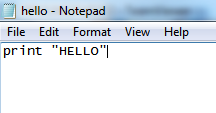
- We want to create a file. In that file, we enter the following command:
print "HELLO"
- Then, save and close it. In order to run it, we need to enter the following command:
$ python hello.py
It runs and prints HELLO.
Usually, when you install Python on Windows, it fails to correct the path, so you have to execute the following commands to create a symbolic link; otherwise, Python will not start correctly from the command line:
- cd c: \Windows
- mklink /H python.exe
- c: \python27\python.exe
In the next section, we will look at the Caesar cipher and ROT13 obfuscation techniques.
