In the keyboard, there is one interesting key, the backward quote such as "`". This key is normally situated below the Esc key. If we place text between two successive back quotes, then echo will execute those as commands instead of processing them as plane text.
Alternate syntax for $(command) is the backtick character "`", which we can see as follows:
$(command) or `command`
For example:
- We need to use proper double quoted inverted commas, as follows:
$ echo "Hello, whoami" - The next command will print the text as it is; such as
Hello, whoami:Hello, whoami - Use proper double inverted commas:
$ echo "Hello, `whoami`." Hello, student
When we enclose
whoamitext in the "`" character, the same text which was printed as plain text will run as a command, and the command output will be printed on screen. - Use proper double inverted commas:
$ echo "Hello, $(whoami)." Hello, student.
Same like the earlier explanation.
echo "Today is date"
Output:
Today is date
A similar example:
echo "Today is `date`"
Or:
echo "Today is $(date)"
Output:
Today is Fri Mar 20 15:55:58 IST 2015
Further, similar examples include:
$ echo $(cal)

In this example, new lines are lost.
Another example:
$ echo "$(cal)"
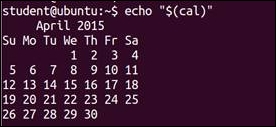
Here, the display is properly formatted.
Next, nesting of commands is as follows:
$ pwd /home/student/work $ dirname="$(basename $(pwd)) " $ echo $dirname
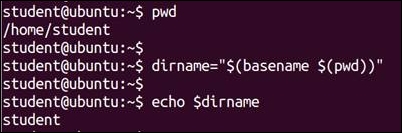
This command shows us that the base directory for the current directory is student.
