Huffman Compression 425
(a)
(b)
(c)
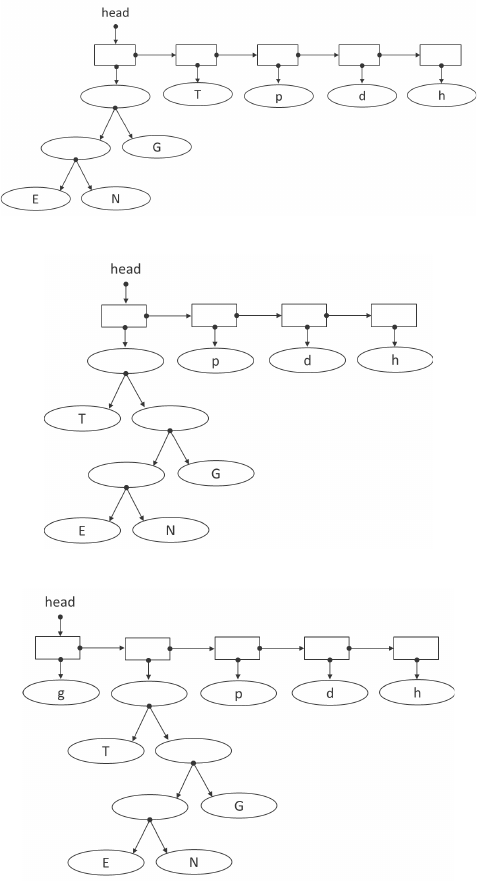
FIGURE 24.13: (a) The next command (the second bit in the eighth byte) is 0. This will
create a common parent for the first two tree nodes. (b) The next command (the third bit
in the eighth byte) is also 0. This will create a common parent for the first two tree nodes.
(c) The next command (the fourth bit in the eighth byte) is 1. This will create a tree node
to store the value g.
426 Intermediate C Programming
(a) (b)
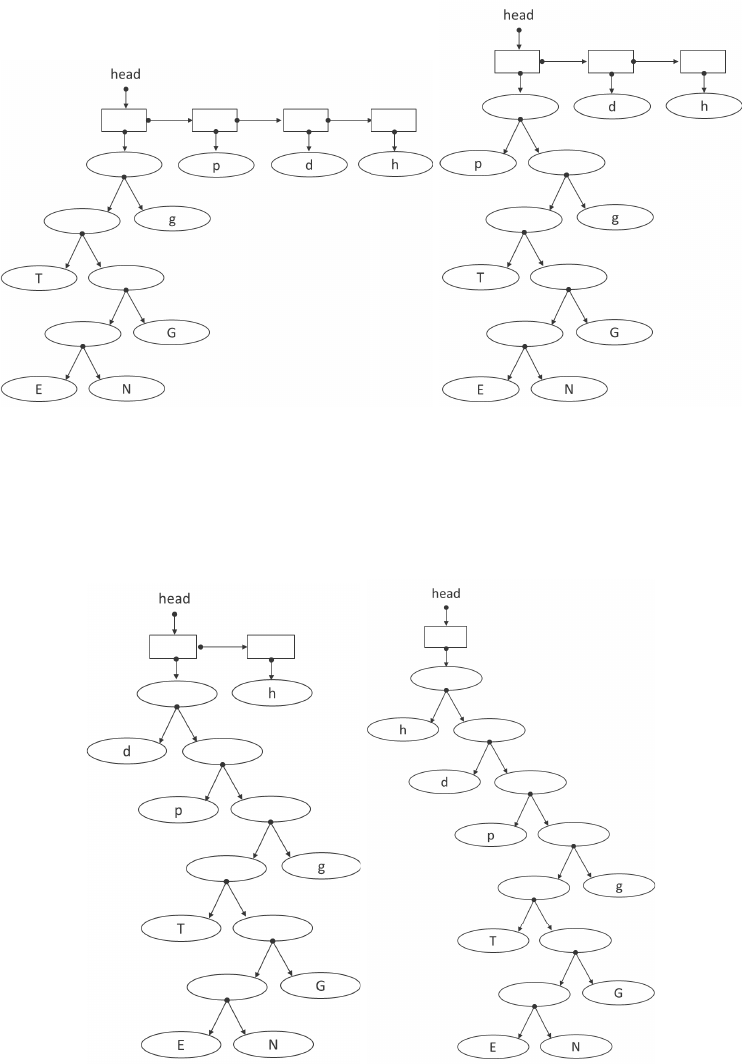
FIGURE 24.14: The remaining commands are 0. Continue building the tree.
(a) (b)
FIGURE 24.15: Finish building the tree.
Huffman Compression 427
The following is the final version of the complete program, for both compression and
decompression.
