Manohar Swamynathan
Mastering Machine Learning with Python in Six Steps
A Practical Implementation Guide to Predictive Data Analytics Using Python
Manohar Swamynathan
Bangalore, Karnataka, India
Any source code or other supplementary material referenced by the author in this book is available to readers on GitHub via the book’s product page, located at www.apress.com/978-1-4842-2865-4 . For more detailed information, please visit http://www.apress.com/source-code .
ISBN 978-1-4842-2865-4
e-ISBN 978-1-4842-2866-1
DOI 10.1007/978-1-4842-2866-1
Library of Congress Control Number: 2017943522
© Manohar Swamynathan 2017
This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved by the Publisher, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specifically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microfilms or in any other physical way, and transmission or information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed.
Trademarked names, logos, and images may appear in this book. Rather than use a trademark symbol with every occurrence of a trademarked name, logo, or image we use the names, logos, and images only in an editorial fashion and to the benefit of the trademark owner, with no intention of infringement of the trademark. The use in this publication of trade names, trademarks, service marks, and similar terms, even if they are not identified as such, is not to be taken as an expression of opinion as to whether or not they are subject to proprietary rights.
While the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of publication, neither the authors nor the editors nor the publisher can accept any legal responsibility for any errors or omissions that may be made. The publisher makes no warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein.
Printed on acid-free paper
Introduction
This book is your practical guide towards novice to master in machine learning with Python in six steps. The six steps path has been designed based on the “Six degrees of separation” theory that states that everyone and everything is a maximum of six steps away. Note that the theory deals with the quality of connections, rather than their existence. So a great effort has been taken to design eminent, yet simple six steps covering fundamentals to advanced topics gradually that will help a beginner walk his way from no or least knowledge of machine learning in Python to all the way to becoming a master practitioner. This book is also helpful for current Machine Learning practitioners to learn the advanced topics such as Hyperparameter tuning, various ensemble techniques, Natural Language Processing (NLP), deep learning, and the basics of reinforcement learning. See Figure 1 .
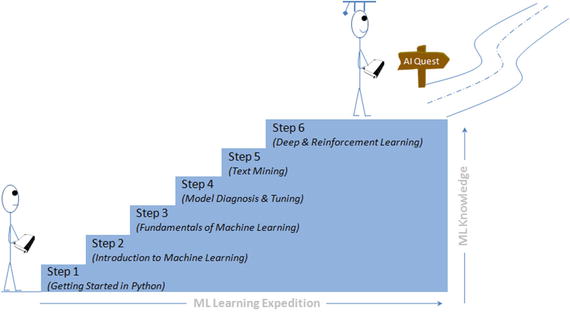
Figure 1. Mastering Python Machine Learning: In Six Steps
Each topic has two parts: the first part will cover the theoretical concepts and the second part will cover practical implementation with different Python packages. The traditional approach of math to machine learning, that is, learning all the mathematics then understanding how to implement it to solve problems needs a great deal of time/effort, which has proven to be not efficient for working professionals looking to switch careers. Hence the focus in this book has been more on simplification, such that the theory/math behind algorithms have been covered only to the extent required to get you started.
I recommend you work with the book instead of reading it. Real learning goes on only through active participation. Hence, all the code presented in the book is available in the form of iPython notebooks to enable you to try out these examples yourselves and extend them to your advantage or interest as required later.
Who This Book Is for
This book will serve as a great resource for learning machine learning concepts and implementation techniques for the following:
Python developers or data engineers looking to expand their knowledge or career into the machine learning area.
A current non-Python (R, SAS, SPSS, Matlab, or any other language) machine learning practitioners looking to expand their implementation skills in Python.
Novice machine learning practitioners looking to learn advanced topics such as hyperparameter tuning, various ensemble techniques, Natural Language Processing (NLP), deep learning, and basics of reinforcement learning.
What You Will Learn
Chapter 1 , Step 1 - Getting started in Python . This chapter will help you to set up the environment, and introduce you to the key concepts of Python programming language in relevance to machine learning. If you are already well versed with Python basics, I recommend you glance through the chapter quickly and move onto the next chapter.
Chapter 2 , Step 2 - Introduction to Machine Learning. Here you will learn about the history, evolution, and different frameworks in practice for building machine learning systems. I think this understanding is very important as it will give you a broader perspective and set the stage for your further expedition. You’ll understand the different types of machine learning (supervised / unsupervised / reinforcement learning). You will also learn the various concepts are involved in core data analysis packages (NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib) with example codes.
Chapter 3 , Step 3 - Fundamentals of Machine Learning This chapter will expose you to various fundamental concepts involved in feature engineering, supervised learning (linear regression, nonlinear regression, logistic regression, time series forecasting and classification algorithms), unsupervised learning (clustering techniques, dimension reduction technique) with the help of scikit-learn and statsmodel packages.
Chapter 4 , Step 4 - Model Diagnosis and Tuning. in this chapter you’ll learn advanced topics around different model diagnosis, which covers the common problems that arise, and various tuning techniques to overcome these issues to build efficient models. The topics include choosing the correct probability cutoff, handling an imbalanced dataset, the variance, and the bias issues. You’ll also learn various tuning techniques such as ensemble models and hyperparameter tuning using grid / random search.
Chapter 5 , Step 5 - Text Mining and Recommender System. Statistics says 70% of the data available in the business world is in the form of text, so text mining has vast scope across various domains. You will learn the building blocks and basic concepts to advanced NLP techniques. You’ll also learn the recommender systems that are most commonly used to create personalization for customers.
