Preface
A Brief History of Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) in which computers learn from data - usually to improve their performance on some narrowly defined task - without being explicitly programmed. The term machine learning was coined as early as 1959 - by Arthur Samuel, a legend in the field of artificial intelligence - but there were few major commercial successes in machine learning during the twenty-first century. Instead, the field remained a niche research area for academics at universities.
Early on - in the 1960s - many in the AI community were too optimistic about its future. Researchers at the time, such as Herbert Simon and Marvin Minsky, claimed that AI would reach human-level intelligence within a matter of decades.1
Machine will be capable, within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do.
Herbert Simon, 1965
From three to eight years, we will have a machine with the general intelligence of an average human being.
Marvin Minsky, 1970
Blinded by their optimism, researchers focused on so-called strong AI or general artificial intelligence (AGI) projects, attempting to build AI agents capable of problem solving, knowledge representation, learning and planning, natural language processing, perception, and motor control. This optimism helped attract significant funding into the nascent field from major players such as the Department of Defense, but the problems these researchers tackled were too ambitious and ultimately doomed to fail.
AI research rarely made the leap from academia to industry, and a series of so-called AI winters followed. In these AI winters - an analogy based on the nuclear winter during this Cold War era - interest in and funding for AI dwindled. Occasionally, hype cycles around AI occurred but had very little staying power. By the early 1990s, interest in and funding for AI had hit a trough.
AI is Back, but Why Now?
AI has re-emerged with a vengeance over the past two decades - first as a purely academic area of interest and now as a full-blown field attracting the brightest minds at both universities and corporations.
Three critical developments are behind this resurgence: breakthroughs in machine learning algorithms, the availability of lots of data, and superfast computers.
First, instead of focusing on overly ambitious strong AI projects, researchers turned their attention to narrowly defined sub-problems of strong AI, also known as weak AI or narrow AI. This focus on improving solutions for narrowly defined tasks led to algorithmic breakthroughs, which paved the way for successful commercial applications. Many of these algorithms - often developed first at universities or private research labs - were quickly open-sourced, speeding up the adoption of these technologies by industry.
Second, data capture became a focus for most organizations, and the costs of storing data fell dramatically driven by advances in digital data storage. Thanks to the Internet, lots of data also became widely and publicly available at a scale never before seen.
Third, computers became increasingly powerful and available over the cloud, allowing AI researchers to easily and cheaply scale their IT infrastructure as required without making huge upfront investments in hardware.
The Emergence of Applied AI
These three forces have pushed AI from academia to industry, helping attract increasingly higher levels of interest and funding every year. AI is no longer just a theoretical area of interest but rather a full-blown applied field. Figure P-1 displays a chart from Google Trends, indicating the growth in interest in machine learning over the past five years.
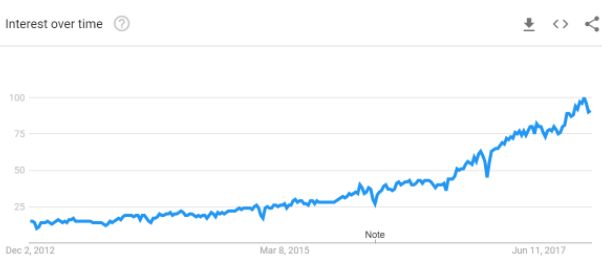
Figure P-1. Interest in machine learning over time
AI is now viewed as a breakthrough horizontal technology - akin to the advent of computers and smartphones - that will have a significant impact on every single industry over the next decade.2
Successful commercial applications involving machine learning include - but are certainly not limited to - optical character recognition, email spam filtering, image classification, computer vision, speech recognition, machine translation, group segmentation and clustering, generation of synthetic data, anomaly detection, cybercrime prevention, credit card fraud detection, internet fraud detection, time series prediction, natural language processing, board game and video game playing, document classification, recommender systems, search, robotics, online advertising, sentiment analysis, DNA sequencing, financial market analysis, information retrieval, question answering, and healthcare decision-making.
Major Milestones in Applied AI over the Past 20 Years
-
1997: IBM develops the AI bot Deep Blue, which beats world chess champion Garry Kasparov in a highly publicized chess event.
-
2004: DARPA introduces the DARPA Grand Challenge, an annually held autonomous driving challenge held in the desert. In 2005, Stanford takes the top prize. In 2007, Carnegie Mellon University performs this feat in an urban setting. In 2009, Google builds a self-driving car. By 2015, many major technology giants, including Tesla, Alphabet’s Waymo, and Uber, have launched well-funded programs to build mainstream self-driving technology.