// main . c1
#in clude " encode .h "2
#in clude " constant .h "3
#in clude < stdlib .h >4
#in clude < string .h >5
int main ( i n t argc , char ** argv )6
{7
// argv [1]: " e" encode8
// "d" decode9
// argv [2]: name of input file10
// argv [3]: name of output file11
i f ( argc != 4)12
{13
return EXIT _FAILUR E ;14
}15
i f ( strcmp ( argv [1] , " e") == 0)16
{17
encode ( argv [2] , argv [3]) ;18
}19
i f ( strcmp ( argv [1] , " d") == 0)20
{21
decode ( argv [2] , argv [3]) ;22
}23
return EXIT _SUCCES S ;24
}25
// encode . h1
#i f n d e f ENCODE_H2
#d ef in e ENCODE_H3
// encode the input ( text ) file4
// save the result in the output ( binary ) file5
// return 0 if cannot read from file or write to file6
// return 1 if success7
int encode ( char * infile , char * outfile );8
// decode the input ( binary ) file9
// save the result in the output ( text ) file10
// return 0 if cannot read from file or write to file11
// return 1 if success12
int decode ( char * infile , char * outfile );13
#e ndif14
// encode . c1
#in clude " encode .h "2
#in clude " constant .h "3
#in clude " freq .h "4
#in clude " list .h "5
#in clude " utility . h"6
#in clude < stdio .h >7
#in clude < strings .h >8
428 Intermediate C Programming
#in clude < stdlib .h >9
#in clude < values .h >10
#d ef in e ENCODE MODE 011
#d ef in e DECODE MODE 112
void prin tFre q uenc yLate x ( CharFreq * freq u encies );13
void buil dCod e Book Helpe r ( TreeNode * tn , i n t * * codebook ,14
int * row , in t col )15
{16
i f ( tn == NULL )17
{18
return ;19
}20
// is it a leaf node ?21
TreeNode * lc = tn -> left ;22
TreeNode * rc = tn -> right ;23
i f (( lc == NULL ) && ( rc == NULL ) )24
{25
// finish one code26
codebook [* row ][0] = tn -> value ;27
(* row ) ++;28
return ;29
}30
i f ( lc != NULL )31
{32
// populat e this column of the entire s u b t r e e33
int numRow = Tree_le af ( lc );34
int ind ;35
for ( ind = * row ; ind < (* row ) + numRow ; ind ++)36
{37
codebook [ ind ][ col ] = 0;38
}39
buil dCod e Book Helpe r ( lc , codebook , row , col + 1) ;40
}41
i f ( rc != NULL )42
{43
int numRow = Tree_le af ( rc );44
int ind ;45
for ( ind = * row ; ind < (* row ) + numRow ; ind ++)46
{47
codebook [ ind ][ col ] = 1;48
}49
buil dCod e Book Helpe r ( rc , codebook , row , col + 1) ;50
}51
}52
void build CodeBoo k ( T reeNode * root , i n t * * cod e book )53
{54
int row = 0;55
// column start at 1 because [0] stores the char acter56
buil dCod e Book Helpe r ( root , codebook , & row , 1) ;57
}58
void print CodeBoo k ( i n t * * codebook , i n t numRow )59
Huffman Compression 429
{60
int row ;61
for ( row = 0; row < numRow ; row ++)62
{63
// print the characte r64
printf (" %c: " , code b oo k [ row ][0]) ;65
int col = 1;66
while ( codebook [ row ][ col ] != -1)67
{68
printf (" %d ", code b o ok [ row ][ col ]) ;69
col ++;70
}71
printf (" \n" );72
}73
}74
int compress ( char * infile , char * outfile ,75
int * * codebook , i n t * mapping )76
{77
FILE * infptr = fopen ( infile , "r ") ;78
i f ( infptr == NULL )79
{80
return 0;81
}82
FILE * outfptr = fopen ( outfile , "a "); // append83
i f ( outfptr == NULL )84
{85
fclose ( outfptr );86
return 0;87
}88
unsigned char whichbit = 0;89
unsigned char curbyte = 0;90
while (! feof ( infptr ) )91
{92
int onechar = fgetc ( infptr ) ;93
i f ( onechar != EOF )94
{95
int ind = mapping [ o n e c h a r ];96
int ind2 = 1;97
while ( codebook [ ind ][ ind2 ] != -1)98
{99
writeBit ( outfptr , ( codebook [ ind ][ ind2 ] == 1) ,100
& whichbit , & curbyte );101
// fprintf ( outfptr , "%d ", c o d ebook [ ind ][ ind2 ]) ;102
ind2 ++;103
}104
}105
}106
padZero ( outfptr , & whichbit , & curbyte );107
fclose ( infptr ) ;108
fclose ( outfptr );109
return 1;110