Chapter 6 , Step 6 - Deep and Reinforcement Learning. There has been a great advancement in the area of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) through deep learning techniques and it has been the buzzword in recent times. You’ll learn various aspects of deep learning such as multilayer perceptrons, Convolution Neural Network (CNN) for image classification, RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) for text classification, and transfer learning. And you’ll also learn the q-learning example to understand the concept of reinforcement learning.
Chapter 7 , Conclusion. This chapter summarizes your six step learning and you’ll learn quick tips that you should remember while starting with real-world machine learning problems.
Acknowledgments
I’m grateful to my mom, dad, and loving brother; I thank my wife Usha and son Jivin for providing me the space for writing this book.
I would like to express my gratitude to my mentors, colleagues, and friends from current/previous organizations for their inputs, inspiration, and support. Thanks to Jojo for the encouragement to write this book and his technical review inputs. Big thanks to the Apress team for their constant support and help.
Finally, I would like to thank you the reader for showing an interest in this book and sincerely hope to help your pursuit to machine learning quest.
Note that the views expressed in this book are author’s personal.
Contents
-
Chapter 1: Step 1 – Getting Started in Python
- The Best Things in Life Are Free
- The Rising Star
- Python 2.7.x or Python 3.4.x?
-
Key Concepts
- Python Identifiers
- Keywords
- My First Python Program
- Code Blocks (Indentation & Suites)
- Basic Object Types
- When to Use List vs. Tuples vs. Set vs. Dictionary
- Comments in Python
- Multiline Statement
- Basic Operators
- Control Structure
- Lists
- Tuple
- Sets
- Dictionary
- User-Defined Functions
- Module
- File Input/Output
- Exception Handling
- Endnotes
- Chapter 2: Step 2 – Introduction to Machine Learning
-
Chapter 3: Step 3 – Fundamentals of Machine Learning
- Machine Learning Perspective of Data
- Scales of Measurement
- Feature Engineering
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Supervised Learning– Regression
-
Supervised Learning – Classification
- Logistic Regression
- Evaluating a Classification Model Performance
- ROC Curve
- Fitting Line
- Stochastic Gradient Descent
- Regularization
- Multiclass Logistic Regression
- Generalized Linear Models
- Supervised Learning – Process Flow
- Decision Trees
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- k Nearest Neighbors (kNN)
- Time-Series Forecasting
- Unsupervised Learning Process Flow
- Endnotes
- Chapter 4: Step 4 – Model Diagnosis and Tuning
- Chapter 5: Step 5 – Text Mining and Recommender Systems
-
Chapter 6: Step 6 – Deep and Reinforcement Learning
- Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
- What Goes Behind, When Computers Look at an Image?
- Why Not a Simple Classification Model for Images?
- Perceptron – Single Artificial Neuron
- Multilayer Perceptrons (Feedforward Neural Network)
- Restricted Boltzman Machines (RBM)
- MLP Using Keras
- Autoencoders
- Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
- Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
- Transfer Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Endnotes
- Chapter 7: Conclusion
- Index
Contents at a Glance
- About the Author
- About the Technical Reviewer
- Acknowledgments
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Step 1 – Getting Started in Python
- Chapter 2: Step 2 – Introduction to Machine Learning
- Chapter 3: Step 3 – Fundamentals of Machine Learning
- Chapter 4: Step 4 – Model Diagnosis and Tuning
- Chapter 5: Step 5 – Text Mining and Recommender Systems
- Chapter 6: Step 6 – Deep and Reinforcement Learning
- Chapter 7: Conclusion
- Index
About the Author and About the Technical Reviewer
About the Author

Manohar Swamynathan is a data science practitioner and an avid programmer, with over 13 years of experience in various data science-related areas that include data warehousing, Business Intelligence (BI), analytical tool development, ad hoc analysis, predictive modeling, data science product development, consulting, formulating strategy, and executing analytics program.
He’s had a career covering life cycles of data across different domains such as U.S. mortgage banking, retail, insurance, and industrial IoT. He has a bachelor’s degree with specialization in physics, mathematics, and computers; and a master’s degree in project management. He’s currently living in Bengaluru, the Silicon Valley of India, working as Staff Data Scientist with General Electric Digital, contributing to the next big digital industrial revolution.
You can visit him at http://www.mswamynathan.com to learn more about his various other activities.
About the Technical Reviewer

Jojo Moolayil is a Data Scientist and the author of the book: Smarter Decisions – The Intersection of Internet of Things and Decision Science . With over 4 years of industrial experience in Data Science, Decision Science and IoT, he has worked with industry leaders on high impact and critical projects across multiple verticals. He is currently associated with General Electric , the pioneer and leader in data science for Industrial IoT and lives in Bengaluru—the silicon valley of India.
He was born and raised in Pune, India and graduated from University of Pune with a major in Information Technology Engineering. He started his career with Mu Sigma Inc., the world's largest pure play analytics provider and worked with the leaders of many Fortune 50 clients. One of the early enthusiasts to venture into IoT analytics, he converged his learnings from decision science to bring the problem solving frameworks and his learnings from data and decision science to IoT Analtyics.
To cement his foundations in data science for industrial IoT and scale the impact of the problem solving experiments, he joined a fast growing IoT Analytics startup called Flutura based in Bangalore and headquartered in the valley. After a short stint with Flutura, Jojo moved on to work with the leaders of Industrial IoT - General Electric, in Bangalore, where he focused on solving decision science problems for Industrial IoT use cases. As a part of his role in GE, Jojo also focuses on developing data science and decision science products and platforms for Industrial IoT.
Apart from authoring books on Decision Science and IoT, Jojo has also been Technical Reviewer for various books on Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Business Analytics with Apress. He is an active Data Science tutor and maintains a blog at http://www.jojomoolayil.com/web/blog/ .
Profile
https://www.linkedin.com/in/jojo62000
I would like to thank my family, friends and mentors.
—Jojo Moolayil