-
2006: Geoffrey Hinton of the University of Toronto introduces a fast learning algorithm to train neural networks with many layers, kicking off the deep learning revolution.
-
2006: Netflix launches the Netflix Prize competition, with a one million dollar purse, challenging teams to use machine learning to improve its recommendation system’s accuracy by at least 10%. A team won the prize in 2009.
-
2007: AI achieves superhuman performance at checkers, solved by a team from the University of Alberta.
-
2010: ImageNet launches an annual contest - the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) - in which teams use machine learning algorithms to correctly detect and classify objects in a large, well-curated image dataset. This draws significant attention from both academia and technology giants. The classification error rate falls from 25% in 2011 to just a few percent by 2015, backed by advances in deep convolutional neural networks. This leads to commercial applications of computer vision and object recognition.
-
2010: Microsoft launches Kinect for Xbox 360. Developed by the computer vision team at Microsoft Research, Kinect is capable of tracking human body movement and translating this into gameplay.
-
2010: Siri, one of the first mainstream digital voice assistants, is acquired by Apple and released as part of iPhone 4S in October 2011. Eventually, Siri is rolled out across all of Apple’s products. Powered by convolutional neural networks and long short term memory recurrent neural networks, Siri performs both speech recognition and natural language processing. Eventually, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google enter the race, releasing Alexa (2014), Cortana (2014), and Google Assistant (2016), respectively.
-
2011: IBM Watson, a question answering AI agent developed by a team led by David Ferrucci, beats former Jeopardy! winners Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings. IBM Watson is now used across several industries, including healthcare and retail.
-
2012: Google Brain team, led by Andrew Ng and Jeff Dean, trains a neural network to recognize cats by watching unlabeled images taken from YouTube videos.
-
2013: Google wins DARPA’s Robotics Challenge, involving trials in which semi-autonomous bots perform complex tasks in treacherous environments, such as driving a vehicle, walking across rubble, removing debris from a blocked entryway, opening a door, and climbing a ladder.
-
2014: Facebook publishes work on DeepFace, a neural network-based system that can identify faces with 97% accuracy. This is near human-level performance and is a more than 27% improvement over previous systems.
-
2015: AI goes mainstream, commonly featured in media outlets around the world.
-
2015: Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo beats world-class professional Fan Hui at the game Go. In 2016, AlphaGo defeats Lee Sedol, and in 2017, AlphaGo defeats Ke Jie. In 2017, a new version called AlphaGo Zero defeats the previous AlphaGo version 100 to zero. AlphaGo Zero incorporates unsupervised learning techniques and masters Go just by playing itself.
-
2016: Google launches major revamp to its language translation, Google Translate, replacing its existing phrase-based translation system with a deep learning-based neural machine translation system, reducing translation errors by up to 87% and approaching near human-level levels of accuracy.
-
2017: Libratus, developed by Carnegie Mellon, wins at head-to-head no-limit Texas hold’em.
-
2017: OpenAI-trained bot beats professional gamer at Dota 2 tournament.
From Narrow AI to General AI
Of course, these successes in applying AI to narrowly defined problems are just a starting point. There is a growing belief in the AI community that - by combining several weak AI systems - we can develop strong AI. This strong AI or general artificial intelligence agent will be capable of human-level performance at many broadly-defined tasks.
Soon after AI achieves human-level performance, some researchers predict this strong AI will surpass human intelligence and achieve so-called superintelligence. Estimates for such superintelligence range from as little as 15 years from now to as many as 100 years, but most researchers believe AI will advance enough to achieve this in a few generations. Is this inflated hype once again - like what we saw in previous AI cycles - or is it different this time around?
Only time will tell.
Objective and Approach
Most of the successful commercial applications to date - in areas such as computer vision, speech recognition, machine translation, and natural language processing - have involved supervised learning, taking advantage of labeled datasets. But, most of the world’s data is unlabeled, not labeled.
In this book, we will cover the field of unsupervised learning, which is a branch of machine learning used to find hidden patterns and learn the underlying structure in unlabeled data.
According to many industry experts, such as Yann LeCun, the Director of AI Research at Facebook and Professor at NYU, unsupervised learning is the next frontier in AI and may hold the key to general artificial intelligence. For this and many other reasons, unsupervised learning is one of the trendiest topics in artificial intelligence today.
The book’s goal is to provide the concepts, intuition, and tools necessary for you to apply this technology to everyday problems that you work on. In other words, this is an applied book, one which will allow you to build real-world systems.
We will also explore how to efficiently label unlabeled datasets to turn unsupervised learning problems into semi-supervised ones.
