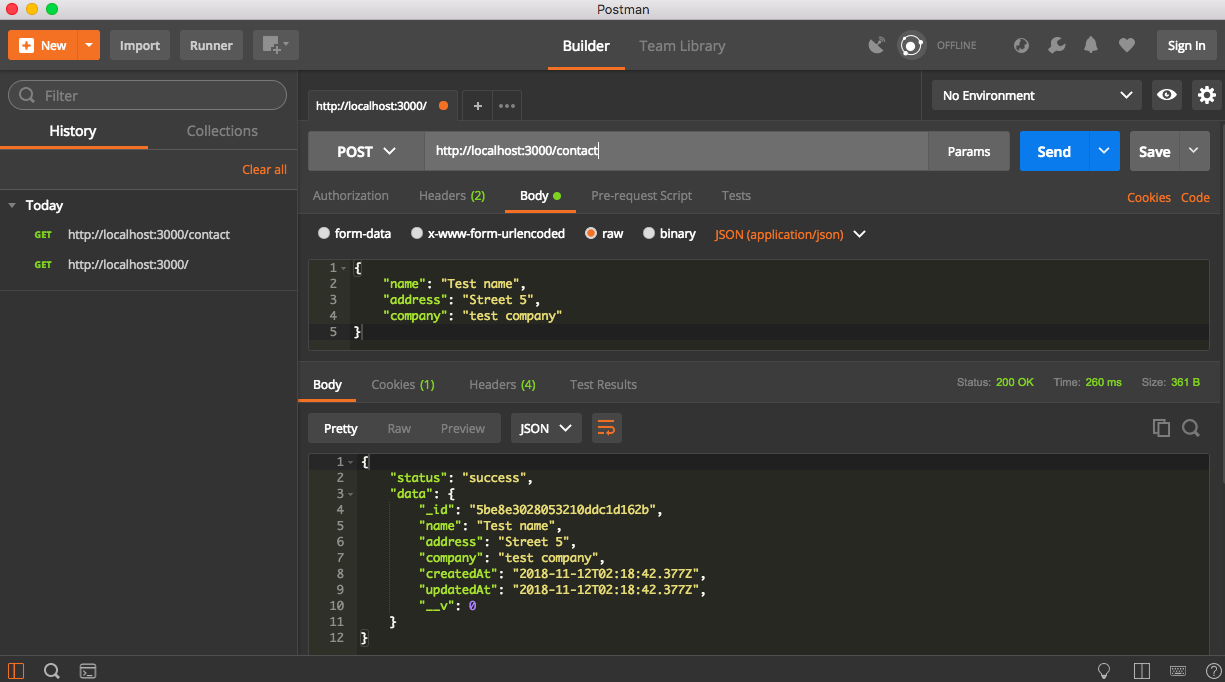
The store route will create new contact documents and save them to the database. It will send the created contacts back as a JSON response.
The store action will receive the JSON request body as data to use for creating the contact document. In order to be able to read the request body properly, we need to register koa-body, a body parser middleware for Koa.
According to its documentation, koa-body is the following:
To register the koa-body middleware, we can update our index.js with the following content:
// ./index.js
// ...
const bodyParser = require('koa-body');
app.use(bodyParser());
// ...
To add the store route, we will update the controller actions, as follows:
// ./controllers/ContactController.js
// ...
module.exports = {
// ...
async store(ctx) {
const { body } = ctx.request;
let contact = new Contact(body);
contact = await contact.save();
ctx.body = {
status: 'success',
data: contact
};
}
};
Then, we register the corresponding route, as follows:
// ./middleware/router.js
// ...
router
.get('/', async ctx => (ctx.body = 'Welcome to the contacts API!'))
.get('/contact', contactController.index)
.post('/contact', contactController.store);
// ...
Now, we can call the POST /contact endpoint to create a contact with Postman, as seen in the following screenshot: