Glossary
anonymous remailer An e-mail system that allows a sender to send a message anonymously to a receiver over an insecure network.
ANSI American National Standards Institute.
ANSI C Version of the C programming language that was standardized by ANSI.
API Application Programming Interface.
ARDA Advanced Research and Development Activity. ARDA is an Intelligence Community (IC) center for conducting advanced research and development related to information technology.
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
BIOS Basic Input Output System.
bus error A bus error occurs in a computer when an invalid address is issued from the processor to the memory bus.
call-back function A function that has its address passed as an argument to another function. The receiving function will invoke the call-back function under prespecified conditions. Typically, the address of a call-back function is passed to an operating system routine.
cascaded encryption An encryption is cascaded if the plaintext was encrypted using two or more different keys, thereby consisting of multiple ciphertext layers.
CERT Computer Emergency Response Team. Founded by DARPA in 1988.
cleartext Data that has not been enciphered in any way.
composite quadratic residuosity problem A computational decision problem that is believed to be intractable. The problem is to distinguish quadratic residues from pseudosquares modulo n where n is a large composite number. (They both have a Jacobi symbol of unity.)
COMSEC Communications Security. COMSEC products are capable of encrypting data, digitally signing data, and so on.
CRL Certificate Revocation List. Used by a certification authority to publicly disclose key pairs that have been revoked. It lists revoked key pairs and is digitally signed by the certification authority. A CRL is typically updated on a regular basis (for example, every day or two).
Cyberpunk A term used to describe a futuristic sci-fi genre involving greedy multinational corporations and rebellious computer hackers.
DARPA Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
DCR Decision Composite Residuosity assumption. This is a decision problem that is believed to be intractable when defined over a suitable set of parameters.
DDH Decision Diffie-Hellman assumption. This is a decision problem that is believed to be intractable when defined over a suitable set of parameters.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) An attack that denies a victim or group of victims access to some service. Examples include deleting data, clogging up computer networks with data packets, hogging up CPU time, and so on.
DES Data Encryption Standard. The Data Encryption Standard defines a symmetric encryption algorithm with a 56-bit key space and a 64-bit block size. The standard also covers the corresponding decryption algorithm.
Diffie-Hellman secret This term is often used to refer to the key that results from conducting a Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
directed graph A graph in which each edge is an arrow from one vertex to another. Sometimes referred to as a digraph.
DLL Dynamic Linked Library.
double-spending An attempt to spend a given e-money note more than once.
DOS Disk Operating System.
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. A type of ROM chip that can actually be written to by performing a specialized operation. Such chips often support at most 100,000 or so writes.
efficiently computable A problem is efficiently computable if it is solvable by a probabilistic poly-time Turing machine. A decision problem is efficiently computable if it is contained in BPP.
entropy extractor An entropy extractor is an algorithm that takes data from an entropy source as input and that extracts entropy from this data. The extractor outputs values that are uniformly distributed provided that the input data adheres to the underlying assumptions associated with the extractor.
forward secrecy A cryptosystem or protocol has the forward secrecy property if the disclosure of confidential secrets does not compromise previous communications between Alice and Bob.
ftp File Transfer Protocol.
GNU Gnu's Not Unix. GNU is the name of a complete Unix-compatible software system that is freely available in binary and source code form, but that may not be used for commercial purposes.
GNU MP The GNU project's multiprecision library.
Gnutella A decentralized Internet protocol developed in 1999 for sharing files indiscriminately.
graph A graph G is a pair (V, E) where V is a set of vertices and E is a set of edges defined over the vertices.
GUI Graphical User Interface.
Halting Problem The problem of constructing a Turing machine that can decide whether or not an arbitrary Turing machine halts on all inputs. Alan Turing proved that this problem is not computable using a Cantor diagonalization argument.
hash function A computationally efficient function that maps arbitrary length binary strings to binary strings that are fixed in length called hashes or hash values. In practice hash functions are often assumed to exhibit various properties, such as mapping their inputs to pseudorandom output values. When the domain of a hash function is larger than its range collisions result (at least two inputs map to the same output).
hexadecimal Base-16 number system. The hexadecimal numbering system consists of the digits 0,1,2,...,9, A,B,C,D,E,F.
honest but curious A model for multiparty computation in which the honest but curious party does not hinder with the computations, but wants to know the values involved in the computation.
hybrid encryption A method of encryption that employs both symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. Used to encrypt bulk data efficiently.
