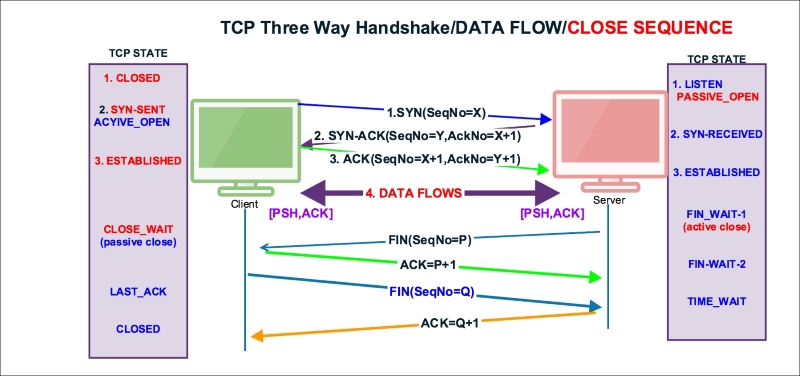
TCP normal close appears when the client or server decides that all data has been sent to the receiver and we can close the connection. There are three ways a TCP connection is closed:
- The client initiates closing the connection by sending a
FINpacket to the server - The server initiates closing the connection by sending a
FINpacket to the client - Both client and server initiate closing the connection
Open the normal-connection.pcap file and select packet #5 in the Packet List pane. Go to the Wireshark Packet Details pane, as shown in the screenshot, and examine the TCP protocol.
In Wireshark add the Sequence number and Acknowledgement number to the column. To add the sequence number and acknowledgement number, choose the TCP header packet, right-click on the field (Sequence number / Acknowledgement number) in the packet details and select Display as Column. Or implement these settings to add a new column:
- Go to Edit | Preferences | Columns. Then add a new column and select "custom" : tcp.seq.
- Go to Edit | Preferences | Columns. Then add a new column and select "custom" : tcp.ack.
The server has initiated the FIN packet. When the data transfer is completed, see packet#5 in the following screenshot:
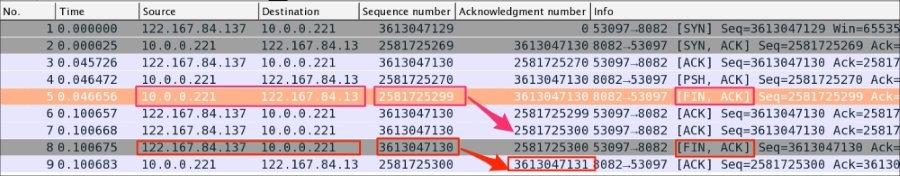
As you can see in the preceding screenshot:
- The server initiates the
FINpacket to close the connection in packet#5 - The server set
[FIN,ACK] (tcp.flags.fin == 1) && (tcp.flags.ack == 1)and sends it to the client - The server sequence number
tcp.seq == 2581725299is acknowledged in packet#7 - The client is initiating
FINto close the connection in packet#8 - The client sets
[FIN,ACK] (tcp.flags.fin == 1) && (tcp.flags.ack == 1)and sends it to the server - The client sequence number
tcp.seq == 3613047130is acknowledged in packet#9
The TCP state machine when the server and client close the socket connection, server initiated FIN:
|
Sr. No. |
TCP-A (122.167.84.137) state |
Flow CTL |
TCP-B (10.0.0.221) state | ||
|
From |
To |
From |
To | ||
|
1 |
CLOSED |
CLOSED |
LISTEN | ||
|
2 |
CLOSED |
SYN_SENT |
<SEQ=3613047129><CTL=SYN> |
LISTEN | |
|
3 |
SYN_SENT |
<SEQ=2581725269><ACK=3613047130><CTL=SYN,ACK> |
LISTEN |
SYN-RECEIVED | |
|
4 |
SYN_SENT |
ESTABLISHED |
SEQ=3613047130>><ACK=2581725270><CTL=ACK> |
SYN-RECEIVED |
ESTABLISHED |
|
5 |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
<SEQ=3613047130>><ACK=2581725270><CTL=PSH,ACK> |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
|
6 |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
<SEQ=3613047130>><ACK=2581725299><CTL=ACK> |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
|
7 |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
<SEQ=2581725299>><ACK=3613047130><CTL=FIN.ACK> |
ESTABLISED |
FIN_WAIT-1 |
|
8 |
ESTABLISHED |
CLOSE_WAIT |
<SEQ=3613047130>><ACK=2581725300><CTL=ACK> |
FIN_WAIT-1 |
FIN_WAIT-2 |
|
9 |
CLOSE_WAIT |
LAST_ACK |
SEQ=3613047130>><ACK=2581725300><CTL=FIN.ACK> |
FIN_WAIT-2 |
TIME_WAIT |
|
10 |
LAST_ACK |
CLOSED |
TIME_WAIT |
CLOSED | |
Wireshark filters used in this scenario are as follows:
tcp.analysis:SEQ/ACK: Provides links to the segments of the matching sequence/ack numberstcp.connection.fin: Provides expert informationtcp.flags == 0x0011: Displays all the[FIN,ACK]packets
