In this recipe, we successfully reported memory bugs to the Dynamic Analysis section of the dashboard. We can gain further insights by browsing the defects (under Defect Count):
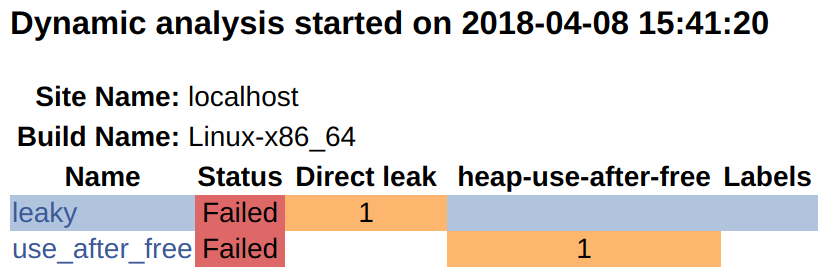
By clicking on the individual links, it is possible to browse the full output.
Note that it is also possible to generate the AddressSanitizer report locally. In this example, we need to set ENABLE_ASAN, as follows:
$ mkdir -p build
$ cd build
$ cmake -DENABLE_ASAN=ON ..
$ cmake --build .
$ cmake --build . --target test
Start 1: leaky
1/2 Test #1: leaky ............................***Failed 0.07 sec
Start 2: use_after_free
2/2 Test #2: use_after_free ...................***Failed 0.04 sec
0% tests passed, 2 tests failed out of 2
Running the leaky test executable directly produces the following:
$ ./build/tests/leaky
=================================================================
==18536==ERROR: LeakSanitizer: detected memory leaks
Direct leak of 8000 byte(s) in 1 object(s) allocated from:
#0 0x7ff984da1669 in operator new[](unsigned long) /build/gcc/src/gcc/libsanitizer/asan/asan_new_delete.cc:82
#1 0x564925c93fd2 in function_leaky() /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/src/buggy.cpp:7
#2 0x564925c93fb2 in main /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/tests/leaky.cpp:4
#3 0x7ff98403df49 in __libc_start_main (/usr/lib/libc.so.6+0x20f49)
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: 8000 byte(s) leaked in 1 allocation(s).
Correspondingly, we can obtain detailed output by running the use_after_free executable directly, as follows:
$ ./build/tests/use_after_free
=================================================================
==18571==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: heap-use-after-free on address 0x6250000004d8 at pc 0x557ffa8b0102 bp 0x7ffe8c560200 sp 0x7ffe8c5601f0
READ of size 8 at 0x6250000004d8 thread T0
#0 0x557ffa8b0101 in function_use_after_free() /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/src/buggy.cpp:28
#1 0x557ffa8affb2 in main /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/tests/use_after_free.cpp:4
#2 0x7ff1d6088f49 in __libc_start_main (/usr/lib/libc.so.6+0x20f49)
#3 0x557ffa8afec9 in _start (/home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/build/tests/use_after_free+0xec9)
0x6250000004d8 is located 984 bytes inside of 8000-byte region [0x625000000100,0x625000002040)
freed by thread T0 here:
#0 0x7ff1d6ded5a9 in operator delete[](void*) /build/gcc/src/gcc/libsanitizer/asan/asan_new_delete.cc:128
#1 0x557ffa8afffa in function_use_after_free() /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/src/buggy.cpp:24
#2 0x557ffa8affb2 in main /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/tests/use_after_free.cpp:4
#3 0x7ff1d6088f49 in __libc_start_main (/usr/lib/libc.so.6+0x20f49)
previously allocated by thread T0 here:
#0 0x7ff1d6dec669 in operator new[](unsigned long) /build/gcc/src/gcc/libsanitizer/asan/asan_new_delete.cc:82
#1 0x557ffa8affea in function_use_after_free() /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/src/buggy.cpp:19
#2 0x557ffa8affb2 in main /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/tests/use_after_free.cpp:4
#3 0x7ff1d6088f49 in __libc_start_main (/usr/lib/libc.so.6+0x20f49)
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: heap-use-after-free /home/user/cmake-recipes/chapter-14/recipe-03/cxx-example/src/buggy.cpp:28 in function_use_after_free()
Shadow bytes around the buggy address:
