How qmgr Works
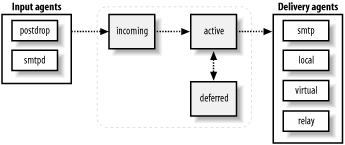
Figure 5-1 illustrates how messages move through the queue. The
incoming queue is where messages first enter Postfix. The queue manager
provides protection for the queue filesystem through the queue_minfree parameter. The default value is 0. You can make sure the
disk that stores your queue doesn’t run out of space by setting a
limit.
From the incoming queue, the queue manager moves messages to the active queue and invokes the appropriate delivery agent to handle them. For the most part, if there are no problems with delivery, movement through the queue is so fast that you won’t see messages in the queue. If Postfix is trying to deliver to a slow or unavailable SMTP server, you may see messages in the active queue. Postfix waits 30 seconds to decide if a remote system is unreachable.
A message that cannot be delivered is placed in the deferred queue. Messages are deferred only when they encounter a temporary problem in delivery, such as a temporary DNS problem or when a destination mail server reports a temporary problem. Messages that are rejected, or encounter a permanent error, are immediately bounced back to the sender in an error report and don’t stay in the queue.
Deferred Mail
Messages in the deferred queue stay there until they are
either delivered successfully or expire and are bounced back to the
sender. The bounce_size_limit
parameter determines how much of a message that could
not be delivered is bounced back to the sender in the error report.
The default is 50,000 bytes.
Once a message has failed delivery, Postfix marks it with a timestamp to indicate when the next delivery attempt should occur. Postfix keeps a short-term list of systems that are down to avoid unnecessary delivery attempts. If there are deferred messages scheduled for a redelivery attempt, and there is space available in the active queue, the queue manager alternates between taking messages from the deferred and incoming queues, so that new messages are not forced to wait behind a large backlog of deferred ones.
Queue Scheduling
Postfix periodically scans the queue to see if there are
deferred messages whose timestamps indicate they are ready for another
delivery attempt. Subsequent failed attempts at delivery cause
scheduled delays to double, so Postfix waits longer each time
before it attempts to deliver a message. You can configure the maximum
delay with the maximal_queue_lifetime parameter. When the time has expired, Postfix gives up
trying to deliver the message and bounces it back to the sender. By
default the period is five days (5d). You can set it to any length of
time, or to 0 to have undeliverable mail returned immediately.
Queue scans occur at an interval specified by the queue_run_delay parameter. By default the parameter is set to 1,000
seconds (1000s). With this setting, every 1,000 seconds, Postfix
checks the deferred queue to see if there are any messages due for
another delivery attempt.
The parameters minimal_backoff_time and maximal_backoff_time set minimum and maximum
time limits on how often Postfix attempts to redeliver deferred
messages. Each time a message is deferred, the queue manager increases
the amount of time it waits to attempt to deliver that message again.
The calculated increase of time is never allowed to exceed maximal_backoff_time (default 4,000 seconds)
and is never less than minimal_backoff_time (default 1,000
seconds). If you find that you have a large backlog of deferred
messages, you may want to increase the maximal_backoff_time so that Postfix doesn’t
expend system resources in trying to deliver messages to unavailable
servers.
Message Delivery
The queue manager arranges for the delivery of messages by invoking the appropriate delivery agent. Postfix is careful not to overwhelm destination systems and provides several parameters to control resources for outgoing messages. For most situations the default settings are correct, but if you are experiencing resource problems or you are trying to optimize deliveries, you may want to experiment with the queue manager configuration.
Outgoing messages might be delivered over any of the transports
available in the master.cf
file. Each transport can have a limit on its total
number of processes, specified in the maxproc column (see Section 4.5). If a value is not
specified there, Postfix uses default_process_limit for its limit.
The initial_destination_concurrency parameter limits the number of messages initially sent
(default is five). You can increase the value, but it can’t go higher
than the maxproc value or default_process_limit for the transport
used. After the initial delivery of messages, if there are more
messages in the queue for a particular destination, Postfix increases
the number of concurrent delivery attempts, as long as it doesn’t
detect any problem from the destination system at the current load.
Postfix continues to increase the number of simultaneous deliveries up
to the number specified in the default_destination_concurrency_limit
parameter, which is 20 by default. In general, you
don’t want to increase the concurrency limit, or you risk overwhelming
the receiving system.
You can override the default_destination_concurrency_limit value
for any transport by setting a parameter of the form
transport _destination_concurrency_limit. For example,
you can limit concurrent connections to external systems with the
parameter smtp_destination_concurrency_limit
, or limit local deliveries with local_destination_concurrency_limit
.
There are also parameters of the form
transport _destination_recipient_limit that control
how many recipients Postfix specifies for a single copy of an email
message. If a transport-specific parameter is not configured, it takes
its default value from default_destination_recipient_limit
. If the number of recipients for a message exceeds the
limit, Postfix breaks up the list of recipients into smaller groups of
addresses and sends separate copies of the message to each group of
addresses.
Corrupt Messages
The corrupt queue is simply used to store damaged or otherwise unreadable messages. If a message is too damaged to do anything with it, Postfix places it here. If you want to investigate an issue, the problem message is available in this queue where you can view it manually, if necessary. Corrupt messages are very rare. If you have them, they may be a symptom of an underlying operating system or hardware problem.
Error Notifications
Postfix can report certain errors by sending error messages to an administrator.
Postfix classifies errors for notification, as shown in Table 5-1. The notify_classes parameter in main.cf contains the list of error
classes that should generate error notices. By default
the parameter includes " resource” and “software” errors.
Each class of error can be configured to send the
notification to a particular email address, using parameters of the
form class _notice_recipient.
By default they all go to postmaster . Table 5-1
provides a list of possible error classes, along with the parameters
that indicate who should receive the error notices.
Error class | Description | Notice recipient parameter |
bounce | Send headers for all bounced messages. | |
2bounce | Send undeliverable bounced messages. | |
delay | Send headers of delayed messages. | |
policy | Send the transcript of any SMTP transaction when a message is rejected due to anti-spam restrictions. | |
protocol | Send the transcript of any SMTP transaction that had errors. | |
resource | Send notice that a message could not be delivered because of system resource problems. | |
software | Send notice that a message could not be delivered because of software problems. | |
If you would like to receive all problem notices, set the parameter as follows:
notify_classes = bounce, 2bounce, delay, policy, protocol, resource, software