Flowable can be regarded as a special type of Observable (but internally it isn't). It has almost the same method signature such as the Observable as well.
The difference is that Flowable allows you to process items that emitted faster from the source than some of the following steps can handle. It might sound confusing, so let's analyze an example.
Assume that you have a source that can emit a million items per second. However, the next step uses those items to do a network request. We know, for sure, that we cannot do more than 50 requests per second:
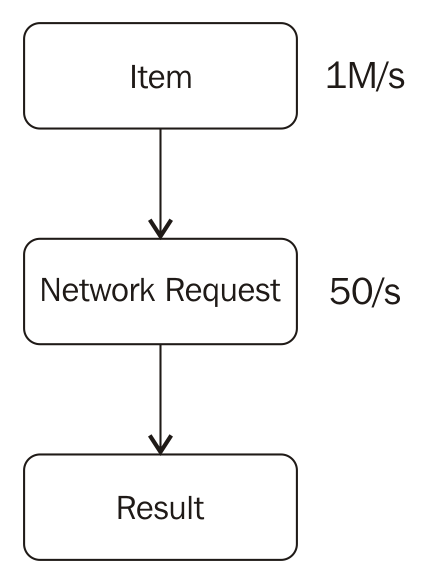
That poses a problem. What will we do after 60 seconds? There will be 60 million items in the queue waiting to be processed. The items are accumulating at a rate of 1 million items per second between the first and the second steps because the second step processes them at a much slower rate.
Clearly, the problem here is that the available memory will be exhausted and the programming will fail with an OutOfMemory (OOM) exception.
For example, this script will cause an excessive memory usage because the processing step just won't be able to keep up with the pace the items are emitted at:
PublishSubject<Integer> observable = PublishSubject.create();
observable
.observeOn(Schedulers.computation())
.subscribe(v -> log("s", v.toString()), this::log);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
observable.onNext(i);
}
private void log(Throwable throwable) {
Log.e("APP", "Error", throwable);
}
By converting this to a Flowable, we can start controlling this behavior:
observable.toFlowable(BackpressureStrategy.MISSING)
.observeOn(Schedulers.computation())
.subscribe(v -> log("s", v.toString()), this::log);
Since we have chosen not to specify how we want to handle items that cannot be processed (it's called Backpressuring), it will throw a MissingBackpressureException. However, if the number of items was 100 instead of a million, it would have been just fine as it wouldn't hit the internal buffer of Flowable. By default, the size of the Flowable queue (buffer) is 128.
There are a few Backpressure strategies that will define how the excessive amount of items should be handled.