The book will use a hands-on approach, introducing some theory but focusing mostly on applying unsupervised learning techniques to solve real world problems. The datasets and code are available online as Jupyter notebooks on GitHub.
Armed with the conceptual understanding and hands-on experience provided in this book, you will be able to apply unsupervised learning to large unlabeled datasets to uncover hidden patterns, gain deeper business insight, detect anomalies, cluster groups based on similarity, perform automatic feature engineering and selection, generate synthetic datasets, and more.
Prerequisites
This book assumes that you have some Python programming experience, including familiarity with NumPy and Pandas.
For more on Python, please visit the official Python website. For more on Jupyter Notebook, please visit the official Jupyter website.
For a refresher on college-level understanding of calculus, linear algebra, probability, and statistics, please read Part I of the Deep Learning textbook by Ian Goodfellow and Yoshua Bengio.
For a refresher on machine learning, please read The Elements of Statistical Learning.
Roadmap
The book is organized into four parts. Below is a preview of the topics covered in each part.
Part I: Fundamentals of Unsupervised Learning
-
Differences between supervised and unsupervised learning
-
Overview of popular supervised and unsupervised algorithms
-
An end-to-end machine learning project
Part II: Unsupervised Learning using Scikit-Learn
-
Dimensionality reduction
-
Anomaly detection
-
Clustering and group segmentation
Part III: Unsupervised Learning using TensorFlow and Keras
-
Representation learning and automatic feature extraction
-
Autoencoders
-
Semi-supervised learning
Part IV: Deep Unsupervised Learning
-
Restricted boltzmann machines
-
Deep belief networks
-
Generative adversarial networks
Other Resources
Conventions Used in This Book
The following typographical conventions are used in this book:
- Italic
-
Indicates new terms, URLs, email addresses, filenames, and file extensions.
Constant width-
Used for program listings, as well as within paragraphs to refer to program elements such as variable or function names, databases, data types, environment variables, statements, and keywords.
Constant width bold-
Shows commands or other text that should be typed literally by the user.
Constant width italic-
Shows text that should be replaced with user-supplied values or by values determined by context.
Tip
This element signifies a tip or suggestion.
Note
This element signifies a general note.
Warning
This element indicates a warning or caution.
Using Code Examples
Supplemental material (code examples, etc.) is available for download on GitHub.
This book is here to help you get your job done. In general, if example code is offered with this book, you may use it in your programs and documentation. You do not need to contact us for permission unless you’re reproducing a significant portion of the code. For example, writing a program that uses several chunks of code from this book does not require permission. Selling or distributing a CD-ROM of examples from O’Reilly books does require permission. Answering a question by citing this book and quoting example code does not require permission. Incorporating a significant amount of example code from this book into your product’s documentation does require permission.
We appreciate, but do not require, attribution. An attribution usually includes the title, author, publisher, and ISBN. For example: “Book Title by Some Author (O’Reilly). Copyright 2012 Some Copyright Holder, 978-0-596-xxxx-x.”
If you feel your use of code examples falls outside fair use or the permission given above, feel free to contact us at permissions@oreilly.com.
O’Reilly Safari
Note
Safari (formerly Safari Books Online) is a membership-based training and reference platform for enterprise, government, educators, and individuals.
Members have access to thousands of books, training videos, Learning Paths, interactive tutorials, and curated playlists from over 250 publishers, including O’Reilly Media, Harvard Business Review, Prentice Hall Professional, Addison-Wesley Professional, Microsoft Press, Sams, Que, Peachpit Press, Adobe, Focal Press, Cisco Press, John Wiley & Sons, Syngress, Morgan Kaufmann, IBM Redbooks, Packt, Adobe Press, FT Press, Apress, Manning, New Riders, McGraw-Hill, Jones & Bartlett, and Course Technology, among others.
For more information, please visit http://oreilly.com/safari.
How to Contact Us
Please address comments and questions concerning this book to the publisher:
- O’Reilly Media, Inc.
- 1005 Gravenstein Highway North
- Sebastopol, CA 95472
- 800-998-9938 (in the United States or Canada)
- 707-829-0515 (international or local)
- 707-829-0104 (fax)
We have a web page for this book, where we list errata, examples, and any additional information. You can access this page at http://www.oreilly.com/catalog/<catalog page>.
To comment or ask technical questions about this book, send email to bookquestions@oreilly.com.
For more information about our books, courses, conferences, and news, see our website at http://www.oreilly.com.
Find us on Facebook: http://facebook.com/oreilly
Follow us on Twitter: http://twitter.com/oreillymedia
Watch us on YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/oreillymedia