IDE Integrated Drive Electronics.
inter-mix detour A method that reroutes a mix net message by sending it on a short series of randomly chosen mix net nodes.
intractable problem A problem is intractable if in general it cannot be solved efficiently. A problem cannot be solved efficiently if there does not exist a probabilistic poly-time Turing machine that solves it.
ITAR International Traffic in Arms Regulations. U.S. federal regulations that govern the traffic of articles that are considered to be munitions. This includes various enciphering/deciphering machines.
Jacobi symbol The Jacobi symbol of a ≥ 0 with respect to n is defined whenever n is an odd positive integer. It is defined in terms of the Legendre symbol. The Jacobi symbol of a number with respect to n is 0, 1, or −1.
Las Vegas algorithm A Las Vegas algorithm is an algorithm that may never halt, but if it does, it halts with the correct answer.
logic bomb Code surreptitiously inserted into a program that causes it to perform some destructive or security-compromising activity whenever a specified condition is met.
malleable ciphertexts A ciphertext is malleable if its corresponding plaintext can be modified in a known way by modifying the ciphertext such that decryption yields the modified plaintext. The notion of non-malleable cryptography was put forth by Dolev et al [95].
malware Malicious Software. Examples of malicious software include computer viruses, worms, and Trojan horses.
MITM Man-In-The-Middle. An active attack that is carried out when two users exchange their public key over the network. The man in the middle is able to read and potentially even modify messages that are later sent between the two users.
mix network A tool for sending information anonymously. A mix net is an interconnected network consisting of several nodes that takes as input encrypted messages, mixes them by bouncing them from node to node, and eventually sends them to their final destinations.
model of computation A general method for computing those problems that are computable. Examples include Grammars, μ-recursive functions, and Turing machines. It has been proven that Turing machines can be imitated by Grammars, that can be imitated by μ-recursive functions, that can be imitated by Turning machines. Hence, these models are all equivalent.
Monte Carlo algorithm A Monte Carlo algorithm is an algorithm with a bounded running time, but that may halt with an incorrect answer.
MOTD Message-of-the-Day.
MP3 MPEG-1 Layer 3. MP3 is an audio file format for compressing sound (usually a song) into a small file with hardly any noticeable loss in quality.
MSCAPI Microsoft Cryptographic API.
Multics Multiplexed Information and Computing Service is a timesharing mainframe operating system that began in 1965. It was originally a research project and influenced the design of operating systems. Multics became a commercial product sold by Honeywell.
multipartite virus A virus that resides in two or more distinct forms. For example, the virus may propagate from an executable, to the boot sector, to a patched operating system interrupt routine in memory, and then back again.
multiprecision library A set of functions that perform elementary operations on multiprecision numbers. For example, it may implement addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modular exponentiation, logic operations, and so forth.
multiprecision number A number whose word length exceeds that of the underlying computer's native word length. For example, on a 32-bit machine a multiprecision number may be 512 bits in length, consisting of sixteen 32-bit words.
nonce A word often used in the descriptions of cryptographic algorithms to denote a randomly chosen value or parameter.
NSA National Security Agency. The branch of the U.S. government responsible for establishing information superiority through cryptologic prowess, among other disciplines.
OAEP Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding. A PKCS based on RSA that is secure in the random oracle model.
onion routing A method used to implement mix networks. Each message is encrypted multiple times and each encryption layer is removed by performing decryption as the message travels through the mix network to its final destination.
PDP Programmed Data Processor. A series of computers manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation.
PIR Private Information Retrieval. A method of retrieving information from a database without revealing to the database administrator which entry has been queried. Schemes exist to solve this problem that are information theoretically secure and other schemes exist that are only computationally secure.
