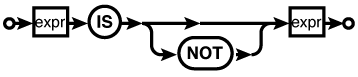
Description
The IS and IS
NOT operators are very similar to the equal (
= or == ) and not equal ( != or <> ) operators. The main
difference is how NULLs are handled. The standard equality tests
are subject to the rules of three valued logic, which will
result in a NULL if either parameter expression is NULL.
The IS operator considers NULL to be “just another
value,” and will always return a 0 or 1. For example, the
expression NULL IS NULL is
considered to be true (1) and
the expression NULL IS 6 is
considered to be false (0).