Daemon-Based Filtering
Daemon-based filtering offers a more advanced architecture over the command-based method with lower cost in I/O and CPU usage. It can provide better error handling than is possible with the command method. If implemented as a resident process, the startup overhead per message is eliminated. A daemon-based content filter can pass email messages back and forth with Postfix using the standard SMTP or LMTP protocol. Such a filter can run as a standalone daemon or it can be started by Postfix if configured to do so in master.cf.
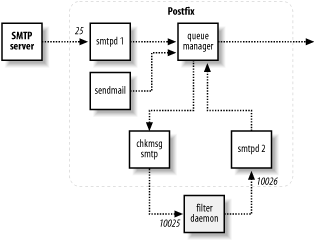
In this configuration, we want the content filter to handle all
messages, whether delivered locally (via sendmail) or to the smtpd daemon. You have to configure Postfix in
master.cf to use a special smtp client component to deliver the messages
to your filter and an additional smtpd daemon to receive messages back from
your filter. Figure 14-2
illustrates how a filtered message travels through Postfix to your
content filter and back into Postfix for delivery. In this diagram, the
filter receives mail via localhost port 10025 from the additional
smtp client and submits it back to
Postfix via localhost port 10026 to the additional smtpd server component.
If the filter wants to reject a message, it should reply with an SMTP code of 550 along with the reason for the rejection. Otherwise, it should accept the message and perform its operations before passing it back to Postfix. If your filter rejects a message, Postfix bounces it back to the sender address with the message your filter provides.
Configuration
For the purposes of this discussion, I’ll assume that you are running a standalone content filter daemon that listens for incoming messages using SMTP. After processing, it sends the message back to Postfix using SMTP. The basic steps to configure this setup are:
Create a pseudoaccount for your filter.
Install and configure your content filter.
Edit master.cf to add two additional Postfix components.
Edit main.cf to add the
content_filterparameter.Restart Postfix so that it recognizes the changes to its configuration files.
When setting up a daemon-based content filter, make sure it does
not use the same hostname that Postfix has set in its myhostname parameter, or the Postfix SMTP client will consider it
an error and not deliver the message to your filter. The rest of this
section walks you through the details of setting up a daemon-based
content filter.
Creating a pseudoaccount
As with the simple filtering solution described earlier, you should create a pseudoaccount for your filter. The account shouldn’t have access to other resources on your system. If your filter needs to write files, you should create a directory for that purpose. Your filter should be started as the designated user or configured to become that user after starting. Check your filter’s configuration options. For this example, I’ll assume that you’ve created a user called filter.
Installing a content filter
Your content filter package should provide you with instructions for installation and configuration. In this example, assume that the filter listens on the loopback interface on port 10025. After processing messages, the filter should pass them back to Postfix on port 10026. You should be able to configure your filter accordingly, or if your filter listens and reinjects on a different port, keep that in mind as you follow the example. If possible, test your filter first to make sure that it operates correctly before trying to connect it to Postfix.
Configuring additional Postfix components
You may encounter "mail loops back to myself” problems when creating
additional SMTP components. One solution is to give the additional
component a different value for myhostname.
Edit master.cf to add the
new components you need. A second smtp component will be used to send
messages to your content filter. (See Section 4.5 in Chapter 4 for more information on
editing master.cf.) We’ll call
this additional smtp entry
chkmsg:
chkmsg unix - - n - 10 smtp
-o myhostname=localhostLater, when you turn on content filtering in main.cf, you’ll tell Postfix to send the message to your filter on port 10025 using this component.
In addition to the extra smtp client, you also need a second
smtpd service to receive messages
back from the content filter program. The second smtpd instance is configured slightly
differently from the normal one because you want Postfix to handle
traffic from your filter differently from messages coming from
outside. Set options with an entry like the following:
localhost:10026 inet n - n - 10 smtpd
-o content_filter=
-o local_recipient_maps=
-o mynetworks=127.0.0.0/8
-o smtpd_helo_restrictions=
-o smtpd_client_restrictions=
-o smtpd_sender_restrictions=
-o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,rejectThis instance of smtpd is
configured to listen on the loopback interface on port 10026. You
configure your filter to send the processed messages to this
service. There are several options in this example. These override
the settings in the main.cf file
and are explained below:
content_filterThe default
smtpdinstance has content filtering turned on in main.cf. This instance of smtpd should not have the content filter process messages again.local_recipient_mapsSome lookup maps convert an address when it is received by the external
smtpd. When your filter tries to reinject it, Postfix may not recognize the recipient and reject the message. Set this option to blank to make sure the filtered messages are always accepted from your filter.-
mynetworks Since your filter runs on the same system as Postfix, the filter and Postfix can communicate over the local loopback interface, a pseudonetwork device not associated with any real hardware interface. The loopback interface always uses an address of 127.0.0.1. Since 127 is the first byte of its address, it’s a class A network that you identify with a
/8network prefix. By settingmynetworksto the loopback network andsmtpd_recipient_restrictionsto permit only this network, this instance ofsmtpdaccepts connections from your filter only and isn’t exposed to any (potentially hostile) traffic from the network.-
smtpd_helo_restrictions,smtpd_client_restrictions,smtpd_sender_restrictions You can turn off any restrictions that were already checked by the original
smtpdinstance. If you’re not already using these restrictions in main.cf, you don’t need to turn them off here.smtpd_recipient_restrictionsFinally, tell
smtpdto accept connections on the loopback interface and reject everything else.
Turning on filtering
After you have made the necessary changes to master.cf, you have to configure Postfix to pass all messages it receives to your content filter. Edit the main.cf file to add a line like the following:
content_filter = chkmsg:[127.0.0.1]:10025
This parameter tells Postfix to pass messages to the content
filter via the chkmsg service
that you created in master.cf.
You also tell it to send the messages to port 10025, which should
match what you have configured your content filter program to use.
Be sure to reload Postfix to recognize the changes in its
configuration files. Once Postfix is reloaded, it will start passing
all messages through your content filter for processing.
Daemon-Based Filter Example
To demonstrate setting up a daemon-based content filter, this section walks through installing Vexira AntiVirus from Central Command. Vexira is a commercial anti-virus product available on the Central Command web page, http://www.centralcommand.com/. Its Vexira AntiVirus for Mail servers product is written to work with Postfix among other MTAs. It is available for Linux, FreeBSD, and OpenBSD platforms. If you are using a different daemon-based anti-virus solution, the configuration should be similar to the procedure presented here:
Install Vexira according to the documentation from Command Central. The rest of this procedure assumes that your configuration files are in /etc per the installation instructions.
Configure Vexira to listen on the local loopback interface on port 10024. Edit /etc/vamailarmor.conf and set the parameter
ListenAddressas follows:ListenAddress localhost port 10024
Also set the
ForwardToparameter to pass messages back to Postfix over the loopback interface on port 10025:ForwardTo SMTP: localhost port 10025
Restart Vexira using the method or scripts installed on your system. See your Vexira documentation.
Edit the Postfix main.cf file to have all messages sent to the Vexira daemon for virus scanning. Edit the
content_filterparameter as follows:content_filter = smtp:[127.0.0.1]:10024
Edit the Postfix master.cf file to add another SMTP daemon to accept messages back from Vexira after virus scanning:
localhost:10025 inet n - n - 10 smtpd -o content_filter= -o local_recipient_maps= -o mynetworks=127.0.0.0/8 -o smtpd_helo_restrictions= -o smtpd_client_restrictions= -o smtpd_sender_restrictions= -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_mynetworks,rejectReload Postfix so that it recognizes the changes in its configuration files:
#
postfix reload