PKCS Public Key Cryptosystem
PKI Public Key Infrastructure
polymorphic virus A virus that is designed to change its outward appearance to avoid being detected by antiviral programs.
poly-time Polynomial time. A polynomial time algorithm M (i.e., a poly-time Turing machine M) is an algorithm for which there exists a polynomial p(·) such that the running time of M on any given input x is at most p(|x|), where |x| denotes the length of x.
PRNG Pseudorandom Number Generator.
probabilistic poly-time Turing machine A Turing machine in which zero or more state transitions are random choices among a finite number of alternatives. The running time of the machine is bounded by a polynomial.
pseudocode Source code, usually in an imperative programming language, which may not conform to a specific language but is readily understood.
public key infrastructure An infrastructure that is designed to distribute the public keys of users securely, thereby avoiding man-in-the-middle attacks.
random oracle A function f that when given any string δ 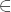 {0,1}* responds with a string Ωδ chosen uniformly at random from {0,1}∞. Furthermore, f always responds with Ωδ when given δ.
{0,1}* responds with a string Ωδ chosen uniformly at random from {0,1}∞. Furthermore, f always responds with Ωδ when given δ.
random oracle model A computational model that assumes the existence and availability of a random oracle. It is a hypothetical model used to argue the security of cryptographic algorithms.
relatively prime Two integers α and β are relatively prime if their greatest common divisor is 1.
RNG Random Number Generator. An algorithm or device that generates truly random numbers. Often used to generate seed values for pseudorandom number generators.
root A user in a UNIX system that has all possible privileges on the machine. System administrators often log in as root to make critical changes to the system.
rootkit A rootkit is a set of tools used after infiltrating a computer system that hides logins, processes, and logs and also often sniff terminals, connections, and the keystrokes. It is called a rootkit after the fact that originally it referred to allowing the attacker to maintain root access to a machine.
security by obscurity The often perilous rationale that a system is secure due to the fact that its inner workings are not publicly known.
semantic security A formal notion of security for public key cryptosystems. A PKCS is semantically secure (against a particular type of attack) if for all probability distributions over the message space, anything that a passive adversary can compute efficiently about the plaintext given the ciphertext can also be efficiently computed without the ciphertext.
smooth integer An integer n is smooth if it consists of no large prime factors. An integer n is p-smooth if it is not divisible by any primes larger than p.
snake oil A liquid sold as medicine (for example, in a traveling medicine show) that is medically worthless. In cryptography it refers to a security product, typically with a proprietary (i.e., secret) design, with questionable or otherwise unachievable security properties.
subliminal channel A communications channel, usually within cryptosystems, that when utilized allows information to be transferred in secret without hindering the normal operation of the cryptosystem.
tractable problem A problem is tractable if in general it can be solved efficiently. A problem is efficiently solvable if there exists a probabilistic poly-time Turing machine that solves it.
trapdoor A trapdoor is a single value or a tuple that can be used as a public key in a public key encryption algorithm.
trapdoor primes It was originally suspected that the primes chosen for the Digital Signature Algorithm might give the U.S. government an advantage in forging signatures, and so on. These primes were referred to as trapdoor primes.
triple-DES An algorithm based on DES that typically utilizes two different keys k1 and k2. The data is DES encrypted using k1, then the result is DES decrypted using k2, and then that result is DES encrypted using k1.
Trojan horse A code segment that is appended, designed, or integrated into another program that does something that the user does not expect.
TSR program A terminate-and-stay resident (TSR) program. This usually refers to DOS programs that remain active in memory while the user runs other programs.
Turing machine A computing device consisting of a finite control, an unbounded sequential tape, and a head that can be used for reading and writing symbols on the tape. It is a conceptual model of computation used for proving computability and complexity results.
Turing undecidable A language (i.e., a finite or countably infinite set of strings) is Turing undecidable if there does not exist a Turing machine that can decide membership for that language.
VLSI Very Large Scale Integration. A term describing semiconductor circuits composed of hundreds of thousands of logic elements.