0x0c4a7fff8040: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff8050: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff8060: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff8070: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff8080: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
=>0x0c4a7fff8090: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd[fd]fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff80a0: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff80b0: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff80c0: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff80d0: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
0x0c4a7fff80e0: fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd fd
Shadow byte legend (one shadow byte represents 8 application bytes):
Addressable: 00
Partially addressable: 01 02 03 04 05 06 07
Heap left redzone: fa
Freed heap region: fd
Stack left redzone: f1
Stack mid redzone: f2
Stack right redzone: f3
Stack after return: f5
Stack use after scope: f8
Global redzone: f9
Global init order: f6
Poisoned by user: f7
Container overflow: fc
Array cookie: ac
Intra object redzone: bb
ASan internal: fe
Left alloca redzone: ca
Right alloca redzone: cb
==18571==ABORTING
If we test without the AddressSanitizer (ENABLE_ASAN is OFF by default), no error is reported in the following example:
$ mkdir -p build_no_asan
$ cd build_no_asan
$ cmake ..
$ cmake --build .
$ cmake --build . --target test
Start 1: leaky
1/2 Test #1: leaky ............................ Passed 0.00 sec
Start 2: use_after_free
2/2 Test #2: use_after_free ................... Passed 0.00 sec
100% tests passed, 0 tests failed out of 2
Indeed, leaky will just waste memory, whereas use_after_free may result in non-deterministic failures. One way to debug these failures is to use valgrind (http://valgrind.org).
In contrast to the previous two recipes, we have used a CTest script to configure, build, and test the code, and to submit the report to the dashboard. To understand how this recipe works, take a closer look at the dashboard.cmake script. First, we define the project name and set the host reporting and the build name, as follows:
set(CTEST_PROJECT_NAME "example")
cmake_host_system_information(RESULT _site QUERY HOSTNAME)
set(CTEST_SITE ${_site})
set(CTEST_BUILD_NAME "${CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME}-${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR}")
In our case, the CTEST_BUILD_NAME evaluates to Linux-x86_64. In your case, you may observe a different result, depending on your operating system.
Next, we specify paths for the source and build directories:
set(CTEST_SOURCE_DIRECTORY "${CTEST_SCRIPT_DIRECTORY}")
set(CTEST_BINARY_DIRECTORY "${CTEST_SCRIPT_DIRECTORY}/build")
We could set the generator to Unix Makefiles:
set(CTEST_CMAKE_GENERATOR "Unix Makefiles")
However, for a more portable test script, we prefer to provide the generator via the command line, as follows:
$ ctest -S dashboard.cmake -D CTEST_CMAKE_GENERATOR="Unix Makefiles"
The next code snippet in dashboard.cmake figures out the number of available cores on the machine and sets the parallel level of the test step to the number of available cores, in order to minimize the total test time:
include(ProcessorCount)
ProcessorCount(N)
if(NOT N EQUAL 0)
set(CTEST_BUILD_FLAGS -j${N})
set(ctest_test_args ${ctest_test_args} PARALLEL_LEVEL ${N})
endif()
Next, we start the testing step and configure the code, with ENABLE_ASAN set to ON:
ctest_start(Experimental)
ctest_configure(
OPTIONS
-DENABLE_ASAN:BOOL=ON
)
The remaining commands in dashboard.cmake map to the build, test, memcheck, and submit steps:
ctest_build()
ctest_test()
set(CTEST_MEMORYCHECK_TYPE "AddressSanitizer")
ctest_memcheck()
ctest_submit()
