I know it well: I read it in the grammar long ago.
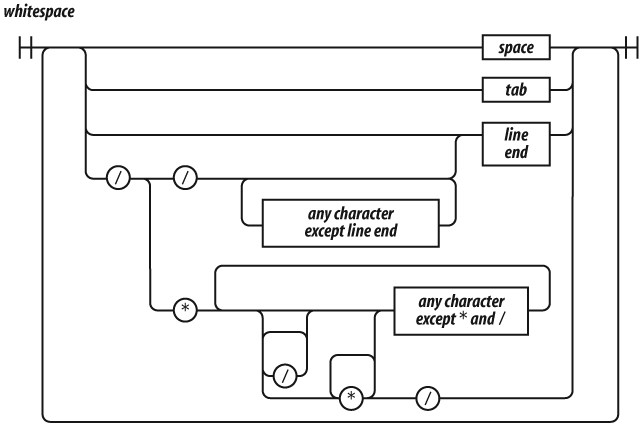
This chapter introduces the grammar of the good parts of JavaScript, presenting a quick overview of how the language is structured. We will represent the grammar with railroad diagrams.
The rules for interpreting these diagrams are simple:
You start on the left edge and follow the tracks to the right edge.
As you go, you will encounter literals in ovals, and rules or descriptions in rectangles.
Any sequence that can be made by following the tracks is legal.
Any sequence that cannot be made by following the tracks is not legal.
Railroad diagrams with one bar at each end allow whitespace to be inserted between any pair of tokens. Railroad diagrams with two bars at each end do not.
The grammar of the good parts presented in this chapter is significantly simpler than the grammar of the whole language.
Whitespace can take the form of formatting characters or comments. Whitespace is usually insignificant, but it is occasionally necessary to use whitespace to separate sequences of characters that would otherwise be combined into a single token. For example, in:
var that = this;
the space between var and that cannot be removed, but the other spaces can be
removed.
JavaScript offers two forms of comments, block comments formed with /* */ and line-ending comments starting with //. Comments should be used liberally to improve the
readability of your programs. Take care that the comments always accurately describe
the code. Obsolete comments are worse than no comments.
The /* */ form of block comments came from a
language called PL/I. PL/I chose those strange pairs as the symbols for comments
because they were unlikely to occur in that language's programs, except perhaps in
string literals. In JavaScript, those pairs can also occur in regular expression
literals, so block comments are not safe for commenting out blocks of code. For
example:
/*
var rm_a = /a*/.match(s);
*/causes a syntax error. So, it is recommended that /*
*/ comments be avoided and //
comments be used instead. In this book, // will
be used exclusively